High throughput approaches to understanding gene function and mapping architecture in bacteria
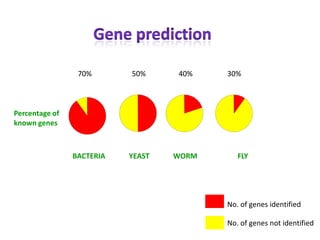
- 1. 70% 50% 40% YEAST WORM 30% Percentage of known genes BACTERIA FLY No. of genes identified No. of genes not identified
- 2. Gene Protein Cellular process Phenotype Biological activity Process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product to generate the macromolecular machinery for life in the form of protein In order to make proteins, the gene from the DNA is copied by each of the chemical bases into mRNA
- 3. Gene is not an independent identity Proteins they encode—function in the intact organism There is no gene in isolation Study true phenotype ‗n‘ number of genes So far there has been means and ways
- 4. High-throughput approaches to understanding gene function and mapping architecture in bacteria
- 5. Outline of Seminar • Approaches to know gene function • Platforms for mapping • Some of the HTA for mapping • Map and their architecture • Some websites and databases for mapping • Applications and its limitation • Future prospective • Conclusion
- 6. Approaches to know gene function Forward genetics Phenotype Genotype Reverse genetics Genotype Phenotype
- 7. Forward genetics Poorly understood phenomenon Forward genetics starts with phenotype and lead to identification of interesting genotype Reverse genetics Protein of known functions Reverse genetics starts with a known genotype and finally end up with phenotype Compared to forward genetic approach , reverse genetics screens are more advanced in gene function discovery in bacteria
- 8. Reverse genetic approaches L OF Loss of function GOF Gain of function Downregulation Upregulation
- 9. • In reverse genetic approaches, LOF/GOF libraries are grown then libraries go through selection and only mutants withstanding the selection are identified • With the use of interaction between proteins and genes, the libraries are then used in a reverse genetics manner and assessed accurately for every mutant in the library
- 10. List of available ordered LOF and GOF libraries in microbes
- 11. Why interactions ? Biological processes Potential new players Pathway architecture Genetic wiring diagrams
- 12. Interaction platforms • Gene–gene interactions • Protein-protein interactions
- 13. Gene–gene interactions Negative interactions Negative interactions (aggravating interactions) describe double mutants exhibiting a more severe phenotype than expected Positive interactions Positive interactions (alleviating interactions) describe double mutants exhibiting a less severe phenotype than expected
- 14. Negative interactions Within pathway genetic interactions
- 15. Between pathway genetic interactions
- 16. Positive interactions Positive interactions are interesting, because it is proposed that they can provide insight into biochemical relationships between gene products and help define the architecture of biological pathways
- 17. Protein-Protein Interactions(PPI) • Protein-protein interaction network and protein interactome is at cutting-edge to expand our understanding on biological processes and networks of bacteria • Comparatively systematic mapping of protein–protein interaction(PPI) can advance understanding of interactome networks with applications ranging from protein functional characterization in a system biology
- 18. Protein-Protein Interactions(PPI) Fundamental to all biological processes Involved in different pathways Understanding -integrated system
- 19. Cont.. Biological processes signal transduction and stress responses At the molecular level, PPI could be important in Phosphorylation, Transcriptional co-factor recruitment, Assembly of cytoskeleton, transporter activation and many others Thus, identifying, quantifying, localizing, and modeling entire PPI map/networks (protein ‗interactome‘) is a key prerequisite for understanding the biophysical basis of all cellular processes and for creating a framework to characterize the function
- 20. Protein-Protein interaction mapping Bacterial -2-hybrid system ( HT- B2H) Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation (BiFC) MALDI-TOF Microarrays
- 21. Bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) • Based on the reconstitution of split non-fluorescent GFP variants to form a fluorescent and active protein complex emitting fluorescent signal • Basically, the bait proteins and target proteins will be fused, binding of the bait and target proteins will lead to the fusion of the two combinatory parts of the fluorescent proteins, which can be observed by fluorescent microscopy
- 22. • Therefore, through the visualization and analysis of the intensity and distribution of fluorescence in these cells, one can identify both the location and interaction partners of proteins of interest • In addition, the intensity of the fluorescence emitted is proportional to the strength of the interaction
- 23. MALDI-TOF • Allows off-line analysis of protein interaction • MALDI-TOF analysis is very fast K. G. Standing 2000
- 24. Select a colony Prepare onto a MALDI target plate Insert the dried target plate into apparatus Data interpretation Run the apparatus
- 25. Steps involved Protein molecules embedded in matrix plate Absorb laser energy Desorption: a rapid, explosive evaporation to carry the proteins into the gas phase Ionization: Matrix is acidic and donates positive charge to the proteins
- 26. Microarray This technique is used to generate data from protein-protein interaction, which allow researchers to investigate the expression state of a large number of genes/proteins a single experiment. Microarrays “appear to be the ideal tool to assess the diversity of the bacterial world” Huyghe et al. 2009
- 27. Steps involved in microarray analysis in bacteria
- 28. Methods Bacterial twohybrid (B2H) Pros Cons High-throughput High false positive rate . Only binary interaction detected. Bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) Localize the interaction complex in cell Highly sensitive to enable detection of weak and transient Interactions Optimal for the highthroughput assay some what slow Matrix Assisted Laser Desroption Ionization Time Of Flight (MALDI-TOF ) High-throughput, High sensitivity Poor mass resolution,Photodegradation by ionization High-throughput Microarray Limited number of samples used
- 29. Protein interaction mapping by using functional shotgun sequence of Rickettsia sibirica Rickettsia….. The bacteria invade endothelial cells and cause lysis after large amounts of progeny have accumulated Rickettsia sibirica Joel et al.,2005
- 30. Along with analysis of the combined genomic sequence and protein-protein interaction data, set of six subunits virulence related Type IV secretion system (T4SS) proteins revealed over 284 interactions and will provide insight into the mechanism of Rickettsial pathogenicity
- 31. • The need for large-scale protein interaction analyses, a bacterial two-hybrid system was coupled with a whole genome shotgun sequencing approach for microbial analysis • The B2H system used in this study was Hochschild et al., developed by • Constructs were renamed pBAIT and pPREY respectively Hochschild et al.,
- 32. Bacterial two-hybrid vectors • A protein of interest (the bait) is fused to λcI, a DNA binding domain, which binds to a λ operator sequence, OR2, placed upstream of a weak promoter • In addition, a second protein of interest (the prey) is fused to the RNA polymerase (RNAP) a subunit, an activation domain, which is part of the RNAP holoenzyme Activation domain RNAP Target bait DNA binding protein λcI
- 33. Bacterial Two-Hybrid System A protein interaction between the bait and prey protein recruits the complex
- 34. Functional shotgun sequencing of Rickettsia sibirica • Randomly sheared fragments of Rickettsia sibirica adapted with BstXI adapters and ligated into pBAIT. • Shotgun library is constructed in the bait vector, followed by determination of open reading frame (ORF) fragments that are cloned in the correct frame and can be used as bait
- 35. (i) Genomic DNA is sheared and cloned into bait and prey vectors (ii) Randomly selected bait clones are sequenced, the data assembled and the genome annotated (iii) Clones determined to contain fragments of genes expressed in the correct frame are re-arrayed for screening. A copy of the set is pooled, and the inserts transferred to the prey vector creating the fragment ORF prey library (iv) Baits from proteins of interest are either screened against the Sequencing of positive clones directly from selected colonies is conducted with pBAIT or previously created sheared genomic pPREY specific primers. prey library, or from the ORF prey library
- 36. Screening in the bacterial two-hybrid system • For screening, the Bacteriomatch reporter strain (Stratagene USA) was used • Each peptide of interest was transformed using 100 µl of Bacteriomatch reporter strain cells, 50 ng of pBAIT and 50 ng of either ORF library or shotgun library pPREY DNA • Dual transformants were plated on LB agar supplemented with 25 mg/ml IPTG 300 mg/ml carbenicillin 2 mg/ml tetracycline, 50 mg/ml kanamycin and 12.5 mg/ml chloramphenicol • Screening was also conducted on minimal media plates containing the same antibiotics, IPTG amounts, but with lactose as the sole carbon source.
- 37. Result : Percent prediction in Rickettsiae genomes Rickettsiae sibirica Average protein-coding gene length (bp) 787 % coding 77.7 Protein-coding regions 1234
- 38. Categorization and validation of interactions Interactions were categorized as follows: • Observed once, were assigned score 1 • More than once were assigned score 2 • More than once by different fragments were assigned score 3
- 39. Screening yielded 284 distinct interactions between 155 protein families 162 interactions -category 1 (observed once) 48 interaction -category 2 (observed two times) 74 interaction - category 3 (observed more than two using different fragments)
- 40. • The region of the genome including the virulence cluster VirD4-VirB8 was selected for further study because of their apparent role in virulence and their relationship to the Type IV secretion system (T4SS) • Among 284 interactions six T4SS subunits were screened, two intra-complex interactions was identified newly among T4SS subunits not previously detected in studies of other organisms using the B2H
- 41. Map of T4SS protein interactions The six T4SS subunits screened
- 42. Bacterial two hybrid system Methods Bacterial twohybrid (B2H) Pros High-throughput Cons High false positive rate . Only binary interaction detected.
- 43. High-throughput, quantitative analyses of genetic interactions in E. coli Athanasios et al., 2011
- 44. • A method based on F factor–driven conjugation, which allows for high-throughput generation of double mutants in Escherichia coli. This method, termed genetic interaction analysis technology for E. coli (GIANT-coli), permits us to systematically generate and array double-mutant cells on solid media in high-density • Genetic interaction analysis technology for E. coli (GIANT-coli) method to permit rapid, large-scale genetic interaction studies in E. coli
- 45. Development of GIANT-coli The high-throughput mating system has 3 steps • In step 1: mated the donor strain, Hfr containing a single gene deletion marked with the kanamycin-resistance gene, (kan)on agar plates to a complete set of E. coli K-12 archives recipient strains, a set of single-gene knockouts marked with the chloramphenicol-resistance gene (cat). In high-throughput format, arrayed recipient strains on agar plates in the desired format • step 2: Transferred cells using a robot from the mating plates onto plates containing kanamycin (‘intermediate selection’) • Step 3: Pinned the cells from the intermediate selection plate onto a plate containing both antibiotics to select for double recombinants
- 46. Flowchart - different steps used in GIANT-coli. An Hfr donor (male) strain carrying a selectable marker (kan) replacing an open reading frame A is mated on agar plates with arrayed F– recipients carrying a different selectable marker (cat) replacing another open reading frame Images of two representative plates used for generating a mating plate are shown below. After mating, cells are subjected to an intermediate selection on kanamycin and then to a final selection for double mutants using both antibiotics.
- 47. Quantification of the plate • To assess our strategy for mapping genetic interactions in E. coli, we performed a 12 x12 genetic cross • Choice of genes surA, ybaY, ycbS, ompC, yraI, cpxR, degP, pal, ompA, yfgL,yraP and basR A representative 1,536- colony format, M9-glycerol plate showing the double mutants resulting from crossing 12 strains
- 48. Validation of GIANT-coli • Genes are allowed to array each recipient multiple times on the same plate so that we could assess reproducibility, compare with different media rich (LB) versus minimal (M9-glycerol)) and evaluate growth differences • Several new positive, lethal and sick interactions were observed
- 49. Heat maps representing 12 x12 crosses in LB and M9-glycerol
- 50. Interactions detected in the 12x12 genetic interaction experiment Pairs Interaction Pairs Interaction degP-surA Lethal degP-surA ND pal-surA Lethal pal-surA ND pal-yfgL Lethal pal-yfgL Lethal pal-ompA Sick pal-ompA Lethal degP-yfgL Sick degP-yfgL ND degP-pal Slightly sick degP-pal ND cpxR-pal Sick cpxR-pal Slightly Sick ompA-yraP Slightly sick ompA-yraP Sick pal-yraP Positive pal-yraP ND ompA-degP Slightly positive ompA-degP Positive ompA-surA Positive ompA-surA ND cpxR-ompA Positive cpxR-ompA Slightly Positive LB versus M9-glycerol
- 51. Optimized critical parameters (i) Efficient mating between donor and recipient (ii) Efficiency of transfer
- 52. Mapping Architecture Proteins as ―nodes‖ Node Protein–protein interaction indicated by ―line or edge‖ Smaller circuit patterns termed NETWORK MOTIFS In protein interaction networks, fully connected sub graphs, i.e. motifs with every node linked to every other node, the so-called CLIQUES Edge Node
- 53. Network model Transcriptional network Protein interaction network Metabolic network
- 55. Bacillus subtilis protein interaction network, which is composed of 112 specific interactions between 78 proteins DNA replication Signal transduction Mobility stress and proteolysis metabolism protein synthesis Transcription Unknown
- 56. The first large-scale genetic interaction map in E. coli was recently published, and focused on biogenesis pathways of the cell envelope
- 57. Databases Sequence EMBL, genbank Enzyme and interaction Brenda Protein Annotation interaction Swissprot, STRING Pathway Ecocyc Libraries Bruker daltonics Structure PDB, SCOP
- 58. STRING Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes/Proteins
- 59. • STRING (De) Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes/Proteins http://www.bork.embl-heidelberg.de/STRING
- 62. Limitation Advantages • A large number of tests can be carried out in a short period of time • It requires skill and experience • Quality Data obtained • Initial cost is more can be
- 63. Future perspective • High-throughput genetic interaction screens provide dynamic cellular network snapshots of a • As high-throughput technologies are applied to bacterial system, we can expect rapid progress towards a comprehensive examination of bacterial interactome • Novel information obtained by using HTA will greatly improve our understanding of the mechanisms that control protein interaction and organize molecular structures of bacteria • In the future, the combination of high-throughput genotyping and phenotypic profiling techniques should provide even higher resolution and functionally relevant genetic interaction maps
- 64. Conclusion