Adrenal Gland- Basic.
- 1. Dr. BIKASH CHANDRA SAH JR (2ND YEAR)
- 2. Content…. • Embryology • Anatomy • Physiology • Pathology • Treatment
- 3. Embryology .
- 4. Embryology • It is composed of 2 endocrine glands. Outer cortex and inner medulla; each with distinct embryologic, anatomic, histologic, and secretory gland.
- 5. Adrenal cortex: • Originate from mesodermal tissue near the gonads on the Adrenogenital ridge. • Around the 5th week • Cortex divided into – Thin definitive cortex: • persist after birth to form adult cortex over first 03 years of life. – Thicker and inner fetal cortex: • Produce adrenal steroids by 8th week of gestation. • Involution (decrease in weight) after birth in 3rd postpartum. • Ectopic adrenocortical tissue may be found in the ovaries, spermatic cord, and testes
- 6. Adrenal medulla • Ectodermal origin and • Arises from neural crest 5th-6th WOG. • Neural crest cells migrate to the paraaortic and paravertebral areas and toward the medial aspect of the developing cortex to form the medulla. • Most extra-adrenal neural tissue regresses but may persist at several sites. – Adrenal medullary tissue also may be found in neck, urinary bladder and para-aortic regions • Some factors for adrenal development: IGF2; GIP; dosage sensitve, sex reserve adrenal hypoplasia (DAX1) gene.
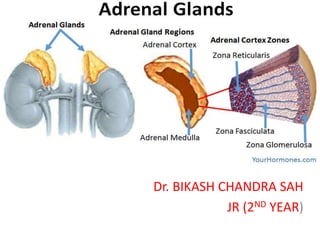
- 8. Anatomy • Each kidney is caped by adrenal gland • 2 Glands; Each 4 -5g. • Right pyramidal. • Left crescent shaped. • Enclosed within Gerota’s( perirenal fascia) • Composed of cortex and medulla. • The adrenals are among the most highly perfused organs in the body, receiving 2000 mL/kg/min of blood, after only the kidney and thyroid.
- 10. Relations..
- 11. Rt. Adrenal gland Lt . Adrenal gland Anterior: Rt. lobe of liver and inferior Venacava Anterior: • pancreas , lesser sac, and stomach • Aorta lies near • spleen lies superior and lateral to it. Posterior :Diaphragm Posterior : Diaphragm
- 12. Blood supply.
- 13. Artery supply: 03 arteries – Superior adrenal arteries derived from inferior Phrenic artery – Middle adrenal arteries derived from the aorta itself – Inferior adrenal arteries derived from the renal artery. • Note: arteries divide into about 50 arterioles to form rich plexus beneath glandular capsule require careful dissection and ligation during adrenalectomy. Lymphatics: • The lymphatic vessels accompany the suprarenal vein and drain into the lumbar lymph nodes.
- 14. Venous drainage: – Right adrenal vein: short and drains into IVC – Left adrenal vein: longer and empties into Lt renal vein. • Accessory vein: – Rt side in 5-10% cases and drains into Rt. hepatic or rt. renal vein. – Lt accessory vein drains directly into lt. renal vein.
- 15. Histology The adrenal cortex • About 80% to 90% of the gland’s volume • Appears yellow due to its high lipid content. • Divided into three zones—the – Zona glomerulosa: outer area, consist of small cell and produce mineralocorticoid hormone and aldosterone – Zona fasciculate: made up larger cell, appear foamy due to multiple lipid inclusions. Produce glucocorticoid – Zona reticularis cells are smaller. Secrete adrenal androgens
- 16. Adrenal medulla: • Reddish-brown in color • Constitutes up to 10% to 20% of the gland’s volume • The cells of the adrenal medulla are arranged in cords and are polyhedral in shape. • Referred to as chromaffin cells because they stain specifically with chromium salts.
- 17. Physiology
- 18. • Adrenal cortex produce steroid hormones, • Cholesterol being precursor are generally derived from plasma or synthesized in adrenal cortex
- 19. Mineralocorticoids • Major mineralcorticoids are 11- deoxycorticosterone (DOC), and cortisol • Aldosterone secretion is regulated primarily by the renin-angiotensin system. – Renin release from juxtaglomerular cells are stimulated by • Decreased renal blood flow, • Decreased plasma sodium, • Increased sympathetic tone • Angiotensin II, not only a potent vasoconstrictor, but also leads to increased aldosterone synthesis and release. • Stimulator of aldosterone synthesis – Hyperkalemia (potent,) – whereas ACTH, pituitary pro-opiomelanocortin, and antidiuretic hormone are weak stimulators.
- 20. Kinetics • Secreted at a rate of 50 to 250 μg/d (depending on sodium intake) • Circulates in plasma – Chiefly as a complex with albumin. • Small amounts of the hormone bind to corticosteroid-binding globulin, and – Circulates in a free form approximately 30% to 50% of secreted aldosterone. • Half-life of only 15 to 20 minutes. • Excretion: rapidly cleared via the liver and kidney. – A small quantity of free aldosterone also is excreted in the urine also. • Mechanism of action: Mineralocorticoids cross the cell membrane and bind to cytosolic receptors. The receptor-ligand complex subsequently is transported into the nucleus where it induces the transcription and translation of specific genes.
- 21. • Function: – Mainly to increase sodium reabsorption and potassium and hydrogen ion excretion at the level of the renal distal convoluted tubule. – Less commonly, aldosterone increases sodium absorption in salivary glands and GI mucosal surfaces.
- 22. Glucocorticoids: • Cortisol, major glucocorticoids • Regulated by ACTH secreted by the anterior pituitary, which, in turn. • 39-amino-acid protein, which is derived by cleavage from a larger precursor, pro-opiomelanocortin. • Has trophic action for the adrenal glands. • Secretion may be stimulated by pain, stress, hypoxia, hypothermia, trauma, and hypoglycemia. • Secretion fluctuates, peaking in the morning and reaching nadir levels in the late afternoon. • Shows a diurnal variation in the secretion of cortisol, – Peak cortisol excretion also occurring in the early morning and – Declining during the day to its lowest levels in the evening.
- 23. Kinetics • Circulation in plasma – Bound primarily to corticosteroid-binding globulin (75%) and albumin (15%). – Approximately 10% of circulating freely and is the biologically active component. • Half-life : 60 to 90 minutes – Determined by the extent of binding and rate of inactivation. • Converted to di- and tetrahydrocortisol and cortisone metabolites in the liver and the kidney. • Excretion: The majority (95%) of cortisol and cortisone metabolites are conjugated with glucuronic acid in the liver, thus facilitating their renal excretion. – A small amount of unmetabolized cortisol is excreted unchanged in the urine
- 24. Mechanism of action: • Glucocorticoid hormones enter the cell and bind cytosolic steroid receptors. The activated receptor- ligand complex is then transported to the nucleus where it stimulates the transcription of specific target genes via a “zinc finger” DNA binding element. • Cortisol also binds the mineralocorticoid receptor with an affinity similar to aldosterone. • However, the specificity of mineralocorticoid action is maintained by the production of 11β- hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, an enzyme that inactivates cortisol to cortisone in the kidney
- 26. Sex Steroids: • Adrenal androgens are produced in the zona fasciculata and reticularis from 17- hydroxypregnenolone in response to ACTH stimulation. • They include – Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and its sulfated counterpart (DHEAS), – Androstenedione, and – Small amounts of testosterone and estrogen.
- 27. • Adrenal androgens are weakly bound to plasma albumin. • They exert their effects – Major effects by peripheral conversion to the more potent testosterone and dihydrotestosterone , – Also have weak intrinsic androgen activity. • Androgen metabolites are conjugated as glucuronides or sulfates. • Excreted in the urine.
- 28. • Function: – During fetal development, adrenal androgens promote the formation of male genitalia. – In normal adult males, the contribution of adrenal androgens is minimal; – They are responsible for the development of secondary sexual characteristics at puberty. – Adrenal androgen excess leads to • Precocious puberty in boys and • Virilization, acne, and hirsutism in girls and women.
- 29. Catecholamine
- 30. • Catecholamine hormones: Epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine • Produced in • In the central and sympathetic nervous system • The adrenal medulla. • The substrate, tyrosine, is converted to catecholamines via a series of steps • Phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase, which converts norepinephrine to epinephrine, is only present in the adrenal medulla and the organ of Zuckerkandl. – Chromogranins: When catecholamines are stored in granules in combination with other neuropeptides, ATP, calcium, magnesium, and water-soluble proteins called Chromogranins.
- 31. Secretion stimulated by • Various stress stimulus. • And mediated by the release of acetylcholine at preganglionic nerve terminals. – In circulation: are bound to albumin and other proteins. – Excretion: Catecholamines are cleared by several mechanisms including • Reuptake by sympathetic nerve endings, • Peripheral inactivation by catechol O-methyltransferase and monoamine oxidase, and • Direct excretion by the kidneys. • – Metabolism: • Takes place primarily in the liver and kidneys. • Leads to the formation of metabolites such as metanephrines, normetanephrines, and VMA. • which may undergo further glucuronidation or sulfation before being excreted in the urine
- 32. Metabolism: • Takes place primarily in the liver and kidneys. • Leads to the formation of metabolites such as metanephrines, normetanephrines, and VMA. • which may undergo further glucuronidation or sulfation before being excreted in the urine
- 33. Mechanism of action: – Adrenergic receptors are transmembrane-spanning molecules that are coupled to G proteins. – Subdivided into α and β subtypes. • The receptor affinities for • α receptors are—epinephrine > norepinephrine>> isoproterenol; • β1 receptors—isoproterenol > epinephrine = norepinephrine; ands • β2 receptors—isoproterenol > epinephrine >> norepinephrine. •