Weitere ähnliche Inhalte Ähnlich wie Plant diversity cheat sheet (20) Mehr von Timothy Welsh (20) 1. AP Biology - Core Concept Cheat Sheet
15: Plant Evolution and Diversity
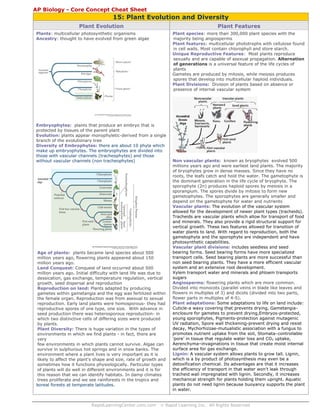
Plant Evolution
Plant Features
Plants: multicellular photosynthetic organisms
Ancestry: thought to have evolved from green algae
Plant species: more than 300,000 plant species with the
majority being angiosperms
Plant features: multicellular phototrophs with cellulose found
in cell walls. Most contain chlorophyll and store starch.
Unique Reproductive Features: Most plants reproduce
sexually and are capable of asexual propagation. Alternation
of generations is a universal feature of the life cycles of
plants
Gametes are produced by mitosis, while meiosis produces
spores that develop into multicellular haploid individuals.
Plant Divisions: Division of plants based on absence or
presence of internal vascular system
Embryophytes: plants that produce an embryo that is
protected by tissues of the parent plant
Evolution: plants appear monophyletic-derived from a single
branch of the evolutionary tree
Diversity of Embrophytes: there are about 10 phyla which
make up embryophytes. The embryophytes are divided into
those with vascular channels (tracheophytes) and those
without vascular channels (non tracheophytes)
Age of plants: plants became land species about 500
million years ago, flowering plants appeared about 150
million years ago.
Land Conquest: Conquest of land occurred about 500
million years ago. Initial difficulty with land life was due to
dessication, gas exchange, temperature regulation, vertical
growth, seed dispersal and reproduction
Reproduction on land: Plants adapted by producing
gametes within gametangia and the egg was fertilized within
the female organ. Reproduction was from asexual to sexual
reproduction. Early land plants were homosporous- they had
reproductive spores of one type, one size. With advance in
seed production there was heterosporous reproduction- in
which two distinctive cells of differing sizes were produced
by plants.
Plant Diversity: There is huge variation in the types of
environments in which we find plants - in fact, there are
very
few environments in which plants cannot survive. Algae can
survive in sulphurous hot springs and in snow banks. The
environment where a plant lives is very important as it is
likely to affect the plant's shape and size, rate of growth and
sometimes how it functions physiologically. Particular types
of plants will do well in different environments and it is for
this reason that we can identify habitats. In damp climates
trees proliferate and we see rainforests in the tropics and
boreal forests at temperate latitudes.
RapidLearningCenter.com.com
Non vascular plants: known as bryophytes evolved 500
millions years ago and were earliest land plants. The majority
of bryophytes grow in dense masses. Since they have no
roots, the leafs catch and hold the water. The gametophyte is
the dominant generation in the life cycle of bryophyte. The
sporophyte (2n) produces haploid spores by meiosis in a
sporangium. The spores divide by mitosis to form new
gametophytes. The sporophytes are generally smaller and
depend on the gametophyte for water and nutrients
Vascular plants: The evolution of the vascular system
allowed for the development of newer plant types (tracheids).
Tracheids are vascular plants which allow for transport of food
and minerals. They also provide a rigid structural support for
vertical growth. These two features allowed for transition of
water plants to land. With regard to reproduction, both the
gametophyte and the sporophyte are independent and have
photosynthetic capabilities.
Vascular plant divisions: includes seedless and seed
bearing forms. Seed bearing forms have more specialized
transport cells. Seed bearing plants are more successful than
non seed bearing plants. They have a more efficient vascular
system and an extensive root development.
Xylem transport water and minerals and phloem transports
sugars
Angiosperms: flowering plants which are more common.
Divided into monocots (parallel veins in blade like leaves and
flowers in multiples of 3) and dicots (divided into two parts,
flower parts in multiples of 4-5).
Plant adaptations: Some adaptations to life on land include:
Cuticle-a waxy covering that prevents drying, Gametangiaenclosure for gametes to prevent drying,Embryos-protected,
young sporophytes, Pigments-protection against mutagenic
UV radiation, Spore wall thickening-prevent drying and resist
decay, Mychorhizzae-mutualistic association with a fungus to
promotes nutrient uptake from the soil, Stomata–controllable
‘pore’ in tissue that regulate water loss and CO2 uptake,
Aerenchyma–invaginations in tissue that create moist internal
surface area for gas exchange.
Lignin: A vascular system allows plants to grow tall. Lignin,
which is a by product of photosynthesis may even be a
detoxification chemical. Its advantages are that it increases
the efficiency of transport in that water won’t leak through
tracheid wall impregnated with lignin. Secondly, it increases
mechanical strength for plants holding them upright. Aquatic
plants do not need lignin because buoyancy supports the plant
in water.
© Rapid Learning Inc. All Rights Reserved