Presentation1.pptx, radiological signs in thoracic radiology.
- 1. Radiological Signs in Thoracic Diseases. Dr/ ABD ALLAH NAZEER. MD. Scimitar syndrome
- 2. SILHOUETTE SIGN This classic roentgenographic sign first described by Felson in 1950 states that “an intrathoracic lesion touching a border of the heart, aorta, or diaphragm will obliterate that border on the roentgenogram An intra-thoracic lesion not anatomically contiguous with a border or a normal structure will not obliterate that border Reliable sign distinguishing anterior lung lesions from posterior or lower lesions When two objects of the same density touch each other the edge between them disappears
- 3. SILHOUETTE SIGN. Chest radiograph shows middle and inferior right lobe pneumonia.
- 4. SILHOUETTE SIGN. Chest radiograph PA and Lateral Views:
- 5. Silhouette sign, right middle lobe pneumonia. Initial frontal (A) and lateral (B) radiographs in a patient with clinical suspicion of pneumonia demonstrate obliteration of the right heart border. Follow-up radiographs the next day (C, D) illustrate dense opacification on the lateral view and persisting loss of the right heart border, confirming the presence of a right middle lobe pneumococcal pneumonia.
- 6. AIR BRONCHOGRAM SIGN It occurs in infiltration or edema in tissues adjacent to patent bronchi Seen on chest radiographs or CT Associated with air-space disease It implies: patency of proximal airways, evacuation of alveolar air by absorption (atelectasis), replacement (pneumonia) or both, consolidation, tumor, lymphoma.
- 7. AIR BRONCHOGRAM SIGN. Chest CT and chest radiograph demonstrate air bronchograms in patients with right upper lobe pneumonia. Schematic drawings.
- 8. AIR BRONCHOGRAM SIGN. Chest CT and chest radiograph demonstrate air bronchograms in patients with left upper lobe pneumonia.
- 9. SIGNET RING SIGN Seen on CT/HRCT scans of chest CT finding in patients with bronchiectasis Ring shadow representing dilated thick-walled bronchus associated with a nodular opacity representing pulmonary artery SIGNET RING SIGN. Chest CT shows small bronchiectasis.
- 10. SIGNET RING SIGN. Chest CT shows small bronchiectasis.
- 11. POPCORN CALCIFICATION A cluster of sharply defined, irregularly lobulated, calcifications, usually in a pulmonary nodule. Popcorn calcifications within a well-circumscribed pulmonary nodule are highly suggestive of pulmonary chondroid hamartoma. POPCORN CALCIFICATION. Chest radiograph demonstrates nodule with "popcorn calcification" in the right lower lobe representing hamartoma.
- 12. TRAM-TRACK SIGN Parallel line opacities (tram tracks) caused by thickened dilated bronchi Seen on chest CT Bronchiectasis- defined as localized irreversible dilatation of part of the bronchial tree Causes: - infection - bronchial obstruction (endobronchial tumors, encroachment of hilar lymph nodes, foreign body aspiration) - cystic fibrosis - primary ciliary dyskinesia - immunodeficiency states - congenital anatomic defects (pulmonary sequestration, Mounier-Kuhn syndrome)
- 13. TRAM-TRACK SIGN. Chest CT demonstrates tram-track sign. Schematic drawing and corresponding picture.
- 14. TREE-IN-BUD SIGN Commonly seen at thin-section CT This sign appears as small, peripheral, centrilobular soft tissue nodules connected to multiple contiguous, linear branching opacities. This radiologic term represents the mucous plugging, bronchial dilatation, and wall thickening of bronchiolitis The histopathological correlate demonstrates small airway plugging with mucus, pus, or fluid, with dilated bronchioles, peribronchiolar inflammation, and wall thickening Initially described in endobronchial spread of tuberculosis Recognized in diverse entities Causes: - infection (bacterial, fungal, viral) - congenital disorders (cystic fibrosis, Kartagener syndrome) - idiopathic disorders (obliterative bronchiolitis) - aspiration - inhalation (toxic fumes and gases) - immunologic disorders - connective tissue disorders (rheumatoid arthritis, Sjogren) - neoplasms (gastric, breast and renal cancer, Ewing sarcoma)
- 15. TREE-IN-BUD SIGN. Chest CT shows tree-in-bud images. Schematic drawings and corresponding picture.
- 16. CT ANGIOGRAM SIGN Finding may be seen on CT of chest after IV contrast material administration. Consists of enhancing branching pulmonary vessels in homogeneous low-attenuating consolidation. Low-attenuating component can be caused by production of mucin within air spaces Initially described in 1990 by Im et al as a specific sign (92%) of lobar bronchoalveolar carcinoma Also seen in: - pneumonia - pulmonary edema - obstructive pneumonitis central tumor - metastasis from GI carcinomas - lymphoma
- 17. CT ANGIOGRAM SIGN. Chest CT and schematic drawing.
- 19. FINGER-IN-GLOVE SIGN Visible on chest radiographs or CT Indicates mucoid impaction within an obstructed bronchus Characterized by branching tubular or fingerlike opacities Originate from the hilum and are directed peripherally Also seen in cases of dilated bronchi with secretions Visualization of the gloved fingers is made possible by collateral air drift through the interalveolar pores of Kohn and canals of Lambert aerating lung distal to the point of mucoid impaction (distal lung remains aerated) There are two broad etiologic categories: non-obstructive and obstructive Non-obstructive: - allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) - asthma - cystic fibrosis (secondary to mucociliary dysfunction and thick mucous secretions) Obstructive: - neoplasms (bronchial hamartomas, lipomas, bronchogenic carcinoma, carcinoid). - congenital (bronchial atresia, intralobar sequestration, bronchogenic cysts).
- 20. FINGER-IN-GLOVE SIGN. Chest CT, schematic drawing and illustrative picture.
- 21. FINGER-IN-GLOVE SIGN. Chest CT.
- 22. HALO SIGN Ground glass attenuation surrounding a pulmonary nodule/mass on CT images Described by Kuhlman in 1985 in patients with invasive aspergillosis In febrile neutropenic patients, the sign suggests angioinvasive fungal infection, (which is associated with a high mortality rate in the immunocompromised host) the zone of attenuation represents alveolar hemorrhage whereas the nodules represent areas of infarction and necrosis caused by thrombosis of small to medium sized vessels Associated with hemorrhagic nodules and may be caused by neoplasms or inflammatory conditions Familiarity with adequate clinical setting helps to narrow differentials: - multiple nodules in immunocompromised patients could be infections, Kaposi or lymphoma - leukemia and fever may represent invasive aspergillosis - immunocompetent patients with a solitary nodule may indicate bronchioloalveolar carcinoma
- 23. HALO SIGN. Chest CT shows halo sign in a patient with schistosomiasis.
- 24. REVERSE HALO SIGN Central ground-glass opacity surrounded by denser consolidation of crescentic or ring shape, at least 2 mm thick First described by Voloudaki in 1996 Kim in 2003 used the term reverse halo Found to be relatively specific for cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP) Seen in other conditions: - Wegener’s and lymphomatoid granulomatosis - paracoccidiodomycosis - neoplastic (metastasis) - invasive aspergillosis - lipoid pneumonia - schistosomiasis
- 25. REVERSE HALO SIGN. Chest CT demonstrates reverse halo images in a patient with schistosomiasis.
- 26. REVERSE HALO SIGN. Chest CT demonstrates reverse halo images
- 27. COIN LESION The term coin lesion was defined by Thornton et al in 1944 as a solitary lesion, 1 to 5 cm in size, round or oval with well defined margins Solitary, round, circumscribed shadows found in the lungs in x- ray or CT examinations Smaller than 3 centimeters in diameter Common causes: - tuberculosis - coccidioidomycosis - histoplasmosis - neoplasms (primary bronchogenic carcinoma, metastatic tumors, bronchial adenomas etc) - cysts - vascular anomalies
- 28. COIN LESION. Chest CT shows a nodule in the left lower lobe. Metastasis. Schematic drawing and illustrative picture.
- 29. MILIARY SHADOWING The term miliary derives from the radiographic picture of diffuse, discrete nodular shadows about the size of a millet seed Innumerable, small (1-4mm) pulmonary nodules are seen scattered throughout the lungs It can be seen in: - tuberculosis - histoplasmosis - sarcoidosis - rheumatoid arthritis - pneumoconiosis - COPD - pulmonary siderosis - bronchoalveolar carcinoma - metastasis (thyroid, kidney, trophoblast and some sarcomas)
- 30. MILIARY SHADOWING. Chest CT. Tuberculosis.
- 31. MONOD’S SIGN Air surrounding fungus ball or mycetoma in preexisting air cavity (old tuberculosis, histoplasmosis, sarcoidosis, neoplasm) It should not be confused with the air crescent sign which is seen in recovering angioinvasive aspergillosis and heralds improvement in the condition The air around the mycetoma is often crescent shaped and hence, the term air crescent sign is often used interchangeably by many to refer to both pathological processes.
- 32. MONOD’S SIGN. Chest CT. Mycetoma.
- 33. MONOD’S SIGN. X-Ray and Chest CT. Mycetoma.
- 34. MONOD’S SIGN. X-Ray chest . Wagner Granuloma.
- 35. FALLEN LUNG SIGN This sign refers to the appearance of the collapsed lung occurring with a fractured bronchus It refers to the collapsed lung in a dependent position, hanging on the hilum only by its vascular attachments and was first described by Oh et al in 1969 and by Kumpe et al in 1970 The bronchial fracture results in the lung to fall away from the hilum, either inferiorly and laterally in an upright patient or posteriorly, as seen on CT in a supine patient.
- 36. FALLEN LUNG SIGN. Chest radiograph and schematic drawing.
- 37. FALLEN LUNG SIGN. Chest radiograph and CT Scan.
- 38. BULGING FISSURE SIGN The bulging fissure sign refers to lobar consolidation causing lobar expansion and bulging of the adjacent fissure inferiorly Historically Klebsiella pneumoniae involving the RUP- Friedlander pneumonia Although previously reported in up to 30% of patients with Klebsiella pneumonia, the finding is identified less commonly today, most likely due to rapid prophylactic implementation of antibiotics. The most common infective causative agents are: - Klebsiella pneumoniae - Streptococcus pneumoniae - Pseudomonas aeruginosa - Staphylococcus aureus It may also be seen with bronchoalveolar carcinoma and tuberculosis
- 39. BULGING FISSURE SIGN. Chest radiograph. Right upper lobe pneumonia.
- 40. FLAT WAIST SIGN Indicates left lower lobe collapse Visualized on frontal views Hilar structures shift downward and rotation of heart produces flattening of cardiac waist FLAT WAIST SIGN. Chest radiograph and schematic drawing.
- 41. GOLDEN S SIGN Described by Ross Golden in 1925 Resembles a reverse S shape It can be seen on PA/lateral views and CT This sign is typically seen with right upper lobe collapse The medial portion of minor fissure is convex inferiorly due to a central mass and the lateral portion of the fissure is concave inferiorly It can be observed in cases of bronchial carcinoma, primary mediastinal tumor, metastasis and enlarged lymph nodes
- 42. GOLDEN S SIGN. Chest radiograph and CT images demonstrate this sign. Bronchial carcinoma.
- 43. GOLDEN S SIGN. Chest radiograph.
- 44. BAT WING APPEARANCE Bat's wing or butterfly pulmonary opacities refer to a pattern of bilateral perihilar shadowing It is classically described on a frontal chest radiograph but can also refer to appearances on chest CT Causes: - pulmonary edema (especially cardiogenic) - pneumonia (aspiration pneumonia, PCP, viral, lipoid) - inhalation injury (noxious gas, liquid) - pulmonary alveolar proteinosis - pulmonary hemorrhage (e.g. Goodpasture syndrome) - lymphoma - leukemia - bronchoalveolar carcinoma
- 45. BAT WING APPEARANCE. Chest radiograph, schematic drawing and corresponding picture.
- 46. GROUND GLASS PATTERN Ground glass opacity is a hazy, increased attenuation of lung with preservation of bronchial and vascular margins. It is a nonspecific radiologic finding It is caused by partial filling of air spaces, interstitial thickening, partial collapse of alveoli, normal expiration, or increased capillary blood volume It can be seen with alveolar wall inflammation or thickening, with partial air-space filling, or with some combination of the two Common causes: - pulmonary edema - adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) - viral, mycoplasmal, and pneumocystis pneumonias hypersensitivity pneumonia - pulmonary hemorrhage - other diffuse interstitial lung diseases
- 47. GROUND GLASS PATTERN. Chest CT images and illustrative picture.
- 48. CRAZY PAVING SIGN Scattered or diffuse ground glass attenuation with superimposed intralobular and interlobular septa thickening Commonly seen at thin-section CT Initially described in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis Recognized in diverse entities Causes: - infection (Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia, organizing pneumonia, usual interstitial pneumonia, non-specific interstitial pneumonia, and exogenous lipoid pneumonia) - neoplasm (bronchioloalveolar carcinoma) - pulmonary alveolar proteinosis - sarcoidosis - respiratory bronchiolitis with interstitial lung disease sanguineous (pulmonary hemorrhage syndromes, ARDS)
- 49. CRAZY PAVING SIGN. Chest CT with schematic drawing and illustrative picture.
- 51. MOSAIC PATTERN Patchy ground glass opacities, resulting in a mosaic pattern of lung attenuation Such a pattern can be seen in infiltrative lung disease, airway abnormalities (e.g., asthma, bronchiolitis obliterans), and chronic pulmonary vascular disease (e.g., chronic thromboembolic disease) The distinction between these three entities can be made by observing the size of the pulmonary vessels in the area of increased lung attenuation (increased in both airway disease and vascular disease, but not in infiltrative disease), and by examining air trapping on expiratory scans (indicating airway disease)
- 52. MOSAIC PATTERN. Chest CT with schematic drawing and illustrative picture.
- 53. SANDSTORM APPEARANCE Seen on CT or chest X-ray The appearance is given by the presence of diffuse, scattered, bilateral areas of micronodular calcifications (sandstorm appearance) Pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis (PAM) should be considered. PAM is an uncommon chronic disease characterized by calcifications within the alveoli which occurs in the absence of any known disorder of calcium metabolism On CT scans diffuse ground-glass opacities throughout both lungs can be seen in association with calcified nodules
- 54. SANDSTORM APPEARANCE. Chest radiograph in a patient with alveolar microlithiasis and illustrative picture.
- 55. HONEYCOMB LUNG The term “honeycomb lung” first appeared in the English literature in 1949 (Oswald and Parkinson) Radiologically, in the latest version from the Fleischner Society, it is defined as “clustered cystic air spaces, typically of comparable diameters on the order of 3–10 mm but occasionally as large as 2.5 cm... usually subpleural and characterized by well-defined walls” Recent understanding indicates that “honeycombing is often considered specific for pulmonary fibrosis and is an important criterion in the diagnosis of usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP)” Causes: - idiopathic interstitial pneumonia - diffuse alveolar damage - asbestosis - interstitial granulomatous diseases - eosinophilic granuloma
- 56. HONEYCOMB LUNG. Chest CT with schematic drawing and illustrative picture.
- 57. WESTERMARK SIGN Described by Neil Westermarck in 1938 Chest radiograph and CT show increased lucency or hypoattenuation Typically signifies either occlusion of a larger lobar/segmental artery or widespread small vessel occlusion Represents oligemia distal to PE; seen only in 2% of patients Sign results from combination of dilatation pulmonary arteries proximal embolus and collapse of distal vasculature Low sensitivity 11%, high specificity 92%
- 58. WESTERMARK SIGN. Chest radiograph and schematic drawing.
- 59. Westermark Sign.
- 60. WAVE SIGN Sign produced by lateral indentation of thymus by adjacent anterior ribs resembling a wave This sign in seen in the pediatric population and represents a normal thymus WAVE SIGN. Chest radiograph with schematic drawing and illustrative picture.
- 61. DEEP SULCUS SIGN The presence of radiolucency in a deep costophrenic sulcus on a supine thoracic radiograph is characteristic of a pneumothorax in a supine patient Seen on X-rays in supine position Intrapleural air rises to the highest portion of the hemithorax leading to the presence of a lucency in the anteromedial, subpulmonic, and lateral basilar space adjacent to the diaphragm 30% pneumothoraces are undetected It is useful in confirming suspected pneumothorax on AP supine radiography in compromised patients, such as those in the intensive care setting
- 62. DEEP SULCUS SIGN. Chest radiograph with schematic drawing and illustrative picture.
- 63. TAPERED MARGINS SIGN Lesions in the chest wall, pleura or mediastinum have smooth tapered borders and obtuse angles While parenchymal lesions usually form acute angles TAPERED MARGINS SIGN. Chest radiographs with schematic drawings. Mesothelioma and thymic lymphosarcoma.
- 64. CERVICOTHORACIC SIGN Used to determine location of mediastinal lesion in the upper chest Based on principle that an intrathoracic lesion in direct contact with soft tissues of the neck will not be outlined by air Uppermost border of the anterior mediastinum ends at level of clavicles, so when the cephalic border of a mass is obscured at or below the level of the clavicles, it is deemed to be a “cervicothoracic lesion” involving the anterior mediastinum Middle and posterior mediastinum extends above the clavicles Mediastinal mass projected superior the level of clavicles must be located either within middle or posterior mediastinum More cephalad the mass extends the most posterior the location
- 65. CERVICOTHORACIC SIGN. Chest radiographs with schematic drawings. Lymphoma.
- 66. CERVICOTHORACIC SIGN. Chest radiographs with MRI images.
- 67. 1-2-3 SIGN Characterized by bilateral hilar and right paratracheal lymphadenopathy so-called Garland triad or 1-2-3 sign Suggestive of sarcoidosis Separation between nodes and heart which is not seen in lymphoma 1-2-3 SIGN. Chest radiographs with schematic drawings. Sarcoidosis.
- 68. 1-2-3 SIGN. Chest radiographs
- 69. HILUM OVERLAY SIGN Described by Benjamin Felson If hilar vessels are sharply delineated it can be assumed that the overlying mass is anterior or posterior If mass is inseparable from pulmonary arteries, structures are adjacent to one another HILUM OVERLAY SIGN. Chest radiograph with schematic drawing.
- 70. HILUM CONVERGENCE SIGN Used to distinguish between a prominent hilum and an enlarged pulmonary artery If branches of PA converge toward central mass, is an enlarged PA If branches of PA converge toward heart rather than mass, is a mediastinal tumor HILUM CONVERGENCE SIGN. Chest radiograph with schematic drawing.
- 71. THORACOABDOMINAL SIGN Posterior costophrenic sulcus extends more caudally than anterior basilar lung Lesion extending below the dome of diaphragm must be in posterior chest whereas lesion terminating at dome must be anterior Thoracoabdominal signs were described by Felson THORACOABDOMINAL SIGN. Chest radiograph with schematic drawing. Hamartoma.
- 72. THORACOABDOMINAL SIGN. Chest radiograph and CT Scan.
- 73. WATER BOTTLE CONFIGURATION Seen in pericardial effusion Causes: - inflammatory - infectious - malignant - autoimmune processes within the pericardium Chest radiography shows an enlarged cardiac silhouette WATER BOTTLE CONFIGURATION. Chest radiograph with schematic drawing and illustrative picture.
- 75. DOUBLE DENSITY SIGN On frontal chest radiographs, this sign presents as a curvilinear density projecting over the right retrocardiac region, indicating left atrial enlargement The curvilinear line represents the inferolateral margin of the left atrium The double density sign may be observed in patients without cardiac disease; however, there is a semiquantitative measurement to estimate the left atrial diameter and better estimate whether it is a real finding DOUBLE DENSITY SIGN. Chest radiograph with schematic drawings.
- 76. SPLIT PLEURA SIGN Seen on contrast enhanced CT of chest Separation and enhancement of the visceral and parietal pleural layers on CT is considered strong evidence of empyema Normally, individual pleural layers are not discernable as discrete structures Empyemic fluid fills the pleural space, resulting in thickening and enhancement of the pleura with a denotable separation It can also be seen with exudative effusion Causes: - bacterial pneumonia - cancer - viral infection - PE
- 77. SPLIT PLEURA SIGN. Chest radiograph with schematic drawing.
- 80. Tree in Bud.
- 81. Tapered Margin Sign. . A lesion in the chest wall, pleural or mediastinum have smooth tapered borders and obtuse angles. . While parenchymal lesions usually form acute angles. Tapered Margin Sign.
- 83. Luftsichel Sign • German for sickle of air (luft: air sichel: crescent) • Para-mediastinal lucency due to interposition of lower lobe apex between mediastinum and shrunken upper lobe • Occurs more commonly on the left than in the right
- 84. Luftsichel Sign
- 85. Double Density Sign • Indicates left atrial enlargement • Occurs when right side of the left atrium pushes into adjacent lung • Splaying of the carina • Superior displacement of left main stem bronchus on frontal view • Posterior displacement of left main stem bronchus on lateral view • Posterior displacement of esophagus on barium study
- 86. Doughnut Sign • Detect mediastinal adenomegaly • Lateral chest radiograph • Subcarinal lymphadenopathy • Mass posterior to bronchus intermedius and inferior hilar window • CT primary modality for detecting mediastinal lymphadenopathy
- 87. Doughnut sign. A normal lateral chest radiograph is shown depicting several of the anatomic landmarks used to localize a subcarinal mass (A: 1, posterior wall of the bronchus intermedius; 2, left upper lobe bronchus; 3, right upper lobe bronchus; 4, approximate level of the carina). Lateral radiograph of the chest (B) shows added density within the infra-hilar window representative of subcarinal lymphadenopathy in a patient with non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Follow-up CT of the chest confirmed the finding of subcarinal lymphadenopathy (C).
- 88. Hampton’s Hump Sign • Described by Audrey Hampton in 1940 • Peripheral wedge-shaped opacity due to infarction • Pleura-based consolidation in the form of truncated cone w base against pleural surface and apex pointing toward hilum.
- 89. Fleischner Sign • Described by Felix Fleischner • Enlargement proximal pulmonary arteries on plain film or angiography • PA enlargement due to embolus • Commonly in the setting of massive PE • It has relatively low sensitivity • Abrupt tapering of an occluded vessel distally (knuckle sign)
- 90. Hilum Overlay Sign • Described by B. Felson • If hilar vessels are sharply delineated it can be assumed that the overlying mass is anterior or posterior • If mass inseparable pulmonary arteries structures are adjacent to one another Hilum Overlay Sign.
- 92. Hilum Convergence Sign • Described by B. Felson • Used to distinguish between a prominent hilum and an enlarged pulmonary artery • If branches of PA converge toward central mass is an enlarged PA • If branches of PA converge toward heart rather than mass is a mediastinal tumor
- 93. Comet Tail Sign • Rounded atelectasis is not rare, described in patients with asbestosis • Other conditions: CHF, Dressler, infarct, TB or parapneumonic effusions, histoplasmosis • Round or oval opacity 2.5-8 cm, acute angles, lower lobes, enhancement • DD includes bronchogenic Ca Comet Tail Sign.
- 94. Comet tail sign. Rounded atelectasis within the right lower lobe (A) and abutting the posterior pleural surface in a patient with previous asbestos exposure. There is adjacent pleural thickening (B, white arrow), calcified pleural plaques, and signs of volume loss with downward retraction of the major fissure. The swirling of the bronchovascular bundle is thought to resemble a comet’s tail.
- 95. Deep Sulcus Sign • Seen on radiographs in supine position • Characteristic of pneumothorax • 30% pneumothoraces are undetected • Lucency in lateral costophrenic angle • Air collects anteriorly and basally • Useful in neonates and ill patients • Include lateral costophrenic angles
- 96. Ring Around Artery Sign • Visualized on lateral chest radiographs • Lucency along or surrounding RPA • Characteristic of pneumomediastinum • Usually is accompanied by other ancillary signs: • continuous diaphragm sign • Naclerio’s V sign • thymic sail sign
- 98. Flat Waist Sign • Described by Kattan and Wlot in 1976 • Indicates left lower lobe collapse • Visualized on frontal views • Perfectly symmetrical PA or AP view • Hilar structures shift downward and rotation of heart produces flattening of cardiac waist
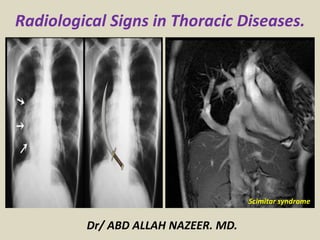
- 99. Scimitar syndrome, also known as hypogenetic lung syndrome, is characterised by a hypoplastic lung that is drained by an anomalous vein into the systemic venous system. It is a type of partial anomalous pulmonary venous return and is one of several findings in pulmonary venolobar syndrome Scimitar-syndrome.
- 100. Scimitar sign. Frontal radiograph of the chest (A) shows a curvilinear opacity paralleling the right heart border representing an anomalous pulmonary vein. Graphic depiction of the curvilinear anomalous vein and its usual common entry into the inferior vena cava (B). A follow-up unenhanced CT (C, D) and cavagram (E) for central line placement confirmed a supradiaphragmatic insertion of the anomalous vein into the inferior vena cava just prior to its entry into the right atrium.
- 101. Thank You.
