21st century skills
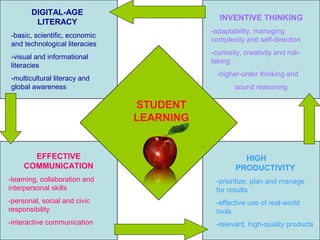
- 1. DIGITAL-AGE INVENTIVE THINKING LITERACY -adaptability, managing -basic, scientific, economic complexity and self-direction and technological literacies -curiosity, creativity and risk- -visual and informational taking literacies -higher-order thinking and -multicultural literacy and global awareness sound reasoning STUDENT LEARNING EFFECTIVE HIGH COMMUNICATION PRODUCTIVITY -teaming, collaboration and -prioritize, plan and manage interpersonal skills for results -personal, social and civic -effective use of real-world responsibility tools -interactive communication -relevant, high-quality products
- 2. 1. Digital-Age Literacy • Proficiency with basic literacy and numeracy skills: writing, reading, oral communication; arithmetic, computing and problem-solving • Basic knowledge of scientific concepts and processes • Identifying economic issues; weighing costs against benefits; examining the changes in economic conditions • Knowing what technology is; how to use it; when to use; the appropriate and responsible use of it • Interpreting, creating and using visual images for the purposes of decision- making, communicating and learning • Locating information; determining its utility, evaluating the credibility • Cultural proficiency • Recognizing the interrelationship of various individuals, groups, nations, etc.
- 4. The Virtual World Has Changed… Our students are contributing to the collective knowledge of cyber space.
- 5. So What? • Participatory reading and writing • Social affiliations and networking • Being online vs. going online • The web as an application platform • Digital self-expression; defining and claiming of one’s voice
- 6. Connectivism • Diversity of opinions. • Connecting specialized nodes or information sources. • Non-human appliances. • Capacity to know more is more critical • Continual learning through nurturing and maintaining connections • Ability to see connections between fields, ideas, and concepts is a core skill
- 7. 2. Effective Communication • Problem-solving • Creating products • Learning and mastering content • Interpersonal skills • Achieving balance in one’s life by managing technology and relationships • Using technology to promote the common good • Using contemporary tools, processes and technologies
- 8. Mastery of Core Subjects: • English • World Languages Interdisciplinary • Arts Themes: • Mathematics *Global Awareness • *Financial/Economi Economics c/Business Literacy • Science *Civic Literacy • Geography *Health Literacy • History • Government and Civics
- 9. 3. High Productivity • Organization to achieve goals efficiently • Using technology to solve problems and achieve goals efficiently • Using real-world tools to create authentic products which address real issues and solve real problems
- 10. High Yield Instructional Strategies • Identifying similarities and differences +45% • Summarizing and note taking +34% • Reinforcing effort and providing recognition +29% • Homework and practice +28% • Nonlinguistic representations +27% • Cooperative learning +27% • Setting objectives and providing feedback +23% • Generating and testing hypotheses +23% • Questions, cues and advanced organizers +22%
- 11. 4. Inventive Thinking • Multi-tasking • Adapting to new surroundings • Meeting deadlines • Independently establishing and achieving goals, and reflecting on learning • Enthusiasm for inquiry-based learning • Creating new ideas/products that add dimension to the existing culture • A willingness to take risks and make mistakes • Higher-order thinking (i.e. Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy)
- 12. Changing Mindsets… What might have prompted the shift in thinking? Why is the ability to create more sophisticated than the ability to evaluate?
- 13. A Change Long- Overdue… To consider… On average, how much time in your teaching practice do you devote to direct teaching vs. facilitating activities that allow students to learn by doing? To teach themselves?
Hinweis der Redaktion
- -these skills were borne out of research conducted by American educational research groups -surveyed employers in the private and public sector; looking to identify areas of deficiency among workers -key issues: creativity and problem solving -workers could take direction, but often struggle when put in situations when they had to devise a plan the processes involved in this sort of decision-making was not natural *CRITICAL LITERACY EMPLOYS THE USE OF CRITICAL THINKING SKILLS THEREFORE, IF ONE CANNOT THINK CRITICALLY, HIS/HER ABILITY TO READ THE WORLD WITH AN ABILITY TO ARTICULATE THAT POSITIONING IS LIMITED
- The term " Web 2.0 " describes the changing trends in the use of World Wide Web technology and web design that aim to enhance creativity, communications, secure information sharing, collaboration and functionality of the web. Web 2.0 concepts have led to the development and evolution of web-culture communities and hosted services, such as social-networking sites, video sharing sites, wikis, blogs, and folksonomies. The term first became notable after the O'Reilly Media Web 2.0 conference in 2004. Although the term suggests a new version of the World Wide Web, it does not refer to an update to any technical specifications, but rather to changes in the ways software developers and end-users utilize the Web. Universities are using Web 2.0 in order to reach out and engage with Generation Y and other prospective students according to recent reports. Examples of this are: social networking websites – YouTube, MySpace, Facebook, Youmeo, Twitter and Flickr; upgrading institutions’ websites in Generation Y-friendly ways (e.g., stand-alone micro-websites with minimal navigation); and virtual learning environments such as Moodle enable prospective students to log on and ask questions.
- 1. The web as an application platform The web is becoming an increasingly popular place to host applications that have traditionally been developed for the desktop. Rich Internet Application technology including AJAX and Adobe Flex are empowering developers to create software that matches and exceeds the ease-of-use, interactivity and power of the desktop. On top of this, web applications inherit the web’s natural strengths as an operating-system-independent medium with easy accessibility, huge “reach” and inherent connectivity. Related trends such as Software-as-a-Service (subscription-based, web-hosted applications) are fueling demand for more web-based software. We are also seeing that protocols such as RSS and XML are doing for inter-web-application/service communication what HTML & Netscape did for web-publishing 10 years ago. The distinctive advantages of the web means we expect to see it become the primary platform for new application development over the next few years. 2. The Read Write Web The web grew up as a relatively primitive medium for publishing and viewing content. Initially there were far more viewers than publishers but over the last couple of years in particular, the tools for publishing have become more accessible, and subsequently the number of people contributing content has grown hugely. Blogs, wikis and more recently “tagging” (adding a keyword to a photo or bookmark or whatever) are becoming mainstream tools - Technorati.com tracks over 40 million blogs! As Kevin Kelly says in his article Unto us the Machine is born - “ As with blogging and BitTorrent, prosumers produce and consume at once. The producers are the audience, the act of making is the act of watching, and every link is both a point of departure and a destination. “ 3. Digital Self-expression One of the key social trends gaining increasing pace - particularly in the west - is growing importance of the individual. This is combined with a shift in the social construction of authority from centralised and hierarchical sources to peer groups and the individual. Together these trends are creating more demand and opportunities for people and groups to express their individuality. In the digital world of cell phones and the Internet this self-expression is taking place via cell phone ringtones (a $6 billion market), blogs, application “skins”, and social networking sites such as Myspace.com . Robert Young, an Internet entrepreneur and commentator says “in many ways, the art-form of self-expression has become the ‘new media’”. As the Internet consumes more and more of our attention we expect to see people investing more and more of their identity in digital forms thereby creating new demands for richer and powerful ways to express ourselves. 4. Social affiliation The Internet has from its very inception been a medium for connecting people of like-minds and values together. In the beginning this was carried via email-based mailing lists, and then web-based discussion forums. Over the last 12 months or so we have seen many new developments in this area, as more powerful vehicles for connecting people together on the Internet have emerged. What is emerging is 2 different types of social affiliation software. The first form is commonly referred to as “social networking” and is predominantly person and network-centric. Social networking sites like Myspace.com enable people to create and personalise their own web page complete with features like blogs, guest books and photo galleries. These sites also allow people to express affiliation with friends and other valued individuals and groups. The 100 million user membership base of Myspace.com is testimony to the previously 2 discussed trends - The Read-Write Web and Self-expression - together with humans natural affinity to “flock” with birds of a feather. The second form of social affiliation software emerging is group-centric and an evolutionary extension of the original forms of social affiliation software. Web-based services such as Basecamp, CollectiveX, and Central Desktop are rising on the back of the increase in SOHO businesses, teleworking, and partnering. With the increasing power and accessibility of the first trend - the web as an application platform - we are now seeing the unstructured modes of group communication being supplemented by more structured forms of group collaboration. The web is proving itself a consummate medium for coordinating action and interest. 5. Being online vs going online As technology has evolved we have witnessed the increasing digitisation of information and sensory experience. This increasing digitisation has created richer representations of digitised elements creating more of a sense of “being there”. Technologies such as VOIP and 3D games have enabled us to create digitally mediated experiences that are more richly rendered. Michael Pinto says “The biggest shift over the next ten years will be one of attitude, as our mindset of ‘going online’ is replaced by one of ‘being online’. This change has already started, as telephones and televisions become more integrated with the Net, and connectivity will grow to include everything from your morning alarm clock to the book you read before falling asleep at night. The ‘Internet’ will no longer be a destination, but the essential glue that holds our world together.” This growing “virtualisation” when combined with the other 4 trends hints at a new web that borrows cues from science-fiction books and movies facilitating virtual spaces where people meet and work together in more immediate and effective ways.
- -re-teaching our students how to interface with human beings fluent in the social graces of cyber space, they understand the etiquette of the internet but seem deficient in face-to-face situations, have difficulties discerning boundaries and establishing the difference in protocol when speaking with different kinds of people (i.e. the teacher vs. their friend) -often expect that our students know how to use technology; it offered as options for final products for assignments do we teach EXPLICITLY how to use the technology ethically? do we help our students discern which applications would work best for a specific purpose? *Do we assume too much? -includes using Web 2.0 software in the day-to-day workings of the classroom (e.g. blogging)
- GLOBAL AWARENESS: Using 21st century skills to understand and address global issues Learning from and working collaboratively with individuals representing diverse cultures, religions and lifestyles in a spirit of mutual respect and open dialogue in personal, work and community contexts Understanding other nations and cultures, including the use of non-English languages FINANCIAL/ECONOMIC/BUSINESS LITERACY: Knowing how to make appropriate personal economic choices Understanding the role of the economy in society Using entrepreneurial skills to enhance workplace productivity and career options CIVIC LITERACY: Participating effectively in civic life through knowing how to stay informed and understanding governmental processes Exercising the rights and obligations of citizenship at local, state, national and global levels Understanding the local and global implications of civic decisions HEALTH LITERACY: Obtaining, interpreting and understanding basic health information and services and using such information and services in ways that are health enhancing Understanding preventive physical and mental health measures, including proper diet, nutrition, exercise, risk avoidance and stress reduction Using available information to make appropriate health-related decisions Establishing and monitoring personal and family health goals Understanding national and international public health and safety issues
- TEACHERS MUST MODEL PRODUCTIVITY! -Teachers need to productive in the instructional strategies they choose. Marzano has quantified and identified the top 9 strategies that yield increases in student achievement -these strategies allow students to be productive in their learning *Organization *Efficiency *High quality input = high quality output
- Bloom’s Taxonomy Revised… FINALLY!!! -an age-old institutional norm has been transformed -students of Bloom shuffled the taxonomy to more accurately reflect the changing needs in education and the world QUESTION: Would you have done this? Might you have taken a different approach? What would you have changed (if at all)?
- -accepting the new taxonomy = believe that experiential learning optimized student achievement more authentic students contribute to growing, collective knowledge more responsibility for their learning; students create opportunities for learning; authenticate their learning experiences