Teacher notes Tansport in plant / EMAD ZEIDAN - IAA
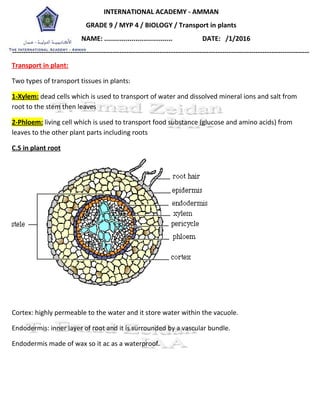
- 1. INTERNATIONAL ACADEMY - AMMAN GRADE 9 / MYP 4 / BIOLOGY / Transport in plants NAME: ................................... DATE: /1/2016 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Transport in plant: Two types of transport tissues in plants: 1-Xylem: dead cells which is used to transport of water and dissolved mineral ions and salt from root to the stem then leaves 2-Phloem: living cell which is used to transport food substance (glucose and amino acids) from leaves to the other plant parts including roots C.S in plant root Cortex: highly permeable to the water and it store water within the vacuole. Endodermis: inner layer of root and it is surrounded by a vascular bundle. Endodermis made of wax so it ac as a waterproof.
- 2. C.S in plant stem Cortex cell: - Store starch. - It contains chlorophyll pigment. Pith: central tissue cells. (Cortex+Pith) are involved in the process of packing and support for the plant. Explain how root is adapted to uptake (absorb) water from soil: - It consists of thin layer of cells for fast diffusion - They are large in number to provide more surface area to absorb water from soil - It has fine hair cell to absorb water from soil particles by osmosis. State the pathway taken by water through root, stem and leaves: 1- Root hair will absorb water from soil particles by osmosis. 2- Water will pass the cortex cell (highly permeable to water) in root 3- Water will pass to the xylem in root then stem till it reaches the xylem of leaves to be used by cells (palisade and spongy cell) for photosynthesis.
- 3. Investigation: xylem to transport water and dissolved ions and salts - Add stain (blue) to the water, then insert small branch of certain plants, - Leave the plant for several hours. - Prepare slide from root, stem and leaves - Observe the place of stain Result: the blue stain was found inside the xylem Conclusion: xylem is used to transport water. ** Name one stain which is used to show that the xylem is responsible for transporting water and dissolved mineral ions and salt. Eosin stain (red stain) Translocation: - Long distance transport (mass flow system) - Movement of sucrose and amino acids from leaves (where is produced by photosynthesis) to the root (sink) to be stored and used in respiration or growth. Transpiration: Evaporation of water at the surface of mesophyll cells followed by loss of water vapour from plant leaves through the stomata. Two types of transpiration: 1- Transpiration from the epidermis (less). 2- Transpiration from the stomata (more): * Water will move by osmosis from xylem to the mesophyll cell * Excess water will be evaporated in the spaces between spongy cell and leave stomata in form of water vapour. Water will be transported in xylem up to reach leaves by: - Transpiration which make pulling forces - Water potential gradient in xylem which draw cohesive water molecules up the plat - High root pressure at the bottom of the plant
- 4. Comparing transpiration and translocation: Discuss the adaptations of the leaf, stem and root to the pond, garden and desert (according to the temperature, light intensity and humidity). 1- Desert plants adaptation: - Small leaves: has small surface area to reduce water loss (transpiration). - Has hair cell to trap humidity to decrease loss of water (transpiration). - Thick cuticle in leaves to reduce loss of water (transpiration). - Long root to go down deep in soil to absorb water. 2- Pond plants adaptation: - Reduce root system because it is sink in water. - Dissected lamina leaves to protect it. - Leaves have air space for floating. - No stomata.
- 5. Explain factors affecting the rate of transpiration: 1- Temperature: - As temperature increase the transpiration rate increase - At high temperature: more rate of transpiration and the plant get wilting. 2- Light intensity: - In bright light there will be more rate of transpiration. - In dim light: less rate of transpiration. 3- Wind: When the speed of wind increase the rate of transpiration will increase, because wind will remove evaporated water which surround the surface of the leaf to increase the transpiration rate. 4- Humidity: When the humidity increase the transpiration rate will decrease. Translocation: Movement of sucrose and amino acids in phloem from region of production (leaves) to region of storage or utilisation in respiration and growth. Application on translocation: Systemic pesticides: - Are pesticides which are absorbed by plants or animals and move to untreated tissues. - The pesticides translocated to kill weeds and pest as it begins to feed or enter the plant - Water and food-conducting tissues are the usual pathways through which these chemicals move over long distances
- 6. Explain factors affecting the rate of transpiration: 1- Temperature: - As temperature increase the transpiration rate increase - At high temperature: more rate of transpiration and the plant get wilting. 2- Light intensity: - In bright light there will be more rate of transpiration. - In dim light: less rate of transpiration. 3- Wind: When the speed of wind increase the rate of transpiration will increase, because wind will remove evaporated water which surround the surface of the leaf to increase the transpiration rate. 4- Humidity: When the humidity increase the transpiration rate will decrease. Translocation: Movement of sucrose and amino acids in phloem from region of production (leaves) to region of storage or utilisation in respiration and growth. Application on translocation: Systemic pesticides: - Are pesticides which are absorbed by plants or animals and move to untreated tissues. - The pesticides translocated to kill weeds and pest as it begins to feed or enter the plant - Water and food-conducting tissues are the usual pathways through which these chemicals move over long distances
