Pre Natal Growth & Development
- 1. Pre Natal Growth And Development PROF (Dr.) SAIBEL FARISHTA
- 2. During this period, the height increases by almost 5000 times as compared to only a threefold increase during the post natal period. It is divided into 3 periods – Period of the Ovum – This period extends for two weeks from the time of fertilization. During this period the cleavage of the ovum and attachment of the ovum to the intra uterine wall occurs. Period of the Embryo – This period extends from the 14th day to the 56th day of intra uterine life. Major part of the development of the facial and cranial region occurs during this time. Period of the Foetus – This phase extends between the 56th day of intrauterine life till birth. In this period, accelerated growth of the cranio- facial structures occurs resulting in an increase in their size. There is also a change in proportion between the various structures.
- 3. Pre Natal Growth Of Cranial Base The earliest evidence of formation of the cranial base is seen in the post/late somitic period [4th – 6th week of intra uterine life]. During this period mesenchymal tissue derived from primitive streak, neural crest and occipital sclerotomes condense around the developing brain and form a capsule which is known as Ectomenix or Ectomeningeal capsule. A portion of this capsule gives rise to the future cranial base. Evidence of skull formation is seen late after development of other cranial structures. From around 40th day onwards, the Ectomeningeal capsule is slowly converted into cartilage. This is the onset of cranial base formation. The conversion of mesenchymal cells into cartilage or chondrification occurs in 4 regions – • Parachordal • Hypophyseal • Nasal • Otic
- 4. • Parachordal – The chondrification centers which form around the cranial end of the notochord are called Parachordal cartilages. • Hypophyseal – Cranial to the termination of notochord, the Hypophyseal pouch develops which gives rise to the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. [i] On both sides of hypophyseal stem two post sphenoid cartilages develop, which fuse together and form the posterior part of the body of sphenoid. [ii] Cranial to pituitary gland, two trabecular cartilages develop which fuse together and form the anterior part of body of sphenoid. [iii] Lateral to pituitary gland, chondrification centers are seen which form the lesser wing and greater wing of sphenoid.
- 5. • Nasal – Initially a capsule is seen around the nasal sense organ. This capsule chondrifies and forms the cartilages of the nostrils, which later fuses with the cartilages of the cranial base. • Otic – Initially a capsule is seen around the vestibulo-cochlear sense organs which condrifies and later ossifies to give rise to the mastoid and petrous portions of the temporal bone. The otic cartilages also fuse with the cartilages of the cranial base. The initially separate centres of cartilage formation in the cranial base fuse together into a single irregular and perforated cranial base. Numerous nerves, blood vessels result in perforations or foramina in the developing cranial base. The ossifying chondro-cranium meets the ossifying cranial vault to form the neurocranium.
- 7. Chondro – Cranial Ossification The cranial base which is in a cartilagenous form undergoes ossification. The bones of the cranial base undergo both endochondral and intramembranous ossification. • Occipital Bone – It shows both types of ossification. Seven ossification centres are seen, 2 intra membranous and 5 endochondrial. • Temporal Bone – It also ossifies both endochondrally and intra- membranously from 11 centres. • Ethmoid Bone – It shows only endochondrial ossification. It ossifies from 3 centres. • Sphenoid Bone – It ossifies by both types from 15 ossification centres. The cranial base or chondrocranium is important as a junction between the cranial vault and the facial skeleton, being shared by both. The cranial base is relatively stable during growth as compared to the cranial vault and the face. Therefore the cranial base can be taken as a basis against which the cranial vault and facial skeleton can be compared.
- 8. Flexure Of The Cranial Base - During the embryonic and early fetal period, the cranial base becomes flexed in the region between the pituitary fossa and the spheno-occipital junction. The face is tucked under the cranium. This flexure of the cranial base is accompanied by a corresponding flexure of the developing brain stem. The spinal chord and foramen magnum, which during the early stages of development were directed backwards, now become directed downwards.
- 9. Uneven growth of Cranial Base The uneven growth of the cranial base is due to the uneven nature of growth seen in different regions of brain. The flexure of cranial base aids in increasing the neurocranial capacity and is the main reason for the downward displacement of face during growth. At 10th week of intra uterine life, the flexion of the base is about 65 degrees. This flattens out a bit at the time of birth.
- 10. Pre-Natal Embryology Of Maxilla Around the 4th week of intra uterine life, a prominent bulge appears on the ventral aspect of the embryo corresponding to the developing brain. Below the bulge, a shallow depression which corresponds to the primitive mouth appears called stomadeum. The floor of the stomadeum is formed by the buccopharyngeal membrane which separates the stomadeum from the foregut. By around 4th week of intrauterine life, 5 brachial arches form in the region of the future head and neck. Each of these arches gives rise to muscles, connective tissue, vasculature, skeletal components and neural components of the future face. The 1st brachial arch is the mandibular arch and plays an important role in the development of the naso- maxillary region. The mesoderm covering the developing forebrain proliferates and forms a downward projection that overlaps the upper part of the stomadeum. This downward projection is called Fronto-nasal process.
- 11. The stomadeum is thus overlapped superiorly by the frontonasal process, while the mandibular arches of both the sides form the lateral walls of the stomadeum. The mandibular arch gives a bud from it’s dorsal end called the Maxillary Process. The maxillary process grows ventro- medio-cranial to the main part of the mandibular arch, which is now called Mandibular Process. Thus, at this stage the primitive mouth or stomadeum is overlapped from above by the frontal process, below by the mandibular process and on either sides by the maxillary processes. The ectoderm overlying the fronto-nasal process shows bilateral localized thickening above the stomadeum. These are called as the Nasal Placodes. These placodes soon sink and form the nasal pits. The formation of these nasal pits divides the fronto nasal process into 2 parts – medial and lateral nasal processes. The two mandibular processes grow medially and fuse to form the lower lip and lower jaw. As the maxillary process undergoes growth, the fronto nasal process becomes narrow so that the two nasal pits come closer.
- 13. Development Of Palate The palate is formed by contributions of the maxillary process, palatal shelves given off by maxillary process and Fronto – nasal process. The fronto-nasal process gives rise to the premaxillary region while the palatal shelves form the rest of the palate. As the palatal shelves grow medially, their union is prevented by the presence of the tongue. Thus, initially the developing palatal shelves grow vertically downwards towards the floor of the mouth.
- 14. Around 7th week of intra-uterine life, a quick transformation in the position of the palatal shelves occurs and they change from a vertical to a horizontal position. By 8.5 weeks of intra-uterine life, the two palatal shelves are in close approximation with each other. Initially they are covered by an epithelial lining but as they join the epithelial cells degenerate. The connective tissue from the palatal shelves intermingle with each other and fuse. The entire palate doesn’t contact and fuse at the same time. Initially contact occurs in the central region of the secondary palate , then closure occurs anteriorly and posteriorly. The mesial edges of the palatal processes fuse with the free lower end of nasal septum and thus separates the two nasal cavities from each other and the oral cavity.
- 15. Ossification of Palate – Occurs from 8th week of intra-uterine life. Its is intra-membranous type of ossification. The palate ossifies from a single center derived from the maxilla. The most posterior part of the palate does not ossify and forms the soft palate. The mid-palatal suture ossifies by 12-14 years. Development of Maxillary Sinus – It forms around 3rd month of intra- uterine life. It develops by expansion of the nasal mucous membrane into the maxillary bone. Later the sinus enlarges by resorption of the internal wall of maxilla.
- 16. Pre-Natal Embryology Of Mandible Around 4th week of intra-uterine life, the developing brain and pericardium form two prominent bulges on the ventral aspect of the embryo. These bulges are separated by the primitive oral cavity or stomadeum. The floor of the stomadeum is by bucco-pharyngeal membrane which separates it from the foregut. The pharyngeal arches are laid down on the lateral and ventral aspects of the cranialmost part of the foregut which lies in close approximation with the stomadeum. Initially there are six pharyngeal arches, but the 5th one disappears as soon as it is formed leaving only five. They are separated by four branchial grooves. The first arch is called as the mandibular arch and the second arch, hyoid arch. The other arches do not have any specific names. Each of these five arches contain a central cartilage rod that forms the skeleton of the arch, a muscular component, a vascular component and a neural component.
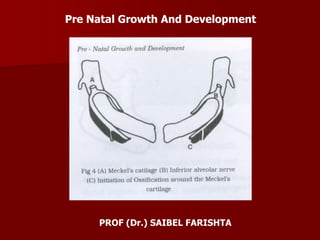
- 17. The mandibular arch forms the lateral wall of the stomadeum. It gives a bud at its dorsal end which is called as maxillary process. It grows ventro-medially, cranial to the main part of the arch, which is now called as the mandibular process. The mandibular processes grow towards each other and fuse in midline. They now form the lower border of the stomadeum i.e. the lower lip and the lower jaw. Meckel’s Cartilage It is derived from the 1st branchial arch around the 41st – 45th day of intra-uterine life. It extends from the cartilagenous otic capsule to the midline or symphysis and provides a template for guiding the growth of the mandible. A major part of Meckel’s cartilage disappears during growth and the remaining part develops into – mental ossicles, incus and malleus, spine of sphenoid bone, anterior ligament of malleus and spheno-mandibular ligament. The first structure to develop in the primordium of the lower jaw is the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve. This is followed by mesenchymal condensation forming the first branchial arch. Neurotrophic factors produced by the nerve induce osteogenesis in the ossification centers.
- 18. A single ossification center for each half of mandible arises in 6th week of intra-uterine life in the region of the bifurcation of the inferior alveolar nerve into mental and incisive branches. The ossifying membrane is located lateral to the Meckel’s cartilage. From this primary center, ossification spreads below and around the inferior alveolar nerve and its incisive and branch and upwards to form a trough for accommodating the developing tooth buds. Spread of the intramembranous ossification dorsally and ventrally forms the body and ramus of the mandible. As ossification continues, the Meckel’s cartilage becomes surrounded and invaded by bone. Ossification stops at the site that later becomes mandibular lingula from where the Meckel;s cartilage continues into the middle ear and develops into the auditory ossicles [malleus and incus].
- 20. Endochondral Bone Formation It is seen only in 3 areas of mandible – condylar process, coronoid process and mental region. • Condylar Process – At about 5th week of intra-uterine life, an area of mesenchymal condensation can be seen above the ventral part of the developing mandible. This develops into a cone shaped cartilage by about 10th week and starts ossification by 14th week. It then migrates inferiorly and fuses with the mandibular ramus by about 4 months. Much of the cone shaped cartilage is replaced by bone by the middlw of fetal life, but its upper end persists into adulthood acting both as a growth cartilage and an articular cartilage. • Coronoid Process – Secondary accessory cartilages appear in the region of the coronoid process by about the 10-14th week of intra-uterine life. This cartilage is believed to grow as a response to the developing temporalis muscle. The coronoid accessory cartilage becomes incorporated into the expanding intra-membranous bone of the ramus and disappears before birth.
- 21. • Mental Region – In the mental region, on either side of the symphysis, one or two small cartilages appear and ossify in the 7th month of intra- uterine life to form variable numbers of mental ossicles in the fibrous tissues of the symphysis. These ossicles become incorporated into the intra-membranous bone when the symphysis ossifies completely during the first year of post-natal life.
- 22. THANK YOU