Difference b/w STP RSTP PVST & MSTP
•
11 gefällt mir•30,645 views
Difference between Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) 1. The main difference between Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP IEEE 802.1W) and Spanning Tree Protocol (STP IEEE 802.1D) is that Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP IEEE 802.1W) assumes the three Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) ports states Listening, Blocking, and Disabled are same (these states do not forward Ethernet frames and they do not learn MAC addresses). Hence Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP IEEE 802.1W) places them all into a new called Discarding state. Learning and forwarding ports remain more or less the same.
Melden
Teilen
Melden
Teilen
Downloaden Sie, um offline zu lesen
Empfohlen
Empfohlen
Weitere ähnliche Inhalte
Was ist angesagt?
Was ist angesagt? (20)
MPLS L3 VPN Tutorial, by Nurul Islam Roman [APNIC 38]![MPLS L3 VPN Tutorial, by Nurul Islam Roman [APNIC 38]](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![MPLS L3 VPN Tutorial, by Nurul Islam Roman [APNIC 38]](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
MPLS L3 VPN Tutorial, by Nurul Islam Roman [APNIC 38]
Dynamic Routing All Algorithms, Working And Basics

Dynamic Routing All Algorithms, Working And Basics
Ähnlich wie Difference b/w STP RSTP PVST & MSTP
Ähnlich wie Difference b/w STP RSTP PVST & MSTP (20)
Spanning Tree Protocol, from a future CCNA´s perspective.

Spanning Tree Protocol, from a future CCNA´s perspective.
Understanding spanning tree protocol topology changes

Understanding spanning tree protocol topology changes
Mehr von Netwax Lab
Mehr von Netwax Lab (20)
Eincop Netwax Lab: HSRP (Hot Standby Router Protocol)

Eincop Netwax Lab: HSRP (Hot Standby Router Protocol)
Kürzlich hochgeladen
💉💊+971581248768>> SAFE AND ORIGINAL ABORTION PILLS FOR SALE IN DUBAI AND ABUDHABI}}+971581248768
+971581248768 Mtp-Kit (500MG) Prices » Dubai [(+971581248768**)] Abortion Pills For Sale In Dubai, UAE, Mifepristone and Misoprostol Tablets Available In Dubai, UAE CONTACT DR.Maya Whatsapp +971581248768 We Have Abortion Pills / Cytotec Tablets /Mifegest Kit Available in Dubai, Sharjah, Abudhabi, Ajman, Alain, Fujairah, Ras Al Khaimah, Umm Al Quwain, UAE, Buy cytotec in Dubai +971581248768''''Abortion Pills near me DUBAI | ABU DHABI|UAE. Price of Misoprostol, Cytotec” +971581248768' Dr.DEEM ''BUY ABORTION PILLS MIFEGEST KIT, MISOPROTONE, CYTOTEC PILLS IN DUBAI, ABU DHABI,UAE'' Contact me now via What's App…… abortion Pills Cytotec also available Oman Qatar Doha Saudi Arabia Bahrain Above all, Cytotec Abortion Pills are Available In Dubai / UAE, you will be very happy to do abortion in Dubai we are providing cytotec 200mg abortion pill in Dubai, UAE. Medication abortion offers an alternative to Surgical Abortion for women in the early weeks of pregnancy. We only offer abortion pills from 1 week-6 Months. We then advise you to use surgery if its beyond 6 months. Our Abu Dhabi, Ajman, Al Ain, Dubai, Fujairah, Ras Al Khaimah (RAK), Sharjah, Umm Al Quwain (UAQ) United Arab Emirates Abortion Clinic provides the safest and most advanced techniques for providing non-surgical, medical and surgical abortion methods for early through late second trimester, including the Abortion By Pill Procedure (RU 486, Mifeprex, Mifepristone, early options French Abortion Pill), Tamoxifen, Methotrexate and Cytotec (Misoprostol). The Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates Abortion Clinic performs Same Day Abortion Procedure using medications that are taken on the first day of the office visit and will cause the abortion to occur generally within 4 to 6 hours (as early as 30 minutes) for patients who are 3 to 12 weeks pregnant. When Mifepristone and Misoprostol are used, 50% of patients complete in 4 to 6 hours; 75% to 80% in 12 hours; and 90% in 24 hours. We use a regimen that allows for completion without the need for surgery 99% of the time. All advanced second trimester and late term pregnancies at our Tampa clinic (17 to 24 weeks or greater) can be completed within 24 hours or less 99% of the time without the need surgery. The procedure is completed with minimal to no complications. Our Women's Health Center located in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, uses the latest medications for medical abortions (RU-486, Mifeprex, Mifegyne, Mifepristone, early options French abortion pill), Methotrexate and Cytotec (Misoprostol). The safety standards of our Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates Abortion Doctors remain unparalleled. They consistently maintain the lowest complication rates throughout the nation. Our Physicians and staff are always available to answer questions and care for women in one of the most difficult times in their lives. The decision to have an abortion at the Abortion Cl+971581248768>> SAFE AND ORIGINAL ABORTION PILLS FOR SALE IN DUBAI AND ABUDHA...

+971581248768>> SAFE AND ORIGINAL ABORTION PILLS FOR SALE IN DUBAI AND ABUDHA...?#DUbAI#??##{{(☎️+971_581248768%)**%*]'#abortion pills for sale in dubai@
Kürzlich hochgeladen (20)
Apidays Singapore 2024 - Modernizing Securities Finance by Madhu Subbu

Apidays Singapore 2024 - Modernizing Securities Finance by Madhu Subbu
A Beginners Guide to Building a RAG App Using Open Source Milvus

A Beginners Guide to Building a RAG App Using Open Source Milvus
Apidays New York 2024 - The value of a flexible API Management solution for O...

Apidays New York 2024 - The value of a flexible API Management solution for O...
Why Teams call analytics are critical to your entire business

Why Teams call analytics are critical to your entire business
Repurposing LNG terminals for Hydrogen Ammonia: Feasibility and Cost Saving

Repurposing LNG terminals for Hydrogen Ammonia: Feasibility and Cost Saving
Exploring the Future Potential of AI-Enabled Smartphone Processors

Exploring the Future Potential of AI-Enabled Smartphone Processors
Apidays New York 2024 - Accelerating FinTech Innovation by Vasa Krishnan, Fin...

Apidays New York 2024 - Accelerating FinTech Innovation by Vasa Krishnan, Fin...
+971581248768>> SAFE AND ORIGINAL ABORTION PILLS FOR SALE IN DUBAI AND ABUDHA...

+971581248768>> SAFE AND ORIGINAL ABORTION PILLS FOR SALE IN DUBAI AND ABUDHA...
ProductAnonymous-April2024-WinProductDiscovery-MelissaKlemke

ProductAnonymous-April2024-WinProductDiscovery-MelissaKlemke
Powerful Google developer tools for immediate impact! (2023-24 C)

Powerful Google developer tools for immediate impact! (2023-24 C)
TrustArc Webinar - Stay Ahead of US State Data Privacy Law Developments

TrustArc Webinar - Stay Ahead of US State Data Privacy Law Developments
Strategies for Landing an Oracle DBA Job as a Fresher

Strategies for Landing an Oracle DBA Job as a Fresher
Axa Assurance Maroc - Insurer Innovation Award 2024

Axa Assurance Maroc - Insurer Innovation Award 2024
Difference b/w STP RSTP PVST & MSTP
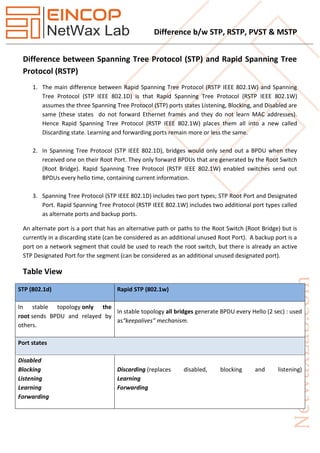
- 1. Difference b/w STP, RSTP, PVST & MSTP Difference between Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) 1. The main difference between Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP IEEE 802.1W) and Spanning Tree Protocol (STP IEEE 802.1D) is that Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP IEEE 802.1W) assumes the three Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) ports states Listening, Blocking, and Disabled are same (these states do not forward Ethernet frames and they do not learn MAC addresses). Hence Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP IEEE 802.1W) places them all into a new called Discarding state. Learning and forwarding ports remain more or less the same. 2. In Spanning Tree Protocol (STP IEEE 802.1D), bridges would only send out a BPDU when they received one on their Root Port. They only forward BPDUs that are generated by the Root Switch (Root Bridge). Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP IEEE 802.1W) enabled switches send out BPDUs every hello time, containing current information. 3. Spanning Tree Protocol (STP IEEE 802.1D) includes two port types; STP Root Port and Designated Port. Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP IEEE 802.1W) includes two additional port types called as alternate ports and backup ports. An alternate port is a port that has an alternative path or paths to the Root Switch (Root Bridge) but is currently in a discarding state (can be considered as an additional unused Root Port). A backup port is a port on a network segment that could be used to reach the root switch, but there is already an active STP Designated Port for the segment (can be considered as an additional unused designated port). Table View STP (802.1d) Rapid STP (802.1w) In stable topology only the root sends BPDU and relayed by others. In stable topology all bridges generate BPDU every Hello (2 sec) : used as“keepalives” mechanism. Port states Disabled Blocking Listening Learning Forwarding Discarding (replaces disabled, blocking and listening) Learning Forwarding
- 2. Difference b/w STP, RSTP, PVST & MSTP To avoid flapping, it takes 3 seconds for a port to migrate from one protocol to another (STP / RSTP) in a mixed segment. Port roles Root (Forwarding) Designated (Forwarding) Non-Designated (Blocking) Root (Forwarding) Designated (Forwarding) Alternate(Discarding)Backup (Discarding) Additional configuration to make an end node port aport fast (in case a BPDU is received). - An edge port (end node port) is an integrated Link type which depends on the duplex : Point-to-point for full duplex & shared for half duplex). Topology changes and convergence Use timers for convergence (advertised by the root): Hello(2 sec) Max Age(20 sec = 10 missed hellos) Forward delay timer (15 sec) - Introduce proposal and agreement process for synchronization (< 1 sec).- Hello, Max Age and Forward delay timer used only for backward compatibility with standard STP Only RSTP port receiving STP (802.1d) messages will behaves as standard STP. Slow transition (50sec): Blocking (20s) =>Listening (15s) =>Learning (15s) =>Forwarding Faster transition on point-to-point and edge ports only:Less states – No learning state, doesn’t wait to be informed by others, instead, actively looks for possible failure by RLQ (Request Link Query) a feedback mechanism. Use only 2 bits from the flag octet:Bit 7 : Topology Change Acknowledgment.Bit 0 : Topology Change Use other 6 bits of the flag octet (BPDU type 2/version 2): Bit 1 : ProposalBit 2, 3 : Port roleBit 4 : LearningBit 5 : ForwardingBit 6 : AgreementBit 0, 7 : TCA & TCN for backward compatibility The bridge that discover a change in the network inform the root, that in turns informs all others by sending BPDU with TCA bit set and instruct them to clear their DB entries after “short timer” (~Forward delay) expire. TC is flooded through the network, every bridge generate TC (Topology change) and inform its neighbors when it is aware of a topology change andimmediately delete old DB entries.
- 3. Difference b/w STP, RSTP, PVST & MSTP If a non-root bridge doesn’t receive Hello for 10*Hello (advertised from the root), start claiming the root role by generating its own Hello. Wait for 3*Hello on a root port (advertised from the root) before deciding to act. Wait until TC reach the root + short timer (~Forward delay) expires, then flash all root DB entries Delete immediately local DB except MAC of the port receiving the topology changes (proposal) Difference between PVST+ (Per VLan Spanning Tree) & MST (Multiple Spanning Tree) 1. PVST+ (Per VLan Spanning Tree)- It's difference from 802.1Q CST because instead of having a single root switch for all VLAN, The PVST+ mean STP is run in each VLAN. 2. MST (Multiple Spanning Tree)- MST maps multiple VLANs into a spanning tree instance, with each instance having a spanning tree topology independent of other spanning tree instances.This architecture provides multiple forwarding paths for data traffic, enables load balancing, and reduces the number of STP instances required to support a large number of VLANs. MST improves the fault tolerance of the network because a failure in one instance (forwarding path) does not affect other instances (forwarding paths).