Fishes
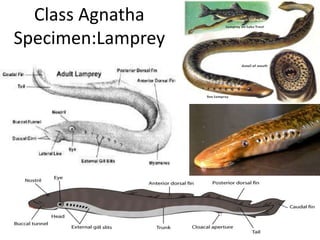
- 2. Lampreys are jawless fish, the adult of which is characterized by a toothed, funnel-like sucking mouth. Parasitic lampreys feed on prey as adults by attaching their mouthparts to the target animal's body, then using their teeth to cut through surface tissues until they reach blood and body fluid. a. Lampreys are both freshwater and anadromous (living mostly in the oceans but returning to freshwater to breed), with the larvae undergoing radical metamorphosis in freshwater. b. Adult lampreys have well-developed, lateral large eyes; one or two dorsal fins; separate sexes; one nostril on the top of the head; seven pairs of external lateral gill openings; and teeth on the oral disk and tongue c. They lack bone, do not have paired fins. d. They do have a vertebrae made of cartilage and retain the notochord in the adult e. Adults have no scales, and can range from 13 to 100 cm (5.0 to 40 inches) long. f. adult lampreys have one nostril on the top of the head g. The unique morphological characteristics of lampreys, such as their cartilaginous skeleton. h. Adult lampreys spawn in rivers and then die. The young larvae, ammocoetes, spend several years in the rivers, where they live burrowed in fine sediment, filter feeding on detritus and microorganisms. Then, ammocoetes undergo a metamorphosis lasting several months. Some species do not feed after metamorphosis, while others migrate to the sea or lakes,[ where they feed on different species of fish and even on marine mammals.[
- 3. 1. External Gill Slits- openings that lead to the internal gills that are used to extract oxygen from the water. Lampreys have seven distinctive gill slits. 2. Buccal Funnel - is the beginning of the mouth cavity. It contains the numerous teeth of the adult lamprey. It is surrounded and supported by the oral disc. 3. Lateral Line System - a system consisting of lines of pores that sense water currents, water pressure changes, and movements and vibrations in the water. The visible external pores of the lateral line system lead to an internal canal, which connect with specialized sensory cells. This system is believed to be related to the sense of hearing in other vertebrates. 4. Medial Nostril - The medial nostril is a primitive feature unique to the lamprey. Other vertebrate animals have paired nostrils. The nostril is responsible for detecting scents and leads to a nasal tube in the dorsal region of the head. A lamprey can “smell” by perceiving chemicals in the water. These scent particles can be detected from great distances. 5. Eye- The eye is a sensory organ responsible for receiving visual input. It leads to the optic nerve, which sends visual impulses to the brain. In the brain the images are deciphered. The adult lamprey eye is structurally very similar to the eyes of other vertebrate animals, consisting of a cornea, iris, lens, and retina. There are no eyelids present in the lamprey. 6. Anterior and posterior Dorsal Fin - used to maintain an upright orientation in the water while moving about. 7. Caudal Fin - A powerful fin used to thrust the lamprey’s body through the water. 8. Cloaca - The common opening of the urinary and reproductive systems. It receives waste from the kidneys and fluids from the reproductive organs and transfers them to the external environment via the opening of the cloaca
- 4. Observations 1. Read the descriptions provided for the external structures and then label the lamprey diagram below. 2. The sea lamprey is a jawless fish. How is the outside covering of the lamprey different than that of other fish? 3. Describe the purpose of the fins labeled 8 and 9. How is this different than the function of the fin labeled 10? 4. Could a sea lamprey bite you? Explain your answer. 5. What exits the body of the lamprey through the cloaca? Analysis and Conclusions 1. Name the four basic characteristics that invertebrate chordates share with jawless fish. What structure have the jawless fish evolved that the invertebrate chordates have not? 2. How is the mouth of the lamprey adapted to prey on other fish?
- 6. Shark is the common name for any member of several orders of cartilaginous fish. Sharks are characterized by a. a streamlined body, b. five to seven gill slits, c. replaceable teeth, and d. a covering of dermal denticles (toothlike scales) to protect their skin from damage and parasites e. paired fins, f. paired nostrils, g. sharks do not have gas-filled swim bladders. h. skeletons made of cartilage rather than bone. i. Since they also lack lungs, sharks lack the natural buoyancy of gas-filled structures. Part of the buoyancy problem is addressed by the fact that sharks have skeletons made of cartilage, which is lighter than bone.
- 7. Familiarize yourself with the following external features: 1. External Nares – These are a pair of openings (nostrils) on each side of the head, cranial from the eyes. Water is taken into the smaller of the two openings and expelled through the larger opening. The water passes by a sensory membrane allowing the shark to detect chemicals in the water. 2. Spiracles – These are small openings caudal from the eyes. These openings allow water to pass through the gills even when the shark’s mouth is closed. 3. Mouth – Although the eating function is evident, the mouth is also used for the intake of water that passes through the gills. 4. Gill Slits – Five vertical slits which allow water to exit after passing over the gills. They are located caudally from the mouth. 5. Lateral Line – A pale line that extends noticeably from the pectoral fin past the pelvic fin. This line is actually a group of small pores which open into the underlying lateral line canal, a sensory organ that detects water movements. 6. Cloaca – This is the exit from the digestive tract combined with being the opening for the sex organs. The cloaca lies between the pelvic fins. 7. Clasper – Found on male sharks only, these are finger-like extensions of the medial edge of each pelvic fin. They may have a single spine associated with each clasper. The claspers aid in sperm transfer during mating. 8. Fins – Refer to Figure 1 and familiarize yourself with each fin and its name. 9. Rostrum – This is the pointed snout at the cranial end of the head. 10. Dorsal Spines – Just cranial to each dorsal fin is a spine that is used defensively by the shark. Each spine has a poison gland associated with it.
- 8. Observations: 1. How is the shark’s nose different from our own? 2. Why are the Spiracles important? 3. The mouth of the shark is part of which organ system(s)? 4. What is the function of the Gill Slits? 5. What does the Lateral Line do? 6. What two organ systems is the Cloaca a part of? 7. Since the Clasper is only present on male dogfish sharks, what gender is your shark? 8. How many fins does a dogfish shark have? 9. What’s another name for the Rostrum? 10. Where are the Dorsal Spines located?
