Pdfa1 2
- 1. Chapter 1
Transparency
2
Introduction To Physics
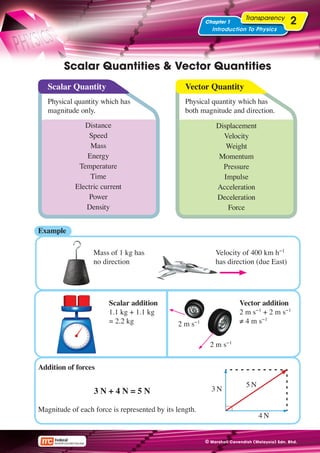
Scalar Quantities & Vector Quantities
Scalar Quantity Vector Quantity
Physical quantity which has Physical quantity which has
magnitude only. both magnitude and direction.
Distance Displacement
Speed Velocity
Mass Weight
Energy Momentum
Temperature Pressure
Time Impulse
Electric current Acceleration
Power Deceleration
Density Force
Example
Mass of 1 kg has Velocity of 400 km h−1
no direction has direction (due East)
Scalar addition Vector addition
1.1 kg + 1.1 kg 2 m s−1 + 2 m s−1
= 2.2 kg 2 m s−1 ≠ 4 m s−1
2 m s−1
Addition of forces
5N
3N+4N=5N 3N
Magnitude of each force is represented by its length.
4N
© Marshall Cavendish ( Malaysia ) Sdn. Bhd.