Motional electromotive force
•Als PPT, PDF herunterladen•
0 gefällt mir•412 views
plz follow us we shall provide you special slides of different subjects
Melden
Teilen
Melden
Teilen
Empfohlen
Empfohlen
Weitere ähnliche Inhalte
Was ist angesagt?
Was ist angesagt? (20)
Magnetic Circuit & Energy Stored In Magnetic Field

Magnetic Circuit & Energy Stored In Magnetic Field
Ähnlich wie Motional electromotive force
Ähnlich wie Motional electromotive force (20)
Lecture 26 emf. induced fields. displacement currents.

Lecture 26 emf. induced fields. displacement currents.
Kürzlich hochgeladen
Kürzlich hochgeladen (20)
Call Girls Alandi Call Me 7737669865 Budget Friendly No Advance Booking

Call Girls Alandi Call Me 7737669865 Budget Friendly No Advance Booking
Labelling Requirements and Label Claims for Dietary Supplements and Recommend...

Labelling Requirements and Label Claims for Dietary Supplements and Recommend...
SAMASTIPUR CALL GIRL 7857803690 LOW PRICE ESCORT SERVICE

SAMASTIPUR CALL GIRL 7857803690 LOW PRICE ESCORT SERVICE
Forensic Biology & Its biological significance.pdf

Forensic Biology & Its biological significance.pdf
TEST BANK For Radiologic Science for Technologists, 12th Edition by Stewart C...

TEST BANK For Radiologic Science for Technologists, 12th Edition by Stewart C...
GUIDELINES ON SIMILAR BIOLOGICS Regulatory Requirements for Marketing Authori...

GUIDELINES ON SIMILAR BIOLOGICS Regulatory Requirements for Marketing Authori...
High Class Escorts in Hyderabad ₹7.5k Pick Up & Drop With Cash Payment 969456...

High Class Escorts in Hyderabad ₹7.5k Pick Up & Drop With Cash Payment 969456...
Pulmonary drug delivery system M.pharm -2nd sem P'ceutics

Pulmonary drug delivery system M.pharm -2nd sem P'ceutics
Hire 💕 9907093804 Hooghly Call Girls Service Call Girls Agency

Hire 💕 9907093804 Hooghly Call Girls Service Call Girls Agency
Biogenic Sulfur Gases as Biosignatures on Temperate Sub-Neptune Waterworlds

Biogenic Sulfur Gases as Biosignatures on Temperate Sub-Neptune Waterworlds
Asymmetry in the atmosphere of the ultra-hot Jupiter WASP-76 b

Asymmetry in the atmosphere of the ultra-hot Jupiter WASP-76 b
9654467111 Call Girls In Raj Nagar Delhi Short 1500 Night 6000

9654467111 Call Girls In Raj Nagar Delhi Short 1500 Night 6000
Motional electromotive force
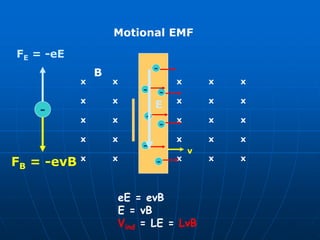
- 1. Motional EMF x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x v B - - - - - - - E - FE = -eE FB = -evB eE = evB E = vB Vind = LE = LvB
- 2. x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x v L d V dt Fi = LdB Ff = L(d+vdt)B |Vind | = dF/dt = LvdtB/dt = LvB
- 3. Motional emf As the negative charges accumulate at the base, a net positive charge exists at the upper end of the conductor As a result of this charge separation, an electric field is produced in the conductor Charges build up at the ends of the conductor until the downward magnetic force is balanced by the upward electric force There is a potential difference between the upper and lower ends of the conductor
- 4. Motional emf, cont The potential difference between the ends of the conductor can be found by • V = B v L • The upper end is at a higher potential than the lower end A potential difference is maintained across the conductor as long as there is motion through the field • If the motion is reversed, the polarity of the potential difference is also reversed
- 5. Motional emf in a Circuit Assume the moving bar has zero resistance As the bar is pulled to the right with velocity v under the influence of an applied force, F, the free charges experience a magnetic force along the length of the bar This force sets up an induced current because the charges are free to move in the closed path
- 6. Motional emf in a Circuit, cont The changing magnetic flux through the loop and the corresponding induced emf in the bar result from the change in area of the loop The induced, motional emf, acts like a battery in the circuit R v B I and v B
- 7. Lenz’ Law Revisited – Moving Bar Example As the bar moves to the right, the magnetic flux through the circuit increases with time because the area of the loop increases The induced current must in a direction such that it opposes the change in the external magnetic flux
- 8. Lenz’ Law, Bar Example, cont The flux due to the external field in increasing into the page The flux due to the induced current must be out of the page Therefore the current must be counterclockwise when the bar moves to the right
- 9. Lenz’ Law, Bar Example, final The bar is moving toward the left The magnetic flux through the loop is decreasing with time The induced current must be clockwise to to produce its own flux into the page
- 10. Lenz’ Law, Moving Magnet Example A bar magnet is moved to the right toward a stationary loop of wire (a) • As the magnet moves, the magnetic flux increases with time The induced current produces a flux to the left, so the current is in the direction shown (b)
- 11. Lenz’ Law, Final Note When applying Lenz’ Law, there are two magnetic fields to consider • The external changing magnetic field that induces the current in the loop • The magnetic field produced by the current in the loop
- 12. Generators Alternating Current (AC) generator • Converts mechanical energy to electrical energy • Consists of a wire loop rotated by some external means • There are a variety of sources that can supply the energy to rotate the loop These may include falling water, heat by burning coal to produce steam
- 13. AC Generators, cont Basic operation of the generator • As the loop rotates, the magnetic flux through it changes with time • This induces an emf and a current in the external circuit • The ends of the loop are connected to slip rings that rotate with the loop • Connections to the external circuit are made by stationary brushed in contact with the slip rings
- 14. AC Generators, final The emf generated by the rotating loop can be found by V =2 B ℓ v=2 B ℓ v sin θ If the loop rotates with a constant angular speed, ω, and N turns V = N B A ω cos ω t V = Vmax when loop is parallel to the field V = 0 when when the loop is perpendicular to the field
- 16. Angular velocity, w: Amount of angle (radian) turned in a second wt = total angle of turn during time t 2pf = w period T = 1/f = 2p/w t = 0: F = 0 wt1 t = t1: F = A B sin(wt1) Vind = - dF/dt = - ABsin(wt1)/t1 Vind = - dF/dt = - ABwcos(wt) AC generation
- 18. 170 V -170 V When we say 120 V, it means rms value!! P v2 or i2 vrms = 0.707va
- 19. Power Transmission City of Gainesville has 120,000 population. On average approximately 200 W/person of electric power is required. Let’s assume that GRU transmit power with 120 V. How much current Should be carried in power line? Pt = 120,000 x 200 W = 24,000,000 W = 24 MW P = IV, I = P/V = 24,000,000/120 = 200,000 A However, if we deliver power with 500,000 V, I = 24,000,000/500,000 = 48 A Now Joule heating due to wire resistance (R) is reduced By (48/200,000)2 = 5.8 x 10-8
- 20. Transformer Iron Core AC V Np Ns Vp/Vs = Np/Ns dF/dt Vp = -Np dF/dt Vs = -Ns dF/dt