Roots of equations
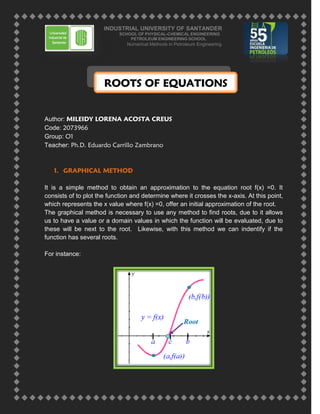
- 1. INDUSTRIAL UNIVERSITY OF SANTANDER SCHOOL OF PHYSICAL-CHEMICAL ENGINEERING PETROLEUM ENGINEERING SCHOOL Numerical Methods in Petroleum Engineering ROOTS OF EQUATIONS Author: MILEIDY LORENA ACOSTA CREUS Code: 2073966 Group: O1 Teacher: Ph.D. Eduardo Carrillo Zambrano 1. GRAPHICAL METHOD It is a simple method to obtain an approximation to the equation root f(x) =0. It consists of to plot the function and determine where it crosses the x-axis. At this point, which represents the x value where f(x) =0, offer an initial approximation of the root. The graphical method is necessary to use any method to find roots, due to it allows us to have a value or a domain values in which the function will be evaluated, due to these will be next to the root. Likewise, with this method we can indentify if the function has several roots. For instance: Root
- 2. INDUSTRIAL UNIVERSITY OF SANTANDER SCHOOL OF PHYSICAL-CHEMICAL ENGINEERING PETROLEUM ENGINEERING SCHOOL Numerical Methods in Petroleum Engineering 2. CLOSED METHODS The key feature of these methods is that we evaluate a domain or range in which values are close to the function root; these methods are known as convergent. Within the closed methods are the following methods: 2.1. BISECTION (Also called Bolzano method) The method feature lie in look for an interval where the function changes its sign when is analyzed. The location of the sign change gets more accurately by dividing the interval in a defined amount of sub-intervals. Each of this sub intervals are evaluated to find the sign change. The approximation to the root improves according to the sub-intervals are getting smaller. The procedure is the following: Step 1: Choose lower, xo, and upper, xf, values, which enclose the root, so that the function changes sign in the interval. Verify if Bolzano method is satisfied: ( ) ( ) Step 2: An approximation of the xr root, is determined by: Step 3: Realize the following evaluations to determine in what subinterval the root is: a) If ( ) ( ) then the root is within the lower or left subinterval. So, to do xf=xr and return to step 2. b) If ( ) ( ) then the root is within the top or right subinterval. So, to do x0=xr and return to step 2. Step 4: If ( ) ( ) the root is equal to xr; the calculations ends.
- 3. INDUSTRIAL UNIVERSITY OF SANTANDER SCHOOL OF PHYSICAL-CHEMICAL ENGINEERING PETROLEUM ENGINEERING SCHOOL Numerical Methods in Petroleum Engineering The maximum number of iterations to obtain the root value is given by the following equation: | | ( ) Where: TOL = Tolerance ( ) 2.2. THE METHOD OF FALSE POSITION Although the bisection method is technically valid to determine roots, its focus is relatively inefficient. Therefore this method is an improved alternative based on an idea for a more efficient approach to the root. This method raises draw a straight line joining the two interval points (x, y) and (x1, y1), the cut generated by the x-axis allows greater approximation to the root. Using similar triangles, the intersection can be calculated as follows: ( ) ( )
- 4. INDUSTRIAL UNIVERSITY OF SANTANDER SCHOOL OF PHYSICAL-CHEMICAL ENGINEERING PETROLEUM ENGINEERING SCHOOL Numerical Methods in Petroleum Engineering The final equation for False position method is: ( )( ) ( ) ( ) The calculation of the root xr requires replacing one of the other two values so that they always have opposite signs, what leads these two points always enclose the root. Note: Sometimes, depending on the function, this method works poorly, while the bisection method leads better approximations. 3. OPEN METHODS These methods are based on formulas that require a single initial value x, or a couple of them but do not necessarily that contain the root. Because of this feature, sometimes these methods diverge or move away from the root, according to grows the number of iterations. It is important to know that when the open methods converge, these are more efficient than methods that use intervals. Opened methods are:
- 5. INDUSTRIAL UNIVERSITY OF SANTANDER SCHOOL OF PHYSICAL-CHEMICAL ENGINEERING PETROLEUM ENGINEERING SCHOOL Numerical Methods in Petroleum Engineering 3.1. SINGLE ITERATION OF FIXED POINT Open methods employ a formula that predicts the root, this formula can be developed for a single iteration of a fixed point (also called point iteration or successive substitution) to change the equation f (x) = 0 so that is: x=g(x) Tal formula es empleada para predecir un nuevo valor de x en función del valor anterior de x, a través de: This formula is employ to predict a new x value in function of the previous x valor, through: xi+1=g(xi) Posteriormente, estas iteraciones son usadas para calcular el error aproximado de tal manera que el mínimo error indique la raíz de la función en cuestión. Subsequently, these iterations are used to calculate the approximate error so that the least error indicates the root of the function in matter. | | Example Use simple iteration of a fixed point to locate the root of f(x) = e-x – x Solution: Like f(x)=0 e-x – x=0 Expressing of the form x=g(x) result us: x= e-x Beginning with an initial value of xo=0, we can apply the iterative equation xi+1=g(xi) and calculate: i xi Ea(%) Et(%) 0 0 100.0 1 1.000000 100.0 76.3 2 0.367879 171.8 35.1 3 0.692201 46.9 22.1 4 0.500473 38.3 11.8
- 6. INDUSTRIAL UNIVERSITY OF SANTANDER SCHOOL OF PHYSICAL-CHEMICAL ENGINEERING PETROLEUM ENGINEERING SCHOOL Numerical Methods in Petroleum Engineering 5 0.606244 17.4 6.89 6 0.545396 11.2 3.83 7 0.579612 5.90 2.20 8 0.560115 3.48 1.24 9 0.571143 1.93 0.705 10 0.564879 1.11 0.399 Thus, each iteration bring near increasingly to the estimated value with the true value of the root, that is to say 0.56714329 3.2. NEWTON-RAPHSON METHOD The most widely used formula to find roots, is the Newton Raphson, argues that if it indicates the initial value of x1 as the value of the root, then it is possible to extend a tangent line from the point (x1,f(x1)). Where this straight line crosses the x-axis will be the point of improve approach. This method could derived in a graphically or using Taylor’s series. Newton Raphson formula ( ) ( ) From its reorder is obtained the value of the desired root. ( ) ( )
- 7. INDUSTRIAL UNIVERSITY OF SANTANDER SCHOOL OF PHYSICAL-CHEMICAL ENGINEERING PETROLEUM ENGINEERING SCHOOL Numerical Methods in Petroleum Engineering Note: The Newton Raphson method has a strong issue for its implementation, this is due to the derivative, as in some functions is extremely difficult to evaluate the derivative. 3.3. SECANT METHOD The secant method allows an approximation of the derivative by means of a divided difference; this method avoids falling into the Newton-Raphson problem, as it applies for all functions regardless of whether they have difficulty in evaluating its derivative. The approximation of the derivative is obtained as follows: ( ) ( ) ( ) Substituting this equation in the Newton Raphson formula we get: ( )( ) ( ) ( ) The above equation is the secant formula. 4. MULTIPLES ROOTS A multiple root corresponds to a point where a function is tangential to the x axis For instance, double root results of: f(x)=(x – 3)(x – 1)(x – 1) ó f(x)=x3 – 5x2 – 7x – 3 Because a value of x makes two terms in the previous equation are zero. Graphically this means that the curve tangentially touches the x axis in the double root. The function touches the axis but not cross in the root.
- 8. INDUSTRIAL UNIVERSITY OF SANTANDER SCHOOL OF PHYSICAL-CHEMICAL ENGINEERING PETROLEUM ENGINEERING SCHOOL Numerical Methods in Petroleum Engineering 4 Double f(x) Root 0 1 3 4 A triple root corresponds to the case where a value of x makes three terms in an equation equal to zero, as: f(x)=(x – 3)(x – 1)(x – 1)(x – 1) ó f(x)=x4 – 6x3 + 12x2– 10x + 3 In this case the function is tangent to the axis at the root and crosses the axis. In general, odd multiplicity of roots crosses the axis, while the pair multiplicity does not cross. 1. The fact that the function does not change sign on multiple pairs roots prevents the use of reliable methods that use intervals. 2. Not only f(x) but also f'(x) approach to zero. These problems affect the Newton- Raphson and the secant methods, which contain derivatives in the denominator of their respective formulas.
- 9. INDUSTRIAL UNIVERSITY OF SANTANDER SCHOOL OF PHYSICAL-CHEMICAL ENGINEERING PETROLEUM ENGINEERING SCHOOL Numerical Methods in Petroleum Engineering Some modifications have been proposed to alleviate these problems, Ralston and Rabinowitz (1978) proposed the following formulas: a) Root Multiplicity ( ) ( ) Where m is the root multiplicity (ie, m=2 for a double root, m=3 for a triple root, etc.). This formulation may be unsatisfactory because it presumes the root multiplicity knowledge. b) New Function ( ) ( ) ( ) The new function is replaced in the Newton-Raphson’s method equation, so you get an alternative: ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) c) Modification of the Secant Method Substituting the new function (explained previously) in the equation of the secant method, we have ( )( ) ( ) ( ) 5. POLYNOMIALS ROOTS Below are described the methods to find polynomial equations roots of the general form: ( )
- 10. INDUSTRIAL UNIVERSITY OF SANTANDER SCHOOL OF PHYSICAL-CHEMICAL ENGINEERING PETROLEUM ENGINEERING SCHOOL Numerical Methods in Petroleum Engineering Where n is the polynomial order and the a are constant coefficients. The roots of such polynomials have the following rules: a. For equation of order n, there are n real or complex roots. It should be noted that these roots are not necessarily different. b. If n is odd, there is at least one real root. c. If the roots are complex, there is a conjugate pair (esto es, λ + µi y λ - µi) where √ 5.1. Müller’s Method A predecessor of Muller method is the secant method, which obtain root, estimating a projection of a straight line on the x-axis through two function values (Figure1). Muller's method takes a similar view, but projected a parabola through three points (Figure2). The method consist in to obtain the coefficients of the three points, replace them in the quadratic formula and get the point where the parabola intersects the x-axis The approach is easy to write, as appropriate this would be: ( ) ( ) ( ) Shape 1 Shape 2 Thus, this parable is used to intersect the three points [x0, f(x0)], [x1, f(x1)] and [x2, f(x2)]. The coefficients of the previous equation are evaluated by substituting one of these three points to make:
- 11. INDUSTRIAL UNIVERSITY OF SANTANDER SCHOOL OF PHYSICAL-CHEMICAL ENGINEERING PETROLEUM ENGINEERING SCHOOL Numerical Methods in Petroleum Engineering ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) The last equation generated that ( ) system of two equations with two unknowns: ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) Defining this way: ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) Substituting in the system: ( ) ( ) The coefficients are: ( ) Finding the root, the conventional solution is implemented, but due to rounding error potential, we use an alternative formulation: √ The great advantage of this method is that we find real and imaginary roots. Finding the error this will be:
- 12. INDUSTRIAL UNIVERSITY OF SANTANDER SCHOOL OF PHYSICAL-CHEMICAL ENGINEERING PETROLEUM ENGINEERING SCHOOL Numerical Methods in Petroleum Engineering | | To be an approximation method, this is performed sequentially and iteratively, where x1, x2, x3replace the points x0, x1, x2 carrying the error to a value close to zero. 5.2. Bairstow’s Method Bairstow's method is an iterative process related approximately with Muller and Newton-Raphson methods. The mathematical process depends of dividing the polynomial between a factor. Given a polynomial fn(x) find two factors, a quadratic polynomial f2(x) = x2 – rx – s y fn-2(x) The general procedure for the Bairstow method is: 1. Given fn(x) y r0 y s0 2. Using Newton-Raphson method calculate f2(x) = x2 – r0x – s0 y fn-2(x), such as, the residue of fn(x)/ f2(x) be equal to zero. 3. The roots f2(x) are determined, using the general formula. 4. Calculate fn-2(x)= fn(x)/ f2(x). 5. Do fn(x)= fn-2(x) 6. If the polynomial degree is greater than three, back to step 2 7. If not, we finish The main difference of this method in relation to others, allows calculating all the polynomial roots (real and imaginaries). To calculate the polynomials division, we use the synthetic division. So given fn(x) = anxn + an-1xn-1 + … + a2x2 + a1x + a0 By dividing between f2(x) = x2 – rx – s, we have as a result the following polynomial
- 13. INDUSTRIAL UNIVERSITY OF SANTANDER SCHOOL OF PHYSICAL-CHEMICAL ENGINEERING PETROLEUM ENGINEERING SCHOOL Numerical Methods in Petroleum Engineering fn-2(x) = bnxn-2 + bn-1xn-3 + … + b3x + b2 With a residue R = b1(x-r) + b0, the residue will be zero only if b1 and b0 are. The terms b and c, are calculated using the following recurrence relation: bn = a n bn-1 = an-1 + rbn bi = ai + rbi+1 + sbi+2 cn = bn cn-1 = bn-1 + rcn ci = bi + rci+1 + sci+2 Finally, the approximate error in r and s can be estimated as: | | | | | | | | When both estimated errors failed, the roots values can be determined as: √ BIBLIOGRAPHY CHAPRA, Steven. Numerical Methods for engineers. Editorial McGraw-Hill. Third edition. 2000. http://lc.fie.umich.mx/~calderon/programacion/Mnumericos/Bairstow.html http://illuminatus.bizhat.com/metodos/biseccion.htm http://aprendeenlinea.udea.edu.co/lms/moodle/mod/resource/view.php?inpopu p=true&id=24508