Cell the unit of life ncert introduction to prokaryotic cells
- 1. CELL: THE UNIT OF L Ncrt
- 2. What is it that an inanimate thing does not have which a living thing has’ ? • The answer to this is the presence of the basic unit of life – the cell in all living organisms. • All organisms are composed of cells. • Some are composed of a single cell and are called unicellular organisms..
- 3. WHAT IS A CELL? • Unicellular organisms are capable of .. • (i) independent existence and • (ii) performing the essential functions of life.
- 4. The cell is the fundamental structural and functional unit of all living organisms. • Anton Von Leeuwenhoek first saw and described a live cell. The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665
- 5. Robert Brown later discovered the nucleus. • The invention of the microscope and its improvement leading to the electron microscope revealed all the structural details of the cell.
- 6. G.N. RAMACHANDRAN, • G.N. RAMACHANDRAN, discovered triple helical structure of collagen.. • He identified conformations of proteins through the use of the ‘Ramachandran plot’… • Ramachandran plot the most outstanding contributions in structural biology.
- 7. CELL THEORY • In 1838, Matthias Schleiden, a German botanist, examined a large number of plants.. • He observed that all plants are composed of different kinds of cells..
- 8. Theodore Schwann (1839), a British Zoologist, studied different types of animal cells… • He reported that cells had a thin outer layer which is today known as the ‘plasma membrane’. • He also concluded, based on his studies on plant tissues, that the presence of cell wall is a unique character of the plant cells.
- 9. Theodore Schwann: proposed the hypothesis that the bodies of animals and plants are composed of cells and products of cells
- 10. Schleiden and Schwann together formulated the cell theory. • This theory however, did not explain as to how new cells were formed.
- 11. Rudolf Virchow (1855): first explained that cells divided and new cells are formed from pre-existing cells (Omnis cellula-e cellula).
- 12. He modified the hypothesis of Schleiden and Schwann to give the cell theory a final shape. • Cell theory as understood today is: • (i) all living organisms are composed of cells and products of cells. • (ii) all cells arise from pre-existing cells.
- 13. AN OVERVIEW OF CELL:::: • Observe onion peel and/or human cheek cells under the microscope. • The onion cell which is a typical plant cell, has a distinct cell wall… • The cells of the human cheek have plasma membrane..
- 14. Inside each cell is a dense membrane bound structure called nucleus. • This nucleus contains the chromosomes which in turn contain the genetic material, DNA.
- 15. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells
- 16. Cells that have membrane bound nuclei are called eukaryotic Cells that lack a membrane bound nucleus are prokaryotic.
- 17. In both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, a semi-fluid matrix called cytoplasm occupies the volume of the cell.; • The cytoplasm is the main arena of cellular activities.. • Various chemical reactions occur in it to keep the cell in the ‘living state’
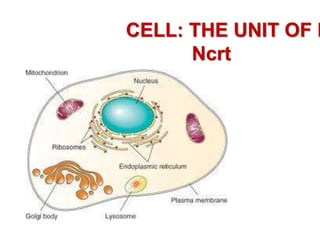
- 18. the eukaryotic cells have membrane bound distinct structures called organelles ….. • Endoplasmic reticulum (ER), • the golgi complex, • lysosomes, • mitochondria, • microbodies • vacuoles. • The prokaryotic cells lack such membrane bound organelles.
- 19. Ribosomes • Ribosomes are non-membrane bound organelles found in all cells – both eukaryotic as well as prokaryotic.
- 20. Ribosomes • Within the cell, ribosomes are found not only in the CYTOPLASAM.. • but also within other organelles like – chloroplasts (in plants) and mitochondria and on rough ER.
- 21. Centriole • Animal cells contain another non-membrane bound organelle called centriole.. • which helps in cell division..
- 22. Cells differ greatly in size, shape and activities • Mycoplasmas, the smallest cells, are only 0.3 µm in length. • The bacteria size 3 to 5 µm.
- 23. The largest isolated single cell is the egg of an ostrich. • Among multicellular organisms, human red blood cells are about 7.0 µm in diameter. • Nerve cells are some of the longest cells.
- 24. Or 3 to 5 micro meters
- 25. Cells also vary greatly in their shape. • They may be disc-like, • polygonal, • columnar, • cuboid, • thread like, • even irregular.
- 28. The prokaryotic cells are represented by • bacteria, • blue-green-algae, • Mycoplasma • PPLO (Pleuro Pneumonia Like Organisms). • PPLO - a mycoplasma resistant to antibiotics that causes a kind of pneumonia in humans.
- 29. Prokaryotic cells are generally smaller and multiply more rapidly than the eukaryotic cells… • They may vary greatly in shape and size. • The four basic shapes of bacteria are • bacillus (rod like), • coccus (spherical), • vibrio (comma shaped) • spirillum (spiral).
- 30. All prokaryotes have a cell wall surrounding the cell membrane except in mycoplasma. • The fluid matrix filling the cell is the cytoplasm. • There is no well-defined nucleus..
- 31. The genetic material is basically naked, not enveloped by a nuclear membrane. • In addition to the genomic DNA (the single chromosome/circular DNA), many bacteria have small circular DNA outside the genomic DNA. • These smaller DNA are called plasmids.
- 32. Plasmid • A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria.. • The plasmid DNA confers certain unique phenotypic characters to such bacteria. • One such character is resistance to antibiotics.
- 33. Plasmid DNA is used to bacterial transformation with foreign DNA
- 34. Organelles are not found in prokaryotic cells except for ribosomes • Prokaryotes have something unique in the form of inclusions .. • Inclusion bodies :Reserve material in prokaryotic cells • Mesosomes present prokaryotes. • They are infoldings of cell membrane.
- 35. Dr. HarinathaReddy Aswartha Assistant professor Department of Microbiology biohari14@gmail.com
