Different types of wbc cells
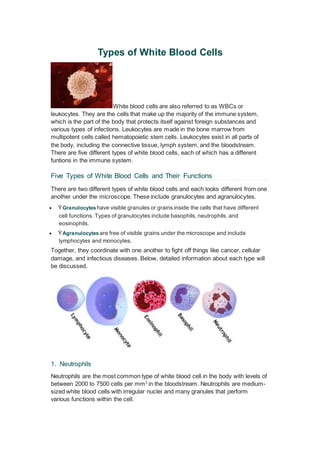
- 1. Types of White Blood Cells White blood cells are also referred to as WBCs or leukocytes. They are the cells that make up the majority of the immune system, which is the part of the body that protects itself against foreign substances and various types of infections. Leukocytes are made in the bone marrow from multipotent cells called hematopoietic stem cells. Leukocytes exist in all parts of the body, including the connective tissue, lymph system, and the bloodstream. There are five different types of white blood cells, each of which has a different funtions in the immune system. Five Types of White Blood Cells and Their Functions There are two different types of white blood cells and each looks different from one another under the microscope. These include granulocytes and agranulocytes. ŸGranulocytes have visible granules or grains inside the cells that have different cell functions. Types of granulocytes include basophils, neutrophils, and eosinophils. ŸAgranulocytes are free of visible grains under the microscope and include lymphocytes and monocytes. Together, they coordinate with one another to fight off things like cancer, cellular damage, and infectious diseases. Below, detailed information about each type will be discussed. 1. Neutrophils Neutrophils are the most common type of white blood cell in the body with levels of between 2000 to 7500 cells per mm3 in the bloodstream. Neutrophils are medium- sized white blood cells with irregular nuclei and many granules that perform various functions within the cell.
- 2. Function: Neutrophils function by attaching to the walls of the blood vessels, blocking the passageway of germs that try to gain access to the blood through a cut or infectious area. Neutrophils are the first cells to reach an area where a breach in the body has been made. They kill germs by means of a process known as phagocytosis or “cell-eating”. Besides eating bacteria one-by-one, they also release a burst of super oxides that have the ability to kill many bacteria at the same time. 2. Lymphocytes Lymphocytes are small, round cells that have a large nucleus within a small amount of cytoplasm. They have an important function in the immune system, being major players in the humoral immune system, which is the part of the immune system that relates to antibody production. Lymphocytes tend to take up residence in lymphatic tissues, including the spleen, tonsils, and lymph nodes. There are about 1300 to 4000 lymphocytes per mm3 of blood. Function: B lymphocytes make antibodies, which is one of the final steps in disease resistance. When B lymphocytes make antibodies, they prime pathogens for destruction and then make memory cells ready that can go into action at any time, remembering a previous infection with a specific pathogen. T lymphocytes are another type of lymphocyte, differentiated in the thymus and important in cell- mediated immunity. 3. Monocytes Monocytes are the largest of the types of white blood cells. There are only about 200-800 monocytes per mm3 of blood. Monocytes are agranulocytes, meaning they have few granules in the cytoplasm when seen under the microscope. Monocytes turn into macrophages when they exit the bloodstream. Function: As macrophages, monocytes do the job of phagocytosis (cell-eating) of any type of dead cell in the body, whether it is a somatic cell or a dead neutrophil. Because of their large size, they have the ability to digest large foreign particles in a wound unlike other types of white blood cells. 4. Eosinophils There aren’t that many eosinophils in the bloodstream—only about 40-400 cells per mm3 of blood. They have large granules that help in cellular functions. Eosinophils are especially important when it comes to allergies and worm infestations. Function: Eosinophils work by releasing toxins from their granules to kill pathogens. The main pathogens eosinophils act against are parasites and worms. High eosinophil counts are associated with allergic reactions. 5. Basophils Basophils are the least frequent type of white blood cell, with only 0-100 cells per mm3 of blood. Basophils have large granules that perform functions that are not
- 3. well known. They are very colorful when stained and looked at under the microscope, making them easy to identify. Function: Basophils have the ability to secrete anticoagulants and antibodies that have function against hypersensitivity reactions in the bloodstream. They act immediately as part of the immune system’s action against foreign invaders. Basophils contain histamine, which dilates the vessels to bring more immune cells to the area of injury. What are White Blood Cells? Our bodies are constantly under siege. If we could see into the world of tiny microorganisms, we would observe the constant attack of viruses and bacteria upon us. These potentially harmful intruders enter through any nook or cranny, be it our mouth and nose or an open cut. Sometimes we succumb to infection. However, fortunately for us, we are protected by an equally tough microscopic army within our own body. A Lymphocyte, One Type of White Blood Cell Welcome to the world of white blood cells. These tiny organisms serve as the armed forces of our body, fighting off intruders, patrolling for invaders, and even cleaning up. Also known as leukocytes, white blood cells represent our immune system. If not for these fighters, we may have succumbed to tiny potential killers long ago. There are five different types of white blood cells, each performing specific jobs to keep us healthy and alive. In this lesson, learn more about these cells and how they work for our body. Where do White Blood Cells Come From? Although there are several different types of white blood cells, they all come from the same place. White blood cells originate from stem cells in our bone marrow.The bone marrowis essentially a blood cell producing factory, pumping out billions of new cells every day. These freshly made white blood cells have the ability to move on their own. Once produced, they leave the marrow and enter the bloodstream. However, it may surprise you to know that most white blood cells do not actually reside in the bloodstream. The majority of leukocytes are found outside the blood, in tissues and interstitial fluid. The ones that are found within the blood are typically just utilizing the bloodstream as a vehicle to get to another location. Like soldiers in charge of certain posts, white blood cells have specific areas and tissues in the body for which they are responsible. The Five Types of White Blood Cells
- 4. Let's take a look at the first type of white blood cell, the basophil. This is the least numerous of all the white blood cells. But it plays an important part in the inflammatory response of the body. For example, have you ever found yourself in a sneezing fit after walking through a field of flowers? This allergic reaction is due to the inflammatory response of the body as it attempts to get rid of the pesky pollen in your nose. A substance called histamine is released, causing your allergic reaction. Basophils produce and store the histamine that is used at a time like this.
