1 - The Chemical Nature of Cells
•Als PPT, PDF herunterladen•
1 gefällt mir•2,538 views
Melden
Teilen
Melden
Teilen
Empfohlen
Weitere ähnliche Inhalte
Was ist angesagt?
Was ist angesagt? (20)
Biological macromolecules, M. Sc. Zoology, University of Mumbai.

Biological macromolecules, M. Sc. Zoology, University of Mumbai.
B.sc. biochemistry sem 1 introduction to biochemistry unit 2 biomolecules

B.sc. biochemistry sem 1 introduction to biochemistry unit 2 biomolecules
Ähnlich wie 1 - The Chemical Nature of Cells
Ähnlich wie 1 - The Chemical Nature of Cells (20)
Organic chemistry review for Anatomy and Physiology Students

Organic chemistry review for Anatomy and Physiology Students
Biology - Chp 2 - The Chemistry Of Life - PowerPoint

Biology - Chp 2 - The Chemistry Of Life - PowerPoint
important slide related to physiology as well different cell structure.pptx

important slide related to physiology as well different cell structure.pptx
Mehr von Martin Jellinek
Mehr von Martin Jellinek (20)
Kürzlich hochgeladen
God is a creative God Gen 1:1. All that He created was “good”, could also be translated “beautiful”. God created man in His own image Gen 1:27. Maths helps us discover the beauty that God has created in His world and, in turn, create beautiful designs to serve and enrich the lives of others.
Explore beautiful and ugly buildings. Mathematics helps us create beautiful d...

Explore beautiful and ugly buildings. Mathematics helps us create beautiful d...christianmathematics
Kürzlich hochgeladen (20)
Mixin Classes in Odoo 17 How to Extend Models Using Mixin Classes

Mixin Classes in Odoo 17 How to Extend Models Using Mixin Classes
ICT Role in 21st Century Education & its Challenges.pptx

ICT Role in 21st Century Education & its Challenges.pptx
Seal of Good Local Governance (SGLG) 2024Final.pptx

Seal of Good Local Governance (SGLG) 2024Final.pptx
Russian Escort Service in Delhi 11k Hotel Foreigner Russian Call Girls in Delhi

Russian Escort Service in Delhi 11k Hotel Foreigner Russian Call Girls in Delhi
Unit-V; Pricing (Pharma Marketing Management).pptx

Unit-V; Pricing (Pharma Marketing Management).pptx
Presentation by Andreas Schleicher Tackling the School Absenteeism Crisis 30 ...

Presentation by Andreas Schleicher Tackling the School Absenteeism Crisis 30 ...
Measures of Central Tendency: Mean, Median and Mode

Measures of Central Tendency: Mean, Median and Mode
Explore beautiful and ugly buildings. Mathematics helps us create beautiful d...

Explore beautiful and ugly buildings. Mathematics helps us create beautiful d...
1 - The Chemical Nature of Cells
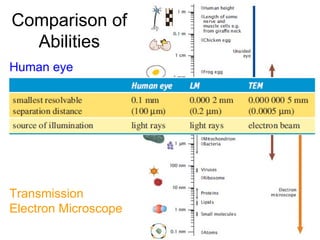
- 1. Comparison of Abilities Human eye Light microscope Transmission Electron Microscope
- 2. Levels of Organisation Living Organisms systems organs tissues cells Biomolecules Organic carbohydrates proteins lipids nucleic acids Inorganic Ions Water (inorganic)
- 3. Levels of Organisation Biomolecules Organic carbohydrates proteins lipids nucleic acids Inorganic Ions Water (inorganic) simple sugars amino acids fatty acids nucleotides glycerol
- 4. Cells!
- 6. What all cells need to do Make specific Biomacromolecules Control and regulate chemical Reactions Produce energy to drive Chemical reactions Take in small molecules Produce useful products for export from the cell Receive and respond to chemical signals Remove waste products Grow, reproduce and pass on genetic information to the next generation of cells
- 10. Animal Cells
- 11. Plant Cells
- 15. WATER
- 16. A little chemistry … Covalent bonding involves atoms joining to form molecules In order to form a stable molecule, each atom must share sufficient electrons in order to result in a full outer shell If an atom only has one shell of electrons, 2 is sufficient to fill it The second shell and onwards all require a minimum of 8 electrons in order to achieve stability
- 18. Oxygen has an atomic number of 8
- 20. Hydrogen has an atomic number of 1
- 21. A little chemistry … … and a hydrogen atom contains 1 proton and 1 electron So an oxygen atom contains 8 protons and 8 electrons
- 22. A little chemistry … When oxygen and hydrogen bond, the hydrogen is stable, it has a full outer shell … but the oxygen is still left short one electron
- 23. A little chemistry … This allows an additional hydrogen atom to bond with the oxygen … thus creating a stable molecule
- 24. A little chemistry … Thus we achieve the structure of a water molecule: One oxygen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms
- 27. Water molecules are cohesive -> they form hydrogen bonds Substances that dissolve in water are called hydrophilic or polar Substances that are insoluble in water are called hydrophobic or non-polar
- 28. Monomers: Polymers: Sugars Carbohydrates (Polysaccharides) Amino Acids Proteins Fatty acids & glycerol Lipids Nucleotides Nucleic Acids
- 30. Glucose, Fructose Sucrose, Lactose Starch, Glycogen & Cellulose
- 31. hexose shape pentose shape Mostly ends in –ose C, H, O => organic Condensation reaction
- 43. Other than phospholipids, which contain P, most others will only contain C, H & O
- 44. DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid RNA: ribonucleic acid
- 45. Nucleic acids contain C, H & O in addition to N & P SUGAR PHOSPHATE
- 46. DNA: Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Cytosine (C) Guanine (G) RNA: Adenine (A) Uracil (U) Cytosine (C) Guanine (G)
- 47. Differences between DNA & RNA DNA RNA A, C, G, T A, C, G, U Paired strands Single strand H + at 2’ OH - at 2’
- 50. 3 groups: Amino group, Carboxyl group & R-group When joined together they form peptide bonds Aside from the C, H, O & N in the base molecule, the R group may also contain S & P
- 52. Primary structure: Secondary structure:
- 53. Tertiary structure: Quaternary structure:
- 56. Biomacromolecule Type of bonding Carbohydrates Glycosidic bond Lipids Ester bond Nucleic acids Phosphodiester bond Proteins Peptide bond