Simplified notes of calculate Wind & Snow loads based on CYS EC1
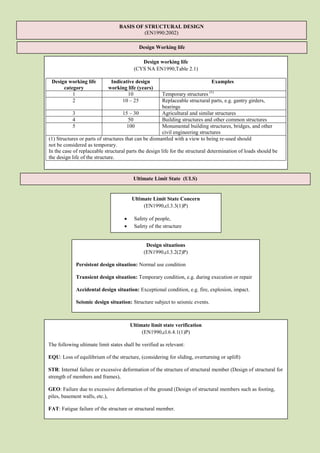
- 1. BASIS OF STRUCTURAL DESIGN (EN1990:2002) Design Working life Design working life (CYS NA EN1990,Table 2.1) Design working life Indicative design Examples category working life (years) 1 10 Temporary structures (1) 2 10 – 25 Replaceable structural parts, e.g. gantry girders, bearings 3 15 – 30 Agricultural and similar structures 4 50 Building structures and other common structures 5 100 Monumental building structures, bridges, and other civil engineering structures (1) Structures or parts of structures that can be dismantled with a view to being re-used should not be considered as temporary. In the case of replaceable structural parts the design life for the structural determination of loads should be the design life of the structure. Ultimate Limit State (ULS) Ultimate Limit State Concern (EN1990,cl.3.3(1)P) Safety of people, Safety of the structure Protection of the contents Design situations (EN1990,cl.3.2(2)P) Persistent design situation: Normal use condition Transient design situation: Temporary condition, e.g. during execution or repair Accidental design situation: Exceptional condition, e.g. fire, explosion, impact. Seismic design situation: Structure subject to seismic events. Ultimate limit state verification (EN1990,cl.6.4.1(1)P) The following ultimate limit states shall be verified as relevant: EQU: Loss of equilibrium of the structure, (considering for sliding, overturning or uplift) STR: Internal failure or excessive deformation of the structure of structural member (Design of structural for strength of members and frames), GEO: Failure due to excessive deformation of the ground (Design of structural members such as footing, piles, basement walls, etc.), FAT: Fatigue failure of the structure or structural member.
- 2. Ultimate Limit State (ULS) Important notes (EN1990,cl.3.2(2)P) Approach 2 (CYS NA EN1990,Table.A1.2(B)) should be used for the design of the structural members of substructure (i.e. footings, piles, basement walls, etc.) (CYS NA EN1990,cl. 2.2.3.4). Actions that cannot exist simultaneously due to physical of functional reasons should not be considered together in combination. The use of expression 6.10a and 6.10b lead to a more economic design in most circumstances. COMBINATION OF ACTIONS FOR PERSISTENT/TRANSIENT DESIGN SITUATION (EN1990,cl.6.4.3.2) Persistent and transient design situation – EQU Equation 6.10 (Set A) Favourable Unfavourable Action γ γ 6.10 Ed=ΣγG Gk +γQ Qk1 + γQ ψ0,2 Qk2 Permanent (dead, 0.9 1.1 earth), γG Variable (imposed, 0 1.5 wind), γQ Note: Single source is not applicable for EQU design situation. Different γ factors can be used in favourable and unfavourable areas. Persistent and transient design situation – STR/GEO Equation 6.10, 6.10a & 6.10b (Set B) 6.10 Ed=ΣγG Gk +γQ Qk1 + γQ ψ0,2 Qk2 Favourable Unfavourable Action γ γ 6.10a Ed=ΣξγG Gk +γQ ψ0,1 Qk1 + γQ ψ0,2 Qk2 Permanent (dead, 1.0 1.35 earth), γG 6.10b Ed=ΣγG Gk +γQ Qk1 + γQ ψ0,2 Qk2 Variable (imposed, 0 1.5 wind), γQ Note: Single source is applicable for STR/GEO design situation. Persistent and transient design situation – GEO Equation 6.10 (Set C) Favourable Unfavourable Action γ γ 6.10 Ed=ΣγG Gk +γQ Qk1 + γQ ψ0,2 Qk2 Permanent (dead, 1.0 1.0 earth), γG Variable (imposed, 0 1.3 wind), γQ Note: Single source is applicable for STR/GEO design situation.
- 3. Combination (sensitivity) factor, ψ (CYS NA EN1990:2002, Table A1.1) ψο ψ1 ψ2 Category Specific Use A Domestic and residential 0.7 0.5 0.3 B Office 0.7 0.5 0.3 C Areas for Congregation 0.7 0.7 0.6 D Shopping 0.7 0.7 0.6 E Storage 1.0 0.9 0.8 F Traffic < 30 kN vehicle 0.7 0.7 0.6 G Traffic < 160 kN vehicle 0.7 0.5 0.3 H Roofs 0.7 0 0 Snow, altitude < 1000 m 0.5 0.2 0 Wind 0.5 0.2 0 Summary table of partial, combination and reduction factors for the STR and GEO ultimate limit states for buildings Unfavourable Permanent action Unfavourable Variable actions Expression Self-weight Imposed floor loads Wind loads Snow loads γG=1.35 γQ,1 =1.5 γQ,iψ0,i =1.5x05=0.75 γQ,iψ0,i =1.5x05=0.75 6.10 γG=1.35 γQ,iψ0,i =1.5x07=1.05 γQ,1 =1.5 γQ,iψ0,i =1.5x05=0.75 γG=1.35 γQ,iψ0,i =1.5x07=1.05 γQ,iψ0,i =1.5x05=0.75 γQ,i =1.5 Less favourable equations 6.10a & 6.10b γG=1.35 γQ,iψ0,i =1.5x07=1.05 γQ,iψ0,i =1.5x05=0.75 γQ,iψ0,i =1.5x05=0.75 6.10a γG=1.35 γQ,iψ0,i =1.5x07=1.05 γQ,iψ0,i =1.5x05=0.75 γQ,iψ0,i =1.5x05=0.75 γG=1.35 γQ,iψ0,i =1.5x07=1.05 γQ,iψ0,i =1.5x05=0.75 γQ,iψ0,i =1.5x05=0.75 ξγG=0.85*1.35 γQ,1 =1.5 γQ,iψ0,i =1.5x05=0.75 γQ,iψ0,i =1.5x05=0.75 6.10b ξγG=0.85*1.35 γQ,iψ0,i =1.5x07=1.05 γQ,1 =1.5 γQ,iψ0,i =1.5x05=0.75 ξγG=0.85*1.35 γQ,iψ0,i =1.5x07=1.05 γQ,iψ0,i =1.5x05=0.75 γQ,i =1.5 Note: Shaded boxes indicate the ‘leading variable action’,
- 4. Serviceability Limit State (SLS) Characteristic value of variable actions For each variable action there are four representative values: 1.The characteristic value Qk (determine by insufficient data). 2.The combination value ψ0Qk (of an action is intended to take account of the reduced probability of the simultaneous of two or more variable actions). 3. Frequent value ψ1Qk (exceeded only for a short period of time and is used primary for the SLS and also the accidental ULS). 4. Quasi-permanent value ψ2Qk (exceeded for a considerable period of time or considered as an average loading over time and used for the long-term affects at the SLS and also accidental and seismic ULS). COMBINATION OF ACTIONS FOR SERVICEABILITY LIMIT STATE (EN1990,cl.6.5.3) Characteristic combination Equation 6.14b Ed=Gk +Qk,1 + ψ0 Qk,2 Frequent combination Equation 6.15b Ed=Gk + ψ1Qk,1 + ψ2 Qk,2 Quasi-permanent combination Equation 6.16b Ed=Gk + ψ2Qk,1 Serviceability Limit State (SLS) – Vertical and Horizontal deformations INDICATIVE LIMITING VALUES FOR VERTICAL DEFLECTIONS (Manual of EC0 &EC1, Table D.1) Serviceability Limit States Vertical deflections Serviceability Requirement Characteristic Combination (Expression 6.14b in EC0) wmax Function and damage to non- structural elements (e.g. partition walls claddings etc) ≤L/500 to L/360 –Brittle ≤L/300 to L/200 -Non-brittle Function and damage to ≤L/300 to L/200 structural elements
- 5. INDICATIVE LIMITING VALUES FOR HORIZONTAL DEFLECTIONS (Manual of EC0 &EC1, Table D.2) Serviceability Limit States Vertical deflections Serviceability Requirement Characteristic Combination (Expression 6.14b in EC0) wmax Function and damage to non- structural elements –Single storey buildings top u≤H/300 of column -Each storey in a multi-storey u≤H/500 to H/300 building -The structure as a whole for u≤H/500 a multi-storey building
- 6. STRUCTURAL LOADS (EN1991:2002) Imposed Loads Category of use (EN1991-1-1:2002,Table 6.1) Category Specific Use Example A Area for domestic and Rooms in residential buildings and houses bedrooms and wards in residential activities hospitals, bedrooms in hotels and hostels kitchens and toilets B Office areas C Areas where people may C1: Areas with tables, etc. e.g. areas in schools, cafés, restaurants, congregate (with the dining exception of areas halls, reading rooms, receptions. defined under category C2: Areas with fixed seats, e.g. areas in churches, theatres or A, B, and D1)) cinemas, conference rooms, lecture halls, assembly halls, waiting rooms, railway waiting rooms. C3: Areas without obstacles for moving people, e.g. areas in museums, exhibition rooms, etc. and access areas in public and administration buildings, hotels, hospitals, railway station forecourts. C4: Areas with possible physical activities, e.g. dance halls, gymnastic rooms, stages. C5: Areas susceptible to large crowds, e.g. in buildings for public events like concert halls, sports halls including stands, terraces and access areas and railway platforms. D Shopping areas D1: Areas in general retail shops D2:Areas in departments stores Imposed loads (EN 1991-1-1:2002, Table 6.2) Category Of loaded areas qk Qk (kN/m2) (kN) Category A -Floors 1.5-2.0 2.0-3.0 -Stairs 2.0-4.0 2.0-4.0 -Balconies 2.5-4.0 2.0-3.0 Category B 2.0-3.0 1.5-4.5 Category C -C1 2.0-3.0 3.0-4.0 -C2 3.0-4.0 2.5-7.0 -C3 3.0-5.0 4.0-7.0 -C4 4.5-5.0 3.5-7.0 -C5 5.0-7.5 3.5-4.5 Category D -D1 4.0-5.0 3.5-7.0 -D2 4.0-5.0 Imposed load on Roof 3.5-7.0 (CYS NA EN1991-1-1, Table 6.10) Imposed load, Sub-category Actions qk Q (kN) (kN/m2) Roof (inaccessible except for H 0.4 1.0 normal maintenance and repair)
- 7. Permanent Loads Permanent load (EN 1991-1-1:2002, Table A.1-A.12) Materials Density, γ Modulus of (kN/m3) Elasticity, E kN/mm2 Reinforced Concrete 25 17-31 Steel 78 210 Glass 25 74 Water 10 - Plastic PTFE 21-22 0.3-0.6 Softwood timber 5 10 Hardwood timber 7 12 Concrete blockwork 18 - Asphalt 22 - Roof tiles 20 5-30 Soil (Sand) 16-18 - Soil (Clay) 20-22 - Insulation board 3 - Aluminium 27 69 Copper 87-89 96 Cement mortar 19-23 20-31 Νylon 11.5 2-3.5 Epoxy resin 16-20 20 Polystyrene 10-13 3-3.3 Carbon fibre 20 415 Fibre glass 15 10 Granite 26 40-70 Typical unit floor Typical loadings Typical unit floor Typical loadings Steel floor kN/m2 Internal ConcreteFloor kN/m2 Self weight of beam 0.25 Partition (minimum) 1.00 Self weight of decking 0.10 Screed (5-70cm) 1.20-1.80 Self weight of meshing 0.05 Raised floor 0.40 Ceiling and services 0.15 Concrete floor (15cm) 3.75 Total 0.55 Celling and services 0.15 Total 6.50-7.10 External Concrete Floor kN/m2 Metal deck roofing kN/m2 Slabs / paving 0.95 Live loading: snow/ Screed (50cm) 1.20 wind uplift 0.6-1.0 Asphalt waterproofing 0.45 Outer covering, insulation and Concrete floor (15cm) 3.75 metal deck liner 0.30 Celling and services 0.15 Purlins-150 deep at 1.5m c/c 0.10 Total 6.50 Services 0.10 Total 1.1-1.5 Timber Floor kN/m2 Timber Flat Roof kN/m2 Partition 1.00 Asphalt waterproofing 0.45 Timber boards/plywood 0.15 Timber joist and insulation 0.20 Timber joist 0.20 Celling and services 0.15 Celling and services 0.15 Total 0.80 Total 1.50
- 8. SNOW LOAD (EN1991-1-3) Monopitch roof Pitch roof Cylinder roof Snow load shape coefficients for cylinder roofs, μ Snow load shape coefficients, μ (EN1991-1-3, Eq. 5.4-5.5) (EN1991-1-3, Table 5.2) μ1 0.8 μs=0 a≤15o ο ο ο ο ο Angle of pitch of 0 ≤α≤30 30 ≤α≤60 α≥60 μ2 μs+μw roof, a μw=(b1+b2)/2h ≤ γh/sk Range must:0.8≤μw≤4 μ1 0.8 0.8(60-α)/30 0 γ:is the weight density of snow may taken as 2kN/m3 μ2 0.8+0.8 α/30 1.6 - For monopitch roof use only μ1 Angle of pitch of roof, a β>60ο β≤60 For pitched roof use μ1andμ2 μ3 should be less than μ3≤2 0 0.2+10 h/b CHARACTERISTIC SNOW LOAD ON GROUND,sk (kN/m2) Exposure coefficient(ΕΝ1991-1-3, Table 5.1) THERMAL COEFFICIENTS C (CYS NA ΕΝ1991-1-3, cl. NA 2.7) (ΕΝ1991-1-3¨2003, cl. 5.2(8)) Topography Ce Ct=1.0 sk = 0.289*(1+(A/452)2) Windswept 0.8 Thermal transmission on the roof Normal 1.0 <1W/m2K A:is the attitude above sea level (m) Sheltered 1.2 Snow load on roof for transient design situations s=μiCeCtsk (EN 1991-1-3Equ.5.1)
- 9. WIND LOAD (EN1991-1-4) BASIC WIND VELOCITY Fundamental Basic wind velocity, vb,0 (CYS NA EN1991-1-4,Fig.1) Season factor (CYS EN1991-1-4,NA 2.4) cseason=1.0 Directional factor (CYSEN1991-1-4,NA 2.4) cdir=1.0 (Conservative value for all direction) Basic wind velocity (EN1991-1-4, Eq. 4.1) vb=cdir.cseasonvb,0
- 10. STRUCTURAL FACTOR (EN1991-1-4, cl.6.0) Determination of cscd Builiding with less than Natural frequency Walls≤100m high Chimney with circular h≤15m f≤5Hz cross-sectional area and, h≤60m h≤6.5·diameter h cscd =1.0 Determine of structural factor cscd Size factor Dynamic factor (EN1991-1-4,Eq.6.2) (EN1991-1-4,Eq.6.3) It is on the safe side to use It is on the safe side to use B2=1 kp=3 B2=1 kp=3 Calculation of R2 can be found in Annex B of Calculation of R2 can be found in Annex B of EN1991-1-4:2005 EN1991-1-4:2005 Can be found TERRAIN OROGRAPHY, (EN1991-1-4, cl.4.3.3) YES Upwind Slope≤3o NO Consider Ignore Detail calculation of terrain orography factor can be found in Annex A of EN1991-1-4:2005
- 11. PEAK VELOCITY PRESSURE Terrain category and terrain parameters (EN1991-1-4, Tab.:4.1) Terrain Description z0 (m) zmin(m) category Sea, costal area exposed to the open 0 SEA 0.003 1 sea. Lakes or area with negligible I 0.01 1 vegetation and without obstacles. COUNTRY Area with low vegetation such as grass and isolated obstacles trees, II 0.05 2 buildings) with separations of at least 20 obstacle height. Area with regular cover of vegetation or buildings or woth isolatd obstacles III with seperations of maximum 20 0.3 5 obstacle height (such as villages, suburban terrain, permanent forest). TOWN Area in which at least 15% of the IV* surface is covered with building and 1.0 10 their average height exceeds 15m. * For buildings in terrain category IV, displacement height hdis should be consider and information can be found in Aneex A.5 of EN1991-1-4:2005 Wind turbulence, Iv(z) Roughness factor, cr(z) Terrain factor, (EN1991-1-4,Eq.4.7) (EN1991-1-4,Eq.4.3-4.5) (EN1991-1-4,cl.4.4) Iv(z)=σv/vm(z)=kl/co(z)ln(z/z0) for cr(z)=kr . ln(z/z0) for zmin≤z≤zmax kr=0.19(z0/z0,II)0.07 zmin≤z≤zmax cr(z)=cr . (zmin) for z≤zmin Iv(z)=Iv(zmin) for z≤zmin z0: is the roughness length Turbulence factor: kl=1.0 Maximum height, zmax (NA CYS EN1991-1-4, cl. NA 2.10) (EN1991-1-4, cl. 4.3.2) zmax=200m Note: for co(z)=1 Iv(z) is not important Orography factor co(z) co(z)=1 Mean wind velocity, vm(z) (EN1991-1-4 cl.4.3.1 ) vm(z)=cr(z).co(z).vb Peak velocity pressure, qpeak(z) (EN1991-1-4 Eq.4.8 ) qpeak(z)=[1+7 Iv(z)]0.5ρ vm2 (z)=ce(z)·0.5·ρ·vb2 Air density:ρ=1.25kg/m3
- 12. EXTERNAL WIND PRESSURE/FORCE ON WALLS Reference height ze, depending on h and b, and corresponding velocity pressure profile (EN1991-1-4, Fig. 7.4) Values of external pressure coefficient for vertical walls of rectangular plan buildings (EN1991-1-4, Tab.:4.1) ZONE A B C D E h/d cpe,10 cpe,1 cpe,10 cpe,1 cpe,10 cpe,1 cpe,10 cpe,1 cpe,10 cpe,1 5 -1.2 -1.4 -0.8 -1.1 -0.5 +0.8 +1.0 -0.7 1 -1.2 -1.4 -0.8 -1.1 -0.5 +0.8 +1.0 -0.5 ≤0.25 -1.2 -1.4 -0.8 -1.1 -0.5 +0.7 +1.0 -0.3 Note: Values for cpe,1 are intended for the design of small elements and fixings with an element of 1m 2 or less such as cladding elements and roofing elements. Values for cpe,10 may be used for the design of the overall load bearing structure of buildings. The external pressure coeffiecient cpe,1 and cpe,10 is using for loadaded area of 1m2 and 10m2 respectively. Key for vertical walls –Mono&dual pitch Key for vertical walls – Flat Roof Roof (EN1991-1-4, Fig.7.5) (EN1991-1-4, Fig.7.5) Pressure on surface &Wind force (EN1991-1-4, Eq. 5.1&5.5) we=qp(ze).(cpe +cpi) & Fw=cscd·Σwe·Aref
- 13. EXTERNAL WIND PRESSURE/FORCE ON FLAT ROOF Recommended values of external pressure coefficients for flat roofs (EN1991-1-4,Tab. 7.2) Zone Roof type F G H I cpe,10 cpe,1 cpe,10 cpe,1 cpe,10 cpe,1 cpe,10 cpe,1 Sharp eaves -1.8 -2.5 -1.2 -2.0 -.07 -1.2 +0.2 hp/h=0.025 -1.6 -2.2 -1.1 -1.8 -0.7 -1.2 -0.2 With hp/h=0.05 -1.4 -2.0 -0.9 -1.6 -0.7 -1.2 +0.2 Parapets hp/h=0.10 -1.2 -1.8 -0.8 -1.4 -0.7 -1.2 -0.2 r/h=0.05 -1.0 -1.5 -1.2 -1.8 -0.4 +0.2 Curved r/h=0.10 -0.7 -1.2 -0.8 -1.4 -0.3 -0.2 Eaves r/h=0.20 -0.5 -0.8 -0.5 -0.8 -0.3 +0.2 a=30o -1.0 -1.5 -1.0 -1.5 -0.3 -0.2 Mansard a=45o -1.2 -1.8 -1.3 -1.9 -0.4 +0.2 Eaves a=60o -1.3 -1.9 -1.3 -1.9 -0.5 -0.2 Note: Values for cpe,1 are intended for the design of small elements and fixings with an element of 1m2 or less such as cladding elements and roofing elements. Values for cpe,10 may be used for the design of the overall load bearing structure of buildings. The external pressure coeffiecient cpe,1 and cpe,10 is using for loadaded area of 1m2 and 10m2 respectively. Pressure on surface &Wind force (EN1991-1-4, Eq. 5.1&5.5) we=qp(ze).(cpe +cpi) & Fw=cscd·Σwe·Aref
- 14. EXTERNAL WIND PRESSURE/FORCE ON MONOPITCH ROOF Recommended values of external pressure coefficients for monopitch roofs (EN1991-1-4,Tab. 7.3a) Pitch Zone for wind direction θ=0o Zone for wind direction θ=180o Angle F G H F G H a cpe,10 cpe,1 cpe,10 cpe,10 cpe,1 cpe,10 cpe,10 cpe,1 cpe,10 cpe,1 cpe,10 cpe,1 5o -1.7 -2.5 -1.2 -2.0 -0.6 -1.2 -2.3 -2.5 -1.3 -2.0 -0.8 -1.2 +0.0 +0.0 +0.0 15o -0.9 -2.0 -0.8 -1.5 -0.3 -2.5 -2.8 -1.3 -2.0 -0/9 -1.2 +0.2 +0.2 +0.2 30o -0.5 -1.5 -0.5 -1.5 -0.2 -1.1 -2.3 -0.8 -1.5 -0.8 +0.7 +0.7 +0.4 45o -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 -0.6 -1.3 -0.5 -0.7 +0.7 +0.7 +0.6 60o +0.7 +0.7 +0.7 -0.5 -1.0 -0.5 -0.5 75o +0.8 +0.8 +0.8 -0.5 -1.0 -0.5 -0.5 Recommended values of external pressure coefficients for monopitch roofs (EN1991-1-4,Tab. 7.3b) Pitch Zone for wind direction θ=90o Angle Fup Flow G H I a cpe,10 cpe,1 cpe,10 cpe,10 cpe,1 cpe,10 cpe,10 cpe,1 cpe,10 cpe,1 5o -2.1 -2.6 -2.1 -2.4 -1.8 -2.0 -0.6 -1.2 -0.5 15o -2.4 -2.9 -1.6 -2.4 -1.9 -2.5 -0.8 -1.2 -0.7 -1.2 30o -2.1 -2.9 -1.3 -2.0 -1.5 -2.0 -1.0 -1.3 -0.8 -1.2 45o -1.5 -2.4 -1.3 -2.0 -1.4 -2.0 -1.0 -1.3 -0.9 -1.2 60o -1.2 -2.0 -1.2 -2.0 -1.2 -2.0 -1.0 -1.3 -0.7 -1.2 75o -1.2 -2.0 -1.2 -2.0 -1.2 -2.0 -1.0 -1.3 -0.5 Note: Values for cpe,1 are intended for the design of small elements and fixings with an element of 1m 2 or less such as cladding elements and roofing elements. Values for cpe,10 may be used for the design of the overall load bearing structure of buildings. The external pressure coeffiecient cpe,1 and cpe,10 is using for loadaded area of 1m2 and 10m2 respectively. Pressure on surface &Wind force (EN1991-1-4, Eq. 5.1&5.5) we=qp(ze).(cpe +cpi) & Fw=cscd·Σwe·Aref
- 15. EXTERNAL WIND PRESSURE/FORCE ON DUOPITCH ROOF Recommended values of external pressure coefficients for duopitch roofs (EN1991-1-4,Tab. 7.4a) Pitch Zone for wind direction θ=0o Angle F G H I J a cpe,10 cpe,1 cpe,10 cpe,10 cpe,1 cpe,10 cpe,10 cpe,1 cpe,10 cpe,1 -45o -0.6 -0.6 -0.8 -0.7 -1.0 -1.5 -30o -1.1 -2.0 -0.8 -1.5 -0.8 -0.6 -0.8 -1.4 -15 o -2.5 -2.8 -1.3 -2.0 -0.8 -1.2 -0.5 -0.7 -1.2 o +0.2 +0.2 -5 -2.3 -2.5 -1.2 -2.0 -0.8 -1.2 -0.6 -0.6 o -1.7 -2.5 -1.2 -2.0 -0.6 -1.2 +0.2 5 -0.6 +0.0 +0.0 +0.0 -0.6 o -0.9 -2.0 -0.8 -1.5 -0.3 -0.4 -1.0 -1.5 15 +0.2 +0.2 +0.2 +0.0 +0.0 +0.0 o -0.5 -1.5 -0.5 -1.5 -0.2 -0.4 -0.5 30 +0.7 +0.7 +0.4 +0.0 +0.0 o -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 -0.2 -0.3 45 +0.7 +0.7 +0.6 +0.0 +0.0 60 o +0.7 +0.7 +0.7 -0.2 -0.3 75 o +0.8 +0.8 +0.8 -0.2 -0.3 Recommended values of external pressure coefficients for duopitch roofs (EN1991-1-4,Tab. 7.4b) Pitch Zone for wind direction θ=90o Angle a F G H I cpe,10 cpe,1 cpe,10 cpe,10 cpe,1 cpe,10 cpe,10 cpe,1 -45o -1.4 -2.0 -1.2 -2.0 -1.0 -1.3 -0.9 -1.2 -30o -1.5 -2.1 -1.2 -2.0 -1.0 -1.3 -0.9 -1.2 -15o -1.9 -2.5 -1.2 -2.0 -0.8 -1.2 -0.8 -1.2 -5o -1.8 -2.5 -1.2 -2.0 -0.7 -1.2 -0.6 -1.2 5o -1.6 -2.2 -1.2 -2.0 -0.7 -1.2 -0.6 15o -1.3 -2.0 -1.2 -2.0 -0.6 -1.2 -0.5 30o -1.1 -1.5 -1.4 -2.0 -0.8 -1.2 -0.5 45o -1.1 -1.5 -1.4 -2.0 -0.9 -1.2 -0.5 60o -1.1 -1.5 -1.4 -2.0 -0.8 -1.2 -0.5 75o -1.1 -1.5 -1.4 -2.0 -0.8 -1.2 -0.5 Pressure on surface &Wind force (EN1991-1-4, Eq. 5.1&5.5) we=qp(ze).(cpe +cpi) & Fw=cscd·Σwe·Aref
