Aconas delegation
- 1. Delegation Aconas, May – June 2010 DELEGATION 1|Page Clio Bellon Consultant @ Kite Consultants Clio.bellon@telenet.be 0475/74.95.26
- 2. Delegation Aconas, May – June 2010 Table of Contents Delegation .................................................................................................................................................................... 4 Person – Situation Fit ....................................................................................................................................... 4 Situational leadership ................................................................................................................................. 4 Readiness......................................................................................................................................................... 6 Leadership - readiness matching ............................................................................................................. 7 Group Development..................................................................................................................................... 7 Keep in mind that… ...................................................................................................................................... 8 Clear tasks ........................................................................................................................................................... 8 Information .................................................................................................................................................... 8 Dialogue........................................................................................................................................................... 9 Parameters...................................................................................................................................................... 9 Follow up ............................................................................................................................................................. 9 Support ..........................................................................................................................................................10 Accountability..............................................................................................................................................10 Feedback........................................................................................................................................................10 Barriers....................................................................................................................................................................13 Barriers in “me”................................................................................................................................................13 Barriers in “ your employees” ......................................................................................................................13 Barriers in “organizational situation” .......................................................................................................13 Skills .........................................................................................................................................................................14 Checklist Readiness.........................................................................................................................................14 Checklist Situational Leadership.................................................................................................................15 Checklist Delegation.......................................................................................................................................18 2|Page Clio Bellon Consultant @ Kite Consultants Clio.bellon@telenet.be 0475/74.95.26
- 3. Delegation Aconas, May – June 2010 “Knowing is not enough… We must apply. Willing is not enough… We must do.” – Johann Wolfgang von Goethe 3|Page Clio Bellon Consultant @ Kite Consultants Clio.bellon@telenet.be 0475/74.95.26
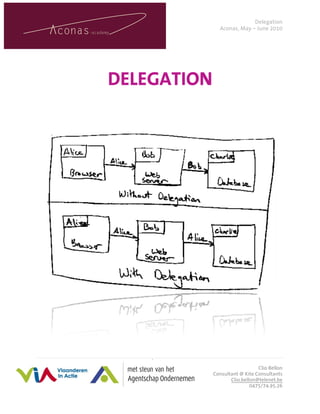
- 4. Delegation Aconas, May – June 2010 Delegation Definition Delegation is about entrusting others with appropriate responsibility and authority for the operation and/or accomplishment of certain activities and decisions. More simply, it is about getting someone else to do part of your job - an assignment that is your responsibility but need not be done by yourself. It should also be positive (for instance as a means of developing staff) rather than negative (for example passing on a job you do not like). Of course there are advantages as well as issues of effective delegation: Advantages of effective delegation Issues involved in delegation • It frees up time for managers; There are no real disadvantages to delegation • It helps managers prioritize their work; but there are some issues to consider: • It requires managers to assess the potential of their people; • Delegation takes time and managers • It is highly motivating for the people to need to put considerable effort and whom work is delegated - they get to do personal investment into it; more challenging work; • There is a level of risk--people take on • It acts as a development tool by part of the job but you keep the increasing the range of skills in a team; effective end responsibility; • It helps with succession planning by • You may simply not have people with exposing people to other levels of work. sufficient resources, time or competence to delegate to. Components of successful delegation Person – Situation Fit Situational leadership Hersey & Blanchard created a model of situational leadership that allows one to analyze the needs of the situation, then adopt the most appropriate leadership style. It has been proven popular with managers over the years because it is simple to understand, and it works in most environments for most people. The model rests on two fundamental concepts: leadership style and readiness. 4|Page Clio Bellon Consultant @ Kite Consultants Clio.bellon@telenet.be 0475/74.95.26
- 5. Delegation Aconas, May – June 2010 Leadership styles Leadership style is characterized in terms of the amount of direction and support that the leader provides to their followers. They categorized all leadership styles into four behaviour types, which they named S1 to S4: • S1: Directing/Telling Leaders define the roles and tasks of the 'follower', and supervise them closely. Decisions are made by the leader and announced, so communication is largely one-way. • S2: Coaching/Selling Leaders still define roles and tasks, but seek ideas and suggestions from the follower. Decisions remain the leader's prerogative, but communication is much more two-way. • S3: Supporting/Participating Leaders pass day-to-day decisions, such as task allocation and processes, to the follower. The leader facilitates and takes part in decisions, but control is with the follower. • S4: Delegating Leaders are still involved in decisions and problem solving, but control is with the follower. The follower decides when and how the leader will be involved. Of these, not one style is considered optimal or desired for all leaders to possess. Effective leaders need to be flexible and can adapt themselves according to the situation. However, each leader tends to have a natural style and in applying Situational Leadership he must know his intrinsic style. 5|Page Clio Bellon Consultant @ Kite Consultants Clio.bellon@telenet.be 0475/74.95.26
- 6. Delegation Aconas, May – June 2010 What is your natural dominant style of leadership? Look for the results of your questionnaire. Readiness The right leadership style will depend on the person being led - the follower, the’ Performance Readiness Level’ of the follower in particular, which is based on their ability and willingness. They stated that the leader's chosen style should be based on the performance readiness level of the follower. They categorized the possible development of followers into four levels, which they named R1 to R4: • R1: Unable but Confident or Willing Follower is unable to complete tasks but has the confidence as long as the leader provides guidance or the follower lacks the ability but is motivated and making an effort. They generally lack the specific skills required for the job in hand. However, they are eager to learn and willing to take direction. • R2: Unable and Insecure or Unwilling Follower is unable and insecure and lacks confidence or the follower lacks commitment and motivation to complete tasks. They may have some relevant skills, but won't be able to do the job without help. The task or the situation may be new to them. • R3: Able but Insecure or Unwilling Follower has the ability to complete tasks but is uneasy about doing it alone or the follower is not willing to use that ability. They are experienced and capable, but may lack the confidence to do it alone, or the motivation to do it well or quickly. • R4: Able and Confident and Willing Follower has the ability to perform and is confident about doing so and is committed. They are experienced at the job, and comfortable with their own ability to do it well. They may even be more skilled than the leader. 6|Page Clio Bellon Consultant @ Kite Consultants Clio.bellon@telenet.be 0475/74.95.26
- 7. Delegation Aconas, May – June 2010 These levels are situational! I might be generally skilled, confident and motivated in my job, but would still drop into Level R1 when faced, say, with a task requiring skills I don't possess. For example, many managers are R4 when dealing with the day-to-day running of their department, but move to R1 or R2 when he/she undertakes a new task. Leadership - readiness matching The leadership style (S1 - S4) of the leader must correspond to the readiness level (R1 - R4) of the follower. Furthermore it is the leader who must adapt, not the follower. To get the most of situational leadership, a leader should train himself in how to operate effectively in various leadership styles, and how to determine the development level of others. For an example of a mismatch, imagine the following scenario. A new person joins your team and you're asked to help him through the first few days. You sit him in front of a PC, show him a pile of invoices that need to be processed today and then excuse yourself to a meeting. He is at level R1, and you've adopted S4, an obvious mismatch. Everyone loses because the new person feels helpless and demotivated and you don't get the invoices processed. For another example of a mismatch, imagine you're handing over your duties to an experienced colleague before you leave for a holiday. You've listed all the tasks that need to be done and given him a detailed set of instructions on how to carry out each one. He is at level R4, and you've adopted S1. The work will probably get done, but your colleague will dislike you for treating him like an idiot. But leave detailed instructions and a checklist for the new person, and they'll thank you for it. Give your colleague a quick chat and a few notes before you go on holiday, and everything will be fine. By adopting the right style to suit the follower's development level, work gets done, relationships are built, and most importantly, the follower's development level will rise, to everyone's benefit. Group Development There is a sequence to the stages of development that groups and teams go through over time. The initial stage is orientation (Stage 1), when group members first come together and are eager to participate, but are unsure of how to work together. Next comes the seemingly inevitable occurrence of dissatisfaction (Stage 2), as working together turns out to be more difficult than anticipated. If the group is able to work through this dissatisfaction, it moves into resolution or integration (Stage 3), where members learn how to work together. If interactions continue to improve, the group reaches the final stage of production (Stage 4). The leadership styles needed to move a group through these stages correspond to the flow of the four leadership styles described above. Style 1, Directing, is appropriate for orientation, where goals have to be made clear and roles defined. Style 2, Coaching, is necessary to move through the dissatisfaction stage, since the group still needs direction but now also needs support, encouragement, and listening behaviours. Once 7|Page Clio Bellon Consultant @ Kite Consultants Clio.bellon@telenet.be 0475/74.95.26
- 8. Delegation Aconas, May – June 2010 a group gets to the resolution or integration stage, the leader’s role could change to Style 3, Supporting, as a facilitator is needed. Now the group provides direction. Finally, in the production stage, the team can take up its task themselves. Here, Style 4, Delegating, is appropriate. When people take on a new task where they are inexperienced, after a while disillusionment sets in. They are often frustrated and overwhelmed—the task is much harder than they thought it would be because they need more time and energy to gain competence than they had anticipated. When that occurs, while they have some competence (more than they had in the beginning) their motivation and confidence drops. The new thinking requires reconstructing the representation of the stages of development in order to depict individual growth that moved from an enthusiastic beginner to a disillusioned learner, on to a capable but cautious performer, and finally to a self-directed achiever. The result is a continuum from “developing” to “developed.” In this case style 2 is the appropriate style. Keep in mind that… …all your collaborators have their differences. Start with a clean piece of paper and really work through what the job is, what skills and attributes are required, and who is the best man/ woman for the job. Ask yourself whether you want someone, for example: • who is reliable, with plenty of experience • who will take a risk but bring about a quick result • whose development will benefit from the challenge • who will simply absorb the workload as a matter of routine Clear tasks Information Be clear on what you want to delegate. Ask yourself what end result you want (in terms of people development as well as activity) and use this as the basis for deciding what to delegate. Give a clear picture of what you want to accomplish. Delegate whole activities rather than parts. If you delegate the whole activity, it raises the satisfaction level of the person carrying it out, develops them, helps them to really understand the job and also is the most efficient in terms of time consumption for you. Show the delegate how the work fits into the overall operation and point what's in it for the delegate. You have to give enough instructions, resources, authority and time to do the job properly. You can point the delegate in the right direction and create a list of resources that could be useful. It can also be useful to contact colleagues to let them know the delegate may need their help. 8|Page Clio Bellon Consultant @ Kite Consultants Clio.bellon@telenet.be 0475/74.95.26
- 9. Delegation Aconas, May – June 2010 Dialogue The act of explaining the activity and what it is worth for the individual taking on the delegated activity is one of the key ways of gaining commitment to it, so you need to be clear about the benefits even at this early stage. Delegation works best when the person taking on the activity fully understands what is required of them, and is enthusiastic and willing to do it. This process may need to be carried out in quite minute detail. If you are delegating the writing of a report, you may need to specify the way the information should be presented, the arguments or hypotheses you need exposed. Sit down with the individual and come to an agreement with them about what they are going to do, when they are going to do it, what resources they will need and the outcome that is expected. Do this in an environment that is conducive to explaining, minimize interruptions and give the delegate your full attention. Writing an e-mail is not the solution. Sell the benefits to the person. Explain exactly what's in it for them and check they are happy doing it. Do obtain, or listen to, the delegate's thoughts or fears and allow for them as you clarify and agree goals. Encourage suggestions, questions, and comments. Remember, they do have the right to say no, and if they do, you must try not to hold this against them. Parameters It is important to work out - with your boss as well as with those for whom you are responsible - the boundaries of responsibility, which enable your people to: • take a decision on their own with no need to report to you • take a decision and then report to you • take a decision only after discussion with you Vagueness about boundaries of responsibility is common and is the cause of much confusion in organisations. Thus, don't wait until after delegating to impose controls and responsibilities. If you are delegating a task that needs authority, make sure that the delegate knows they have your full support, and that other people in the organisation are aware of this too. If the delegated activity involves other parts of the organization, make sure that the appropriate people understand what is happening, why and with whose authority. Follow up You may wish to delegate the activity but not the accountability. Because you are delegating part of your job, you remain ultimately responsible for the outcome. You get the credit if you delegate effectively, but you also get the criticism if your delegation is less than successful. 9|Page Clio Bellon Consultant @ Kite Consultants Clio.bellon@telenet.be 0475/74.95.26
- 10. Delegation Aconas, May – June 2010 It is important not to abandon your employee, and to maintain a fine balance between interest, support and motivation on the one hand, and interference or neglect on the other. Support Allocate the right amount of time. Agree a schedule and arrange to meet up, compare notes and check how the activity is going. Remember you are not simply just dumping work on them--you are actually working with them to make sure they can carry out the work you want. You should make sure you are available to them so that they can come and talk to you if they have a problem or need advice. Once you have provided the resources they need to do the job, make sure you do not interfere but are there to support them. Accountability The routes by which delegates achieve what is required are up to them. The focus of accountability needs to be on results. Clarify the consequences of the task being delegated to them. They are more likely to accept delegation and be motivated to take initiative if it is clear what the rewards for success will be. Do not specify how the job actually has to be done. Remember you have just delegated an activity--it is up to the person concerned to come up with the best way of making sure that it happens. Allow the person to get on with the delegated activity and complete it. Make the delegate responsible for completion of the project: allow delegate to make crucial decisions, make it clear to others that the delegate is in charge and don't take the credit for your delegate's work. Feedback When they have completed the activity, carry out a review to see how well it went. Evaluate the positive outcomes in terms of the activity and the skills or learning which have accrued. Be constructive on any failures and try to establish what could be done better next time for you as much as for the delegate. What exactly is feedback? Feedback is information about performance that leads to action to affirm or develop performance. It is as much about reinforcing effective and strong performance as it is about identifying areas of potential improvement. The outcome of the feedback process should be someone who is engaged, energised and motivated to strive for increased performance. Observing Accurate observation of what was said and done is at the heart of effective feedback. It is vital to record these observations so that they can be used as examples to back-up your 10 | P a g e Clio Bellon Consultant @ Kite Consultants Clio.bellon@telenet.be 0475/74.95.26
- 11. Delegation Aconas, May – June 2010 comments. In your role as a line manager this will be difficult during your busy day of activities – but wherever possible it is useful to try and make notes as and when you have observed such evidence. Preparing the feedback Effective feedback reinforces positive behaviours and strengths as much or more than dwelling on areas where improvement can be made. Give as much attention to the evidence for effective performance as for ineffective performance. Key to successful feedback is giving people a manageable amount to go away with and put into practice. Types of feedback Affirmative feedback tells the person what they did well and rewards them for it. “Jane, you really did well to finish that report at such short notice.” Its purpose is to encourage the person and to reinforce their behaviour. Developmental feedback tells the person what needs to be done better and how to do it. “Jane, please make sure you leave time to check the report for typing errors.” Its purpose is to help the person see how they could do a better job next time. Blockages to feedback Recognising the signals • Negative body language (shaking of the head, turning away) • Loss of eye contact • Blamed placed on the circumstances (‘I was running late that day so I had to rush’) • Blame placed on others (‘My last boss always wanted it done that way’) • Emotional outbursts Blockages to giving feedback Most people are starved of feedback – particularly about their behaviour and the impression they make on other people. Here are some of the reasons why people feel inhibited about the giving and receiving of feedback: • Often people hold back from giving feedback because: o They worry it might upset the person o They are afraid that the person might reject them/the feedback o They fear the person might ‘hit back’ with critical feedback 11 | P a g e Clio Bellon Consultant @ Kite Consultants Clio.bellon@telenet.be 0475/74.95.26
- 12. Delegation Aconas, May – June 2010 o They worry that it might lead to a confrontation that would be difficult to resolve and/or damage future relationships o They feel it is not the time nor the place to grasp the nettle o They feel that the issue is too trivial and that it would be better to save it up for something more substantial • Often people hold back from giving motivational feedback because: o They would feel to embarrassed o They fear that the person complimented might relax and ‘rest on their laurels’ o They think the person might be suspicious of their motives o They feel that compliments are inappropriate (“They are only doing what they are paid for!”) o They think the feedback might be misinterpreted as a plot to fish for return compliments! Blockages to receiving feedback People often react badly when they get feedback from other people because: • They feel threatened • They feel compelled to defend themselves • They feel unworthy of compliments • They have been trained to be modest (“Oh, it was nothing really!”) • They don’t know how to use the feedback to their advantage i.e. how to learn from it Often people hold back from receiving motivational feedback because: • They worry that they might get more than they bargained for • They feel stupid • They think the other person would regard it as fishing for compliments • They don’t consider they have anything to learn • They aren’t interested in another person’s views 12 | P a g e Clio Bellon Consultant @ Kite Consultants Clio.bellon@telenet.be 0475/74.95.26
- 13. Delegation Aconas, May – June 2010 Barriers Managers experience plenty of difficulty in delegating. Here are some of the barriers they experience. Barriers in “me” • Preference for operating rather than delegating • The ‘I can do it better myself’ syndrome • Lack of experience in the job or in delegating • Insecurity about own competence • Fear of being disliked • Refusal to allow mistakes • Lack of confidence in subordinates • Desire for perfection leading to over control • Lack of organizational skill in balancing workloads • Failure to delegate authority commensurate with responsibility • Uncertainty over tasks and my inability to explain them • Unwillingness to develop subordinates • Failure to establish effective control and follow up • Fear that the staff will make a mistake and will be criticized by the superior Barriers in “ your employees” • Lack of experience • Lack of confidence • Avoidance of responsibility • Over-dependency on you • Disorganisation • Overload of work • Lose theirselves in trivia • Fear arising from lack of experience Barriers in “organizational situation” • ‘One-men-show’ syndrome, where there is no room for shared responsibilities and where the delegate can step forward • No tolerance for mistakes • Critically of decisions • Urgency, leaving no time to explain (crisis management) • Confusion of responsibility and authority 13 | P a g e Clio Bellon Consultant @ Kite Consultants Clio.bellon@telenet.be 0475/74.95.26
- 14. Delegation Aconas, May – June 2010 Skills Checklist Readiness High level of employee readiness (maturity) Able and Confident and Willing (High Competence, High Commitment) o The employee has the ability to perform and is confident about doing so and is committed. o The employee is experienced at the job, and comfortable with his/her own ability to do it well. He/She may even be more skilled than the leader. Delegating Moderate level of employee readiness (maturity) Able but Insecure or Unwilling (High Competence, Variable Commitment) o The employee has the ability to complete tasks but is apprehensive about doing it alone or he/she is not willing to use that ability. o The employee is experienced and capable, but may lack the confidence to go it alone, or the motivation to do it well or quickly. Supporting Unable and Insecure or Unwilling (Some Competence, Low Commitment) o The employee is unable and insecure and lacks confidence or he/she lacks commitment and motivation to complete tasks. o The employee may have some relevant skills, but won't be able to do the job without help. The task or the situation may be new to him/her. Coaching Low level of employee readiness (maturity) Unable but Confident or Willing (Low Competence, High Commitment) o The employee is unable to complete tasks but has the confidence as long as the leader provides guidance or he/she lacks the ability but is motivated and making an effort. o The employee generally lacks the specific skills required for the job in hand. However, he/she is eager to learn and willing to take direction. Directing 14 | P a g e Clio Bellon Consultant @ Kite Consultants Clio.bellon@telenet.be 0475/74.95.26
- 15. Delegation Aconas, May – June 2010 Checklist Situational Leadership Directing/Telling = they define the roles and tasks of the 'follower', and supervise them closely. Decisions are made by the leader and announced, so communication is largely one-way. Steps: • Make sure you are well prepared. • Communicate the instruction as a clear message (define the goal(s) and the how the goal(s) can be achieved). • Give clarification if necessary (why, how,…) • Recapitulate How: • Clear voice • Talk calmly • Keep eye contact • Take and keep the initiative in the conversation • Keep it brief and to the point Coaching/Selling = they still define roles and tasks, but seek ideas and suggestions from the follower. Decisions remain the leader's prerogative, but communication is much more two-way. Steps: • Bring your message = inform, clarify, give reflections, arguments and motivations • Give space for the employee ‘s reaction = invite him/her to give remarks and suggestions • Look at the future = set-up an action plan How: • Know where you stand, be prepared • Answer the why-question but don’t discuss it • Bring a convincing message • Be clear about non-discussable matters • Know your employee and know how you can motivate him/her 15 | P a g e Clio Bellon Consultant @ Kite Consultants Clio.bellon@telenet.be 0475/74.95.26
- 16. Delegation Aconas, May – June 2010 • Check if the employee understands what has been said • Keep it firm and cool Supporting/Participating = they pass day-to-day decisions, such as task allocation and processes, to the follower. The leader facilitates and takes part in decisions, but control is with the follower. Steps: • Involve the employee in problem solving • Reflect/Discuss at the same level • Employee talks, leader listens and adjusts How: • Try to make the employee talk • Make time for the analysis of the problem • Help the employee in analyzing the problem and formulating possible solutions • Be aware of the tone of your voice (important for talking at the same level) Delegating = They are still involved in decisions and problem solving, but control is with the follower. The follower decides when and how the leader will be involved. Steps: • Preparation of what you will delegate • Have a delegation conversation • Let the employee do the task • Evaluate the completed task and give feedback How: • Outline the tasks, results, resources, freedom of working method, critical moments and strengths and weaknesses of the employee • Inform the employee and ask for his consent • Talk it over and make clear agreements • Inform third parties • Accept differences • Complaints and mistakes by third parties: protect the employee (“I will discuss it and he/she will get back to you.”) 16 | P a g e Clio Bellon Consultant @ Kite Consultants Clio.bellon@telenet.be 0475/74.95.26
- 17. Delegation Aconas, May – June 2010 • Positive feedback by third parties: forward it immediately • Follow-up • Solve difficulties • Compliment the employee 17 | P a g e Clio Bellon Consultant @ Kite Consultants Clio.bellon@telenet.be 0475/74.95.26
- 18. Delegation Aconas, May – June 2010 Checklist Delegation Person – Situation Fit • Choose the right person for the job o the best qualified who and will deliver the best results o the individual who will benefit most from being given the job o delegate to develop skills that can be used later on • Keep the readiness level of the delegate in mind o use delegating leadership when the delegate has high competence | high commitment and is able and confident | willing o use supporting leadership when the delegate has high competence | variable commitment and is able but insecure | unwilling o use coaching leadership when the delegate has some competence | low commitment and is unable and insecure | unwilling o use directing leadership when the delegate has low competence | high commitment and is unable but confident | willing Define clear tasks • Provide enough information o show how the work fits into the overall operation o point out the "win-win" -- what's in it for the delegate o give enough instructions, resources, authority and time to do the job properly o give a clear picture of what you want to accomplish o point the delegate in the right direction o create a list of resources that could be useful o contact colleagues to let them know delegate may need their help • Establish parameters o decide on conditions and terms of completion before delegating o be clear about your requirements and boundaries o don't wait until after delegating to impose controls • Delegate through dialogue o delegate in an environment that is conducive to explaining o minimize interruptions and give the delegate your full attention o encourage suggestions, questions, and comments 18 | P a g e Clio Bellon Consultant @ Kite Consultants Clio.bellon@telenet.be 0475/74.95.26
- 19. Delegation Aconas, May – June 2010 Follow up • Give guidance without interfering o let delegates know they doesn't have to their fight battles alone o point out the roadblocks your delegate could encounter o don't offer to do the work for the delegate (supporting instead of rescuing) o help your delegate to come up with his or her own solutions o be on delegate's side when dealing with clients, colleagues, etc. o don't micromanage, being too particular about how the job is done o give delegate the freedom to decide on the process o be aware of the status of the project and keep a delegation log to track the status of delegated items o don't let the work be delegated back to you o listen to problems without assuming responsibility for solving them o keep the focus on the delegate and his / her ideas and solutions • Make the delegate accountable o establish solid deadlines, not open-ended completion dates o be as specific as possible about when the task is due o set sub-deadlines for completing milestones along the way o make the delegate responsible for completion of the project o allow delegate to make crucial decisions o make it clear to others that delegate is in charge o don't take the credit for your delegate's work • Offer feedback o let the delegate report on previously agreed dates o don't focus on what's wrong, but focus on what can be done to improve it o give positive and corrective commentary o don't treat your delegate as a scapegoat if unsuccessful Do Plan the delegation properly. Dialogue with the person concerned. Be specific about the outcomes. Let go, and allow them to complete the job effectively. Don’t Leave people to sink or swim. Interfere or dictate how the job should be done. Delegate to the same people all the time. Take all the credit. 19 | P a g e Clio Bellon Consultant @ Kite Consultants Clio.bellon@telenet.be 0475/74.95.26
