4 1 solar system
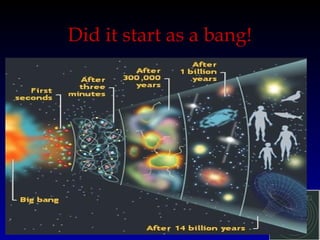
- 1. Did it start as a bang! 1B
- 2. The Expanding Universe A. The Big Bang Theory: Idea that all matter began in an infinitely small point and exploded out in all directions 1B
- 3. 1B
- 4. Galaxies: _____________________ Billions of stars, _____________________________ dust, and gas held ______________________________ together by gravity Edwin Hubble ________________ was an astronomer in the 1920s who gathered many pictures of galaxies • noticed they all didn’t look alike • decided to classify them by the way they looked into 3 types Elliptical • “E” or _____________________ 1B Spiral • “S” or _____________________ Barred Spiral • “SB” or ____________________
- 5. A. Earth’s Galaxy—and Others • Galaxies are grouped • Cluster of galaxies together in clusters. • The cluster the Milky Way belongs to is called the Local Group. • Three types of galaxies:
- 6. Galaxy Morphological Revisted Spiral Irregular Elliptical The Hubble Tuning Fork
- 7. Spiral Galaxies • Spiral Galaxies: • Two spiral galaxies!! Circular galaxies that have arms curve outward from a central hub. – Arms are made up of stars and dust
- 9. halo disk bulge Spiral Galaxy
- 10. Elliptical Galaxies Most common type of galaxy; large three-dimensional football shaped galaxies. -Contain mostly older and dimmer stars. Vary in shape from completely round to extremely elongated ovals. Unlike spiral galaxies No bright nucleus at their center. Elliptical galaxies are represented by the letter E Divided into seven subgroups according to their shape. These subgroups are labeled E0 to E7. E0 galaxies nearly circular in shape while E7 galaxies are extremely elongated or stretched out.
- 11. Illustrate / Draw Elliptical
- 12. Irregular Galaxies • Come in many different shapes and are smaller and less common • Irregular Galaxies - No regular shape, includes nebulas, with no central bulge or spiral arms.
- 14. Earth’s Galaxy • Galaxy: A large group of • Spiral Galaxies stars, gas, and dust held together by gravity. • Milky Way: Our galaxy which contains about 200 billion stars and many nebulas
- 15. The Milky Way Galaxy • The Milky Way is the galaxy that contains our Solar System which is just one of the several galaxies of the universe. • . This name derives from its appearance as a dim "milky" glowing band arching across the night sky, in which the naked eye cannot distinguish individual stars. • 100,000 light years in diameter • Our sun orbits the center of the galaxy once every 240 million years • A barred spiral galaxy • Contains over 200 billion stars • Its where we live!!!!!
- 16. Solar System Our star (Sun), the planets, many moons, and other small bodies that ALL travel around the Sun
- 17. Solar System
- 18. What do we see in the sky? • The stars move in the sky but not with respect to each other • The planets (or “wanderers”) move differently from stars – They move with respect to the stars – They exhibit strange retrograde motion • What does all this mean? • How can we explain these movements? • What does the universe 1B look like?
- 19. The Great Debate! •Heraclides (330 B.C.) developed the first Solar System model, beginning of the geocentric versus heliocentric debate 1B
- 20. Timeline Galileo 1564-1642 Newton 1642-1727 Tycho Copernicus 1546-1601 Kepler 1473-1543 1571-1630 1B
- 21. Geocentric (Ptolemaic) System •The theory (in Greek, geo means earth), which maintained that Earth was the center of the universe, usually referring to the system of Claudius Ptolemy. 1B
- 22. Geocentric (Ptolemaic) System • The accepted model for 1400 years • The earth is at the center • The Sun, stars, and planets on their spheres revolve around the earth: explains daily movement • To account for unusual planetary motion epicycles were introduced • Fit the Greek model of heavenly perfection – spheres are the perfect shape, circular the perfect motion 1B
- 23. Illustrate/ Draw model: 1B
- 24. Heliocentric (Copernican) System • The word "helios" in Greek means "sun." Heliocentric means that the sun is at the center. A heliocentric system is one in which the planets revolve around a fixed sun. Thus Mercury, Venus, the Earth, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn all revolve around the sun. The moon is the only celestial sphere in this system which revolves 1B around the earth, and, together
- 25. Heliocentric (Copernican) System • Sun at center (heliocentric) • Uniform, circular motion – No epicycles (almost) • Moon orbited the earth, the earth orbited the sun as another planet • Planets and stars still on fixed spheres, stars don’t move • The daily motion of the stars results from the Earth’s spin • The annual motion of the stars results from the Earth’s orbit 1B
- 26. Please Illustrate 1B
- 27. Our Solar System A Write On Activity
- 28. Our Solar System Our solar system is made up of: Sun Nine planets Their moons Asteroids Comets Meteoros
- 29. Inner Planets The inner four rocky / Terrestrial planets. These planets have hard rock crusts, and dense rock and metal cores are: Mercury Venus Earth Mars
- 30. Mercury • Mercury is the closest planet to the Sun. • Mercury rotates the Sun in only 88 days. • Mercury rotates very slowly on its axis with one day taking 58 Earth days. • Mercury barely has any atmosphere, but does have glaciers. • Called a morning star. This is because Mercury shines brightly in the early morning just before the sun rises. It has also been called an evening star for the same reason. Mercury is often visible for a brief period of time just after the Sun sets. 1B
- 31. Venus Sister planet to Earth Size and structure is VERY similar to Earth, often called "Earth's Twin" Has no moons or rings Hot, thick atmosphere Brightest object in sky besides sun and moon (looks like bright star) Covered with craters, volcanoes, and mountains
- 32. Earth Third planet from sun Only planet known to have life and liquid water Atmosphere composed of composed of Nitrogen (78%), Oxygen (21%), and other gases (1%).
- 33. Mars Fourth planet from sun Appears as bright reddish color in the night sky Called "the Red Planet" because it surface is covered with iron oxide- RUST! Proves that Mars once had free oxygen molecules in its atmosphere. Surface features volcanoes and huge dust storms Has 2 moons: Phobos and Deimos
- 34. Outer Planets A gas giant (sometimes also known as a jovian planet after the planet Jupiter, or giant planet) is a massive planet with a thick atmosphere of hydrogen and helium Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune
- 35. Jupiter Largest planet in solar system Brightest planet in sky 60+ moons, 5 visible from Earth Strong magnetic field Giant red spot Rings have 3 parts: Halo Ring, Main Ring, Gossamer Ring
- 36. Saturn 6 th planet from sun Seven thin, flat rings not solid but made up of particles of ice, dust and rocks 31 moons Largest moon, Titan, Easily visible in the night sky A lightweight planet and it spins so fast Voyager explored Saturn and its
- 37. Uranus 7 th planet from sun Has a faint ring system 27 known moons Covered with clouds Sits and spins on its side with the north and south poles sticking out the sides.
- 38. Neptune 8 th planet from sun Discovered through math 7 known moons Triton largest moon Storm called the "Great Dark Spot" because it appears as a dark oval shape on the surface of the planet. Great Dark Spot thought to be a hole, similar to the hole in the ozone layer on Earth
- 39. Pluto our dwarf Pluto, the outermost planet, is a small, icy "dwarf planet“ it is smaller than the Earth's Moon.
- 40. Pluto 9 th planet from sun (usually) Never visited by spacecraft Orbits very slowly Moon, Charon, is very close to Pluto and about the same size
- 41. Comet- chunks of ice and dust • Has an elliptical orbit around Sun • Has a head (nucleus and coma) and tail. • Tail always points away from sun.
- 42. Comets: Orbit
- 43. Asteroids- Larger chunks of rock Vary in size and shape In Asteroid Belt between Mars and Jupiter Revolve around sun in 3-6 years
- 45. Meteoroids- smaller chunks of rock and dust in space. 1. randomly move about space ; no specific orbit 2. come from remains of comets and asteroids • Meteor- a meteoroid that burns in the atmosphere- produces a streak of light. nickname: “ Shooting star ” •MeteoriTe- a meteoroid that doesn’t burn up in the Earth’s atmosphere. It T ouches Earth.
- 46. Writing Activity Which does not describe the difference between Gas Giants and Terrestrials? A. Terrestrials are closer to the sun than gas giants. B. Terrestrials are denser than Gas Giants. C. Gas Giants rotate faster on their axis then Terrestrials. D. Terrestrials have rock and metal in their core and Gas Giants do not.
- 47. Solar System Activities Order the Planets Fun with Planets Constellations of the Northern Sky Planets Solar System
Hinweis der Redaktion
- Tail becomes brighter as it gets closer to the sun because of increase heat/radiation. Tail points away from sun because of the radiation/solar wind. Imagine standing in the wind outside. Your hair will always blow in the same direction the wind is blowing.
- Can accidentally get “out” of normal orbit. Scientists monitor this and its likeliness of coming in contact with Earth. “ Armaggedon- The Movie? Ben Affleck” Any other movies??