RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (VK)
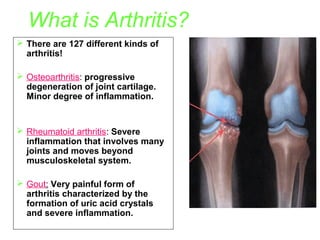
- 1. What is Arthritis? There are 127 different kinds of arthritis! Osteoarthritis: progressive degeneration of joint cartilage. Minor degree of inflammation. Rheumatoid arthritis: Severe inflammation that involves many joints and moves beyond musculoskeletal system. Gout: Very painful form of arthritis characterized by the formation of uric acid crystals and severe inflammation.
- 2. Rheumatoid arthritisChronic progressive, autoimmune disease in which there is joint inflammation, synovial proliferation, and destruction (crippling) of articular cartilages with waxing and waning course. INFLAMMATORY MEDIATORS- Cytokines Interleukin 1 TNF-alpha
- 3. Autoimmune IgM activates complements and release infl. Mediators Neutrophil infiltration Release of Lysosomal enzymes PGs Damage to cartilage, bone errosion vasodilatation edema & pain
- 7. • Diagnosis – – – • Early diagnosis is the first step to easy control History Physical examination Findings 1.Morning stiffness >1hour 2.Symetrical joint swelling for 6 weeks. 3.Swelling in 3 or more joint areas lasting for 6 weeks or more. 4.Rheumatoid nodule. 5.Positve RF. 6.Radiographic erosions.
- 8. The treatment approach: 1. Aims to reduce & possibly prevent damage to the joints & other organs. 2. Relief of pain –primary aim. 3. Rx of pathology- Arrest of disease process - Modification of disease process - Nonpharmacological therapy: o Traditional physical therapy includes-heat & cold therapy o Motion exercises, Aerobic exercise with muscle strength. Pharmacological therapy: o NSAIDs o DISEASE MODIFYING ANTIRHEUMATIC DRUGS [DMARDs] o Adjuvant: GLUCOCORTICOIDS
- 9. NSAIDs• Used in first; they afford symptomatic relief of pain, swelling, morning stiffness, immobility. • Donot arrest disease process. Diclofenac sodium (75-100mg BD) Ibuprofen (200-400mg TDS) Naproxen (500mg single dose) Aspirin (3-5g/day) Indomethacin Special precautions - Peptic ulcer -Bleeding disorder
- 10. DISEASE MODIFYING ANTIRHEUMATIC DRUGS [DMARDs] • Suppress the rheumatoid process i.e. arrest the basic process of joint destruction • Bring about remission. • Also called as SAARDs »Contd.,
- 11. DMARDs • 1.Methotrexate (Mtx.) • 2. Agents used in mild disease or in combination with MTX. • • • • 3.Traditional DMARDs -(limited used currently) • • • • Gold salts (Aurothiomalate sodium)…..X d-Penicillamine………………………..X Azathioprine 4. Biological agents • • • • Hydroxychloroquine Sulfasalazine Minocycline Cyclosporine Infliximab Leflunomide Methoterxate, Azathioprine, Cyclosporine are IMMUNOSUPPRESANT Leflunomide IMMUNO MODULATOR
- 12. METHOTREXATE (Mtx) • An anti metabolite (inhibit dihydrofolate reductase) inhibits folic acid synthesis. • 1st line DMARD at present • RA-Primary MOA is anti-inflammatory rather than antimetabolites -Inhibit cytokine production, cell mediated immune reaction, chemotaxis. • Dose-7.5-10 mg oral weekly. • Onset of symptom relief is relatively rapid – preferred for initial treatment »Contd.,
- 13. • PK- Oral BV of Mtx is variable, may effected by food - Excretions is dec. in renal disease pt. • S/E-GIT distress (parenteral therapy effective to reduce 30mg/wk. i.v, less expensive.) -Oral ulcer -Hair loss -Pneumonia (dec. By use of FA) -Dose dependent progressive liver damage
- 14. Hydroxychloroquine • Antimalarial • Antirheumatic-found to induce remission in 50% patients. • MOA-inhibit inflammatory cells: monocytes interleukins, B lymphocytes. • RA- long periods • Dose-200mg bd • Combined with MTX. • S/ERetinal damage Corneal opacities Neuropathy, Myopathy Rash Graying of hairs Irritable bowel syndrome
- 15. Sulfasalazine • Combination of sulphapyridine and 5 aminosalicylic acid • Inhibits generation of superoxides and cytokines by the inflammatory cells. • Efficacy is equal to chloroquine. • 1-3g/day (3divided dose) • Few adverse effect / good alternative for Mtx Minocycline • Group III broad spectrum antibiotic inhibit arthritic inflammation. • Used in com. With MTX.
- 16. Gold salts (Aurothiomalate sodium) • Introduced in 1929. • Gold is most effective agent for arresting rheumatic process and preventing involvement of additional joints. • It reduce chemotaxis, phagocytosis, macrophages and lysosomal activity and inhibit cell mediated immunity • Benefit - 4-6wks • Starting dose10mg im/wk gradually inc. to 50mg/im/wk up to 1g.then maintain 50mg /im/ for few months. »Contd.,
- 17. • PK:-Gold is heavily bound to plasma and tissue proteins, specially in kidney, stay in the body for years • Toxicity:– Vasodilatation, postural hypotension – Dermtitis, pruritic rash, – Albuminuria – Hepatitis, peripheral neuritis, pulmonary fibrosis – Eosinophilia , bone marrow suppression
- 18. D-Penicillamine • Copper chelating agent • Gold compound like action but less efficacious. • Toxicity is similar like gold • Toxicity: Rash, Proteinurea, Kidney damage, bone marrow depression • Dose: Start with 125-250mg OD, then 250mg BD.
- 19. Azathioprine • Purine antimetabolite • Potent suppressant of cell mediated immunity • Affect differentiation and function of T-cells and natural killer cells • Remission in RA is less but some cases not responding to gold may respond to it. • Given along with corticosteroid • Dose: 2.5-5mg/kg/day
- 20. 4.Biological agents Infliximab• Chimeric IgG1-kappa monoclonal antibody • Anti TNF antibodies • Binds to soluble, bound both the forms of TNF and thus causes dose dependent neutralization of TNF alpha. • Useful in patients resistant to DMARDs and Methotrexate. • Given IV, half life 8-12 days. • A/E: N,V,H and coughing. other use-Crohn’s disease. »Contd.,
- 21. Entanercept • Dimer consisting of TNF receptor joined to Fc domain of human IgG…..binds to TNFα & β. • Given by SC route thrice a wk. • Effective in juvenile RA where Infliximab is found ineffective. Levamisole • Antihelminthic in a dose of 150 mg. • MOA-unknown • A/E- Agranulocytosis
- 22. Leflunomide: • Recently introduced immunomodulator • It inhibits proliferation of activated lymphocytes in patients with active RA. • Arthritic symptoms are suppressed and radiological progression is retarded • It is rapidly converted in the body to active metabolite, which inhibits dihydroorotate dehydrogenase and pyrimidine synthesis in actively growing cells. »Contd.,
- 23. • It is alternative for MTX or Sulfasalazine • Dose: Loading dose of 100mg daily for 3days followed by 20mg OD (t1/2 2 wks) • S/E: Elevation of liver enzymes, renal impairment and teratogenic effect 23
- 24. • Adverse effects:- D, H, N, rashes, loss of hair, thrombocytopenia, chest infection • C/I:children, pregnant and lactating women.
- 25. Corticosteriods • Potent immunosuppressants and antiinflammatory drugs. • Inducted at any stage in RA. • They do not arrest the rheumatoid process nor prevent erosions. • Long term use of corticosteroid carries serious disadvantages.. Low dose 5-10mg • High dose employed over short periods in cases with severe systemic manifestations.
Hinweis der Redaktion
- Exercise recommendations are tricky for arthritis. Research is changing quickly on this topic. Mention that fibromyalgia is also increasingly diagnosed (refer to fact sheets).
- (RF) is the autoantibody (antibody directed against an organism's own tissues) that is most relevant in rheumatoid arthritis.[1] It is defined as an antibody against the Fc portion of IgG. RF and IgG join to form immune complexes that contribute to the disease process Raised rheumatoid factor levels of 25-50 IU/mL, 50.1-100 IU/mL and more than 100 IU/mL were compared with normal levels (less than 25 IU/mL).
- slow acting anti-rheumatic drugs (SAARDs),,,, A period during which symptoms of disease are reduced (partial remission) or disappear (complete remission). With regard to cancer, remission means there is no sign of it on scans or when the doctor examines you. Doctors use the word 'remission' instead of cure when talking about cancer because they cannot be sure that there are no cancer cells at all in the body. So the cancer could come back in the future, although there is no sign of it at the time.
- Chemotaxis is the phenomenon whereby somatic cells, bacteria, and other single-cell or multicellular organisms direct their movements according to certain chemicals in their environment. This is important for bacteria to find food (for example, glucose) by swimming towards the highest concentration of food molecules, or to flee from poisons (for example, phenol). In multicellular organisms, chemotaxis is critical to early development (e.g. movement of sperm towards the egg during fertilization) and subsequent phases of development (e.g. migration of neurons orlymphocytes) as well as in normal function. In addition, it has been recognized that mechanisms that allow chemotaxis in animals can be subverted during cancer metastasis.
