sulfur dioxide ~ atienza
•Als PPTX, PDF herunterladen•
2 gefällt mir•4,077 views
Melden
Teilen
Melden
Teilen
Empfohlen
Presentation by Klaus Butterbach-Bahl, Björn Ole Sander, David Pelster, and Eugenio Díaz-Pinés.
Presentation of the key elements of the the Quantifying Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Managed and Natural Soils chapter in the recently published book Methods for Measuring Greenhouse Gas Balances and Evaluating Mitigation Options in Smallholder AgricultureQuantifying Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Managed and Natural Soils

Quantifying Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Managed and Natural SoilsCCAFS | CGIAR Research Program on Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security
Weitere ähnliche Inhalte
Was ist angesagt?
Was ist angesagt? (20)
Andere mochten auch
Presentation by Klaus Butterbach-Bahl, Björn Ole Sander, David Pelster, and Eugenio Díaz-Pinés.
Presentation of the key elements of the the Quantifying Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Managed and Natural Soils chapter in the recently published book Methods for Measuring Greenhouse Gas Balances and Evaluating Mitigation Options in Smallholder AgricultureQuantifying Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Managed and Natural Soils

Quantifying Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Managed and Natural SoilsCCAFS | CGIAR Research Program on Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security
Andere mochten auch (20)
Quantifying Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Managed and Natural Soils

Quantifying Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Managed and Natural Soils
Ähnlich wie sulfur dioxide ~ atienza
Ähnlich wie sulfur dioxide ~ atienza (20)
Effect of pollutants, human health and possible genetic effects. recent case ...

Effect of pollutants, human health and possible genetic effects. recent case ...
Air pollution (So2, NO2, CO) (1).pdf air pollution occuring in environment by...

Air pollution (So2, NO2, CO) (1).pdf air pollution occuring in environment by...
Environmental Engineering (Air Pollution and its effects and sources)

Environmental Engineering (Air Pollution and its effects and sources)
Mehr von JahNen Novicio
Mehr von JahNen Novicio (13)
sulfur dioxide ~ atienza
- 2. SULFUR DIOXIDE is the chemical compound with the formula SO2. It is a toxic gas with a pungent, colorless irritating smell, that is released by volcanoes and in various industrial processes. Since coal and petroleum often contain sulfur compounds, their combustion generates sulfur dioxide unless the sulfur compounds are removed before burning the fuel. is used to preserve foods. It is one of a group of sulfiting agents, used in wine, on many dried fruits and in numerous other foods. Sulfur dioxide is formed when sulfur-containing fuels, such as coal and oil, are burned.
- 3. SULFUR DIOXIDE The primary sources of sulfur dioxide emissions are power plants, refineries and copper smelting facilities. However, man-made emissions of sulfur dioxide have been the cause of some of the worst air pollution episodes in the last century. Sulfur dioxide is one of the six major air pollutants in the U.S. In the atmosphere, sulfur dioxide can form dangerous sulfates, which can be breathed deep into the lungs, and sulfuric acid, the major acidic component of acid rain, that can harm fish, damage forests and plants, and erode buildings.
- 4. DISEASE - BRONCHIOLITIS OBLITERANS A lung disease caused by inhalation of Sulfur dioxide. Due Sulfur Dioxide Inhalation The exposure can cause scarring of the lungs which can lead to obstruction of the small airways and ultimately impaired lung function. Chronic exposure can lead to gradual worsening of symptoms over a period of time.
- 5. DISEASE - BRONCHIOLITIS OBLITERANS Acute exposure can result in lung damage that may be asymptomatic for a short period of time but can then lead to rapid death due to severe obstructive breathing problems. Severity of symptoms and outcome depend on degree of exposure. from exposure to deleterious agents (usually toxins, gases, inhalants, etc.) while working. at any time, from exposure to toxins, poisons, environmental, or other substances.
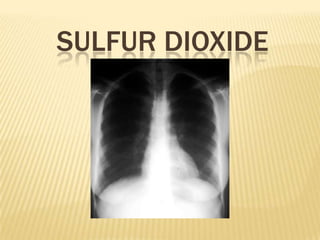
- 6. DIAGNOSIS (TESTS) Chest X-rays tests. Diffusing capacity of the lung (DLCO) tests are usually normal. Spirometry tests show fixed airway obstructions and sometimes restriction. Lung volume tests may show hyperinflation (excessive air in lungs caused by air trapping) High-resolution computerized tomography scans of the chest at full inspiration and expiration may reveal heterogeneous air trapping on the expiratory view as well as haziness and thickened airway walls. Lung biopsies may reveal evidence of constrictive bronchiolitis obliterans
- 7. DIAGNOSIS (SYMPTOMS) Low levels of oxygen in blood shortness of breath dry cough Wheezing Breathing difficulty Tiredness
- 8. TREATMENT This disease is irreversible Require/s a lung transplant Steroid Treatment
- 11. DENTAL CORRELATION Persistent oral malodor though is due to the formation of a series of volatile chemicals, of which the sulfur compounds are the most studied. The volatile substances derived from sulfur, known generically as volatile sulfur compounds (VSC) include hydrogen sulfide (H2S), methyl mercaptan (CH3SH), dimethyl sulfide (CH3) 2S and dimethyl trisulfide (CH3) 2S3, which are often produced in the oral environment by metabolizing protein substrates by some members of the oral microbiota.
