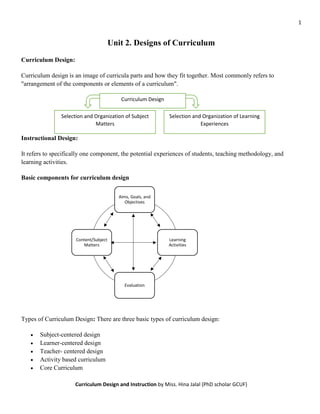
Designs of Curriculum
- 1. 1 Curriculum Design and Instruction by Miss. Hina Jalal (PhD scholar GCUF) Unit 2. Designs of Curriculum Curriculum Design: Curriculum design is an image of curricula parts and how they fit together. Most commonly refers to "arrangement of the components or elements of a curriculum". Instructional Design: It refers to specifically one component, the potential experiences of students, teaching methodology, and learning activities. Basic components for curriculum design Types of Curriculum Design: There are three basic types of curriculum design: • Subject-centered design • Learner-centered design • Teacher- centered design • Activity based curriculum • Core Curriculum Curriculum Design Selection and Organization of Learning Experiences Selection and Organization of Subject Matters Aims, Goals, and Objectives Learning Activities Evaluation Content/Subject Matters
- 2. 2 Curriculum Design and Instruction by Miss. Hina Jalal (PhD scholar GCUF) • Hidden Curriculum • Integrated Curriculum 2.1 Subject-Centered Curriculum Design Subject-centered curriculum design revolves around a subject matter or discipline. For example, a subject- centered curriculum may focus on math or biology. This type of curriculum design tends to focus on the subject rather than the individual. Subject-centered curriculum design describes what needs to be studied and how it should be studied. Characteristics: 1. It focuses on ‘’content’’ of curriculum. 2. It corresponds through ‘’text books’’ in curriculum. 3. It prescribes different and separated books into one broader field. 4. Mastery on subject in central task. 5. The scope of fields depends on number of subjects. 6. Text-books are the only instrument of instruction and teaching. 7. Learning is in sequence and step-by-step. 5. Evaluation the extent of mastery of what was taught 4. Organization of learning experiences 3. Desiding upon learning experiences related to mastery on subject matters 2. Determinition of Objectives a. Topic area within the subjects to be coverd b. Definition of importants generalization c. Identification of intellectual descipline The Subject-Centered Curriculum Design 1. Subjects to be Taught
- 3. 3 Curriculum Design and Instruction by Miss. Hina Jalal (PhD scholar GCUF) 8. Inter-relationship among subjects is not stressed. 9. It focuses on ‘’WHAT’’ rather than ‘’HOW’. 10.It gives knowledge into bits and pieces. 11.Library is the main source of giving knowledge. 2.2 Learner-Centered Curriculum Design In contrast, learner-centered curriculum design takes everyone’s needs, interests, and goals into consideration. In other words, it acknowledges that students are not uniform and adjusts to those student needs. Learner- centered curriculum design is meant to empower learners and allow them to shape their education through choices. Instructional plans in a learner-centered curriculum are differentiated, giving students the opportunity to choose assignments, learning experiences or activities. John –Dewey’s contribution is an important one. He developed and organized several learning activities to promote learner centered curriculum. Principles of Learner-Centered Curriculum Design Freedom to develop naturally. Interest is the motive of all work. Teacher is a guide not a task – master. Scientific study of pupil development. The progressive school a leader in educational movement. Co-operation between the school and home to meet the needs of child-life Forms of Learner learner-centered curriculum design 1. Humanistic Design 2. The activities and experiences It includes to This form emphases on • Active participation of learners. • Students learn through self- experiences. • Learning is an active transmission. • Students activities in laboratory, library, fields, classrooms. • Integration of subject matters. • Teaching methodology. • John Dewey’s “learning by doing”. • Provide conducive environment for learning • Focuses on learning environment more. • Featured humanistic approach of psychology. • May refer subject matters as guidance. • Emphasize of self-learning, self-efficacy. • Independent learning, caring, and support.
- 4. 4 Curriculum Design and Instruction by Miss. Hina Jalal (PhD scholar GCUF) Characteristics: 1. This type of design give importance to the learner and considers child as center of interest which is natural approach. 2. The of child is an important factor. 3. Teachers role is not that a task-master but that of a guide and facilitator. 4. It gives several options to students to develop their ability and skills. 5. Students are actively involved in planning and evaluation in general and specific. 6. It points out “the more experience in life, a child has the more eager he will to learn”. 2.3 Teacher-centered curriculum In teacher centered education, students pull all their focus on the teacher. The teacher talks, while the student exclusively listen. It is primary role of teacher to pass knowledge & information onto their students. In this approach, teaching & assessment are viewed as two separate entities. Student learning is measured through objectively scored test & assessment. According to John Miller, “Curriculum frameworks the teacher-centered approach related to three positions such as transmission, transaction and transformation. 1. Transmission: - The action or process of transmitting knowledge in to learners. 2. Transaction: - What knowledge is achieve and gain as learning outcome. 3. Transformation: - Permanent and positive changes in behavior of learners. Main features: • The underlying concept of the teacher centered approach is based on traditional pedagogy where in knowledge is passed from teacher to children. • The sharing knowledge and learning contents from teacher to children subject standards and methods are determined by the teacher. • This design corresponds that “learning occurs by the transmission of knowledge from the teacher to student”. • In this approach the teacher is center of attention. • This type of curriculum design emphasis on teacher’s involvement in curriculum development. • Teacher participates in several learning activities.
- 5. 5 Curriculum Design and Instruction by Miss. Hina Jalal (PhD scholar GCUF) Role of teacher in teacher-centered Curriculum Development: 1. Adopters: - Teacher became ready to adopt and accept curriculum significantly. 2. Implementers: - Role to apply curriculum efficiently. 3. Developers: - A role to take part in curriculum development. 4. Researchers: - Role to conduct research to bring changes in curriculum development. 5. Experimenters: - Role to Experiment teacher-learning relationship positively. 2.4 Activity Based Curriculum An Activity based curriculum has a long history. The title "Activity Curriculum", however, until 1920 this approach was not very popular in use. Although Dewey used the expression "Activity Program" as early as 1897 in a talk to the parents and teachers at his laboratory school in Chicago (U.S.A.). Activity is the natural urge of the child. He wants to do things by himself. Activity is “a thing that a person or a group does or has done lively action or movement”. Activity based curriculum determine the genuine need and interest of learner which is turn from the basic of curriculum. An importance of claim of this approach is that “people only learn what they experience.” According to A.K Gandhi education is a development of all aspect i-e body, mind, and sprit. So, mind without activities cannot develop the personality perfectly. Component of Activity Based Curriculum Activities should have: • A clear purpose or objective • A definite beginning and ending • Contain complete and understandable directions • Include a description of the technology or tool being used in the exercise. • A feedback mechanism Advantages o The most importance feature of activity of learning based curriculum “learning by doing” o The method also promotes better understanding of a lesson by participating the task themselves. o It inspires the students to apply their creative ideas, knowledge and mind in solving problems.
- 6. 6 Curriculum Design and Instruction by Miss. Hina Jalal (PhD scholar GCUF) o It is one of the teachers centered method of teaching. o Here the experience student is getting here. o Participation of the student is there. 2.5 Core Curriculum The Core Curriculum is the set of common courses required of all undergraduates and considered the necessary general education for students, irrespective of their choice in major. A Core curriculum collectively define district-wide system that include • A set of courses that are considered basics and essentials for futures. • It is a set of educational goals, explicitly taught, and focused on all students involve in learning. • It is set of predetermined body of skills, knowledge, and abilities that is taught to all students. • There is assumption that there is uniform body of knowledge that all students should know. • The content and sequences of subject matters are taught and assessed on performance based. • Sequence of equivalent & equitable Learning experience • Common instruction materials & strategies Characteristics of Core Curriculum 1. This design focuses on the set of learning experiences that are felt to be essential for all students. 2. In school, a general education is the goal of the core curriculum. 3. Problem solving through reflective thinking is encouraged. 4. All courses will introduce students to a broad discipline or field of study. 5. subject mattes line is cut across and attention is given to the need of students. 6. cooperative teaching-learning environment is supportive. Core general education based on common themes that are universally required Group A Group D Group B Group C Universally shared knowledge, skills, activities, inquiry, discourse, responsibilities, and understandings.
- 7. 7 Curriculum Design and Instruction by Miss. Hina Jalal (PhD scholar GCUF) 7. individual respect is promoted. 8. focuses on performance-based assessment. 9. learners have the opportunity of self-evaluation. The hidden or covert curriculum A hidden curriculum can be defined as the lessons that are taught informally, and usually unintentionally, in a school system. These include behaviors, perspectives, and attitudes that students pick up while they're at school. This is contrasted with the formal curriculum, such as the courses and activities students participate in. Longstreet and Shane (1993) offer a commonly accepted definition for this term – the “hidden curriculum,” which refers to the kinds of learnings children derive from the very nature and organizational design of the public school, as well as from the behaviors and attitudes of teachers and administrators”. The following examples will help to illustrate the concept and how it might play out in institution: Cultural expectations: The academic, social, and behavioral expectations established by schools and educators communicate messages to students. Cultural values: The values promoted by schools, educators, and peer groups, such as cliques, may also convey hidden messages. Cultural perspectives: How schools recognize, integrate, or honor diversity and multicultural perspectives may convey both intentional and unintended messages. Teaching strategies: The way that schools and teachers choose to educate students can convey both intentional and unintended messages. Institutional rules: The formal rules in a school may communicate a wide variety of intentional and unintentional messages to students. Religious perspective: The rules, regulations, ethics, values, principles, and practices may communicate a wide variety of messages to students. 2.6 Integrated Curriculum An integrated study is one in which children broadly explore knowledge in various subjects related to certain aspects of their environment. According to Roberts & kellough, (2000) “The term integrated curriculum refers to a way of teaching, planning, & organizing so the discrete disciplines of subject matter are integrated and match
- 8. 8 Curriculum Design and Instruction by Miss. Hina Jalal (PhD scholar GCUF) the developmental needs of the learner, help to meaningfully connect the student’ learning to their current and past experiences”. It includes: • Problem concerns real to the student and real in the community. • Student and teacher work together to select the specific topic of interest to them and together they plan how, when, where and why they pursue it. • Develop essential skills intrinsic to their learning. Approaches of Integrated Curriculum Multidisciplinary Integration: Multidisciplinary approaches focus primarily on the disciplines. Teachers who use this approach organize standards from the disciplines around a theme. Intradisciplinary Approach. When teachers integrate the subdisciplines within a subject area, they are using an intradisciplinary approach. Integrating reading, writing, and oral communication in language arts is a common example.
- 9. 9 Curriculum Design and Instruction by Miss. Hina Jalal (PhD scholar GCUF) Transdisciplinary Integration In the transdisciplinary approach to integration, teachers organize curriculum around student questions and concerns. Fusion. In this multidisciplinary approach, teachers fuse skills, knowledge, or even attitudes into the regular school curriculum.
- 10. 10 Curriculum Design and Instruction by Miss. Hina Jalal (PhD scholar GCUF) Relationship among Curriculum Designs Learned Curriculum Recommende d Curriculum Tested Curriculum Taught Curriculum Supported Curriculum Written Curriculum Hidden Curriculum International Curriculum The written curriculum is an important component of authentic literacy—the ability to read, write, and think effectively The taught curriculum is the delivered curriculum, a curriculum that an observer sees in action as the teacher teaches. The supported curriculum is the curriculum as reflected in and shaped by the resources allocated to support and deliver it. The tested curriculum is that set of learnings that is assessed in teacher-made classroom tests; in district-developed, curriculum- referenced tests; and in standardized tests. The term learned curriculum is used here to denote all the changes in values, perceptions, and behavior that occur because of school experiences. As such, it includes what the student understands, learns, and retains from both the intentional curriculum and the hidden curriculum. The hidden curriculum might be those aspects of the learned curriculum that lie outside the boundaries of the school’s intentional effort, as, social values, norms, cultures, ethics, etc.
