Climate presentation
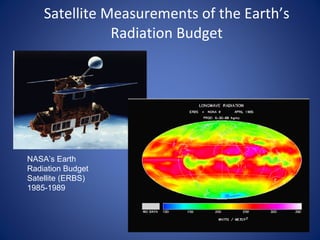
- 1. Satellite Measurements of the Earth’s Radiation Budget NASA’s Earth Radiation Budget Satellite (ERBS) 1985-1989
- 4. Atmospheric influences on radiation Absorption (absorber warms) Reflection Scattering
- 5. Atmospheric Absorption - The Greenhouse Effect Transparent to solar (shortwave) radiation Opaque to earth’s (longwave) radiation Major GH gases: CO 2 , H 2 0 (v) , CH 4
- 6. Global Energy Balance II: The Greenhouse Effect
- 15. Seasonal variation of surface radiation
- 16. Seasonal variation of surface energy budget Storage change = net radiation - latent heat flux - sensible heat flux
- 18. Seasonal variation of surface air temperature
- 20. Temperature Ranges (Summer minus Winter) Large over land, small over ocean
- 21. Presented by: Your Name Here Climate Change: Fitting the pieces together
- 27. “ Greenhouse effect” Increasing greenhouse gases trap more heat
- 29. Greenhouse gases Nitrous oxide Water Carbon dioxide Methane Sulfur hexafluoride
- 33. Could the warming be natural?
- 35. Is it real?
- 36. Effects: Snow and ice Grinnell Glacier, Glacier National Park 1900 and 2008
- 37. Effects: Snow and ice Grinnell Glacier, Glacier National Park 1900 and 2008
- 41. How do we know?
- 43. Increased warmth has also affected living things. For example, the Japanese keep very detailed records on the blossoming of their Tokyo cherry trees, so they know they are blooming 5 days earlier on average than they were 50 years ago. Also mosquitoes, birds, and insects are moving north in the Northern Hemisphere.
- 44. Computer models
- 45. Computer models
- 47. Aspen, CO Forecast: Partly cloudy today High : 28°F Low: 13°F Increasing clouds over night. Colder tomorrow.
- 48. Aspen, CO Forecast: Partly cloudy today High : 28°F Low: 13°F Increasing clouds over night. Colder tomorrow.
- 49. [Image 1] A common critique of climate predictions is, “If weather model forecasts aren’t reliable more than a week out, how can models predict climate decades in the future?” While weather and climate models are based on similar physics, they are not predicting the same thing. Weather forecasts look at the day-to-day changes on a local level, and subtle chaotic atmospheric variations make short-term weather forecasts difficult beyond 8-10 days. [click, Image 2] Climate predictions are focused on longer-term influences of the sun, oceans, land, and ice on the atmosphere. Instead of predicting a temperature at a particular place at a particular hour, climate modules project an average temperature over a year or longer in a large region or over the entire globe.
- 51. Climate models are not only used to look at how climate might change, they’re also used to figure out WHY it’s changing. When models are run with only natural influences from the sun and volcanic eruptions, they say that during the latter half of the 20 th century, we would have expected little change from normal conditions (the blue line). Only the addition of human emissions (greenhouse gases, sulfates, and ozone) produce the model results in red that most closely reproduce the black line of actual observations. So, although they aren’t perfect, climate models can reproduce many of the larger features of climate change in Earth’s distant past, and they replicate the pattern of warming in the last 100+ years. This gives us confidence that they correctly identify that the warming is due to man’s activities, and that projections of future warming are realistic.
- 52. Why should we care?
- 53. Global average temperatures are expected to increase by about 2-13°F (1-7°C) by the end of the century. That may not sound like a lot, so what’s the big deal? The problem is that small changes in global average temperature can lead to really large changes in the environment. Let’s look at some of the expected changes.
- 54. 2003 European Heat Wave Germany: Lowest river levels this century Switzerland: Melting glaciers, avalanches France: >14,000 deaths Portugal: Forest fires U.K.: Train rails buckle
- 55. [Image 1] There will always be natural variability, and some places and some years will be warmer or cooler than average. In general, however, summers will get hotter, not only because of higher temperatures but also because humidities will increase. That means that heat waves, like the one that killed 35,000 people in Europe in 2003, will become more common. [click, Image 2] On the plus side, winters will be warmer in many places, reducing heating bills. And the number of days with frosts is likely to decrease.
- 57. The oceans will continue their rise in the coming century. The IPCC’s best estimates range from a few inches to a few feet by 2100. If the rise is 2 feet, the US could lose 10,000 square miles, If they rise three, they will inundate Miami and most of coastal Florida. Sea-level rise also increases coastal erosion and the loss of coastal wetlands, and saltwater spoils freshwater drinking supplies. Coastal populations become even more vulnerable to storm surge and flooding. Considering that half of the world’s population lives near coasts, sea-level rise is a serious concern. The big unknown in all this is how much the planet’s ice sheets will melt.
- 59. [Image 1] A warming planet means continuing changes in its ecosystems. As the oceans absorb more carbon dioxide, the chemistry of the ocean changes, putting many sea creatures at risk. The IPCC projects that by 2100 the pH of the ocean will drop to its lowest point in at least 20 million years. [click, Image 2] As temperatures get milder, mosquitoes, ticks, rodents, and other disease carriers will expand their range, particularly in developing countries. Here in the U.S., dengue hemorrhagic fever, a tropical, mosquito-borne disease, hit for the first time in modern times in 2005 in the Lower Rio Grande Valley. [click, Image 3] Warmer temperatures will also mean less snow overall at certain latitudes because more will fall as rain, and the snow that does fall will melt faster. This affects people living in areas that depend on snow-fed reservoirs for water. [click, Image 4] The IPCC projects increases of 5-20% in crop yields in the first decades of this century. but the crops will be more prone to failure if climate variability increases and precipitation becomes less dependable. And ironically, with higher temperatures comes an increased potential for killing freezes. This is because plants start growing earlier, making them more vulnerable to sudden spring-time cold spells.
- 62. The IPCC
- 68. What do climate scientists really think?
- 72. What next—what can we do?
- 74. What next—what can we do?
- 76. Here are examples of 8 technologies that could save 8 billion tons, or 8 wedges, of carbon. Some of these we could do right away, while others are based on technologies still being studied, such as capturing and storing carbon. [Details on strategies: Efficient vehicles: Double car fuel efficiency in 2055 from 30 miles per gallon (mpg) to 60 mpg Reduced vehicle use: Halve the miles traveled by the world’s cars in 2055 Efficient buildings: Cut emissions by 25% in all buildings CCS electricity: Capture and store carbon from 800 large coal power plants or 1600 large natural gas power plants Triple the world’s current nuclear capacity Solar electricity: Increase solar capacity 700 times Forest storage: Halve global deforestation and double forest planting in 50 years Soil storage: Apply carbon management strategies to all of the world’s farm fields] This list represents only some of the possible strategies, but choosing strategies will not be easy. However, the longer we wait to reduce emissions, the higher the target will need to be, and the more adaptation will be necessary. In 2004, when the wedges concept was first introduced, the target was only 7 billion tons.
- 77. Individual actions Use mass transit, bike, walk, roller skate Tune up your furnace Unplug appliances or plug into a power strip and switch it off Buy water-saving appliances and toilets; installing low-flow shower heads . Caulk, weatherstrip, insulate, and replace old windows Buy products with a U.S. EPA Energy Star label
Hinweis der Redaktion
- The topic of climate change is like a puzzle with many different pieces—oceans, the atmosphere, ecosystems, polar ice, natural and human influences. Scientists have been working on this puzzle for more than a century, and while there are still gaps in our knowledge, most experts feel we have the puzzle is complete enough to show that human activities are having an adverse effect on our planet. This talks looks at many of those puzzle pieces, the evidence behind them, and the conclusions we can draw from them.
- Talk—and module--outline
- Scientists have a good understanding of what has changed earth’s climate in the past: Incoming solar radiation is the main climate driver. Its energy output increased about 0.1% from 1750 to 1950, increasing temperatures by 0.2°F (0.1°C) in the first part of the 20 th century. But since 1979, when we began taking measurements from space, the data show no long-term change in total solar energy, even though Earth has been warming. Repetitive cycles in Earth’s orbit that occur over tens of thousands of years can influence the angle and timing of sunlight. In the distant past, drifting continents make a big difference in climate over millions of years by changing ice caps at the poles and by altering ocean currents, which transport heat and cold throughout the ocean depths. Huge volcanic eruptions can cool Earth by injecting ash and tiny particles into the stratosphere. Changes in the concentration of greenhouse gases, which occur both naturally and as a result of human activities, also influence Earth’s climate.
- [Image 1] Earth’s surface absorbs heat from the sun and then re-radiates it back into the atmosphere and to space. [click, Image 2] Much of this heat is absorbed by greenhouse gases, which then send the heat back to the surface, to other greenhouse gas molecules, or out to space. Though only 1% of atmospheric gases are greenhouse gases, they are extremely powerful heat trappers. By burning fossil fuels faster and faster, humans are effectively piling on more blankets, heating the planet so much and so quickly that it’s hard for Mother Nature and human societies to adapt.
- While there are many substances that act as greenhouse gases, two of the most important are water and carbon dioxide, or CO2.
- [Image 1] CO2 comes from a variety of sources. For example, plants take up carbon dioxide in the air to make wood, stems, and leaves, and then release it back into the air when the leaves fall or the plants die. The concern today is that fossil fuel use is putting huge amounts of CO2 in the atmosphere at a rate faster than the climate system can adapt to. [click, Image 2] In addition, the warming resulting from CO2 and other greenhouse gases also has the effect of increasing evaporation. This adds water vapor to the atmosphere as well. Water vapor is the most important gas in the natural greenhouse effect, contributing 60% of the effect to carbon dioxide’s 26%. And in fact, satellites have detected an increase in atmospheric moisture over the oceans at a rate of 4% per degree F of warming (7% per degree C) since 1988. This additional water vapor amplifies the warming effect.
- Certainly, past temperatures past have been higher (and lower) than today, and CO 2 concentrations have also varied. Large global swings were probably caused by such things as changes in Earth’s orbit, which changed the distribution of sunlight over the planet. When this caused warming, more CO2 and other greenhouse gases were released, producing additional warming. [click to reveal today’s CO2 level] But today, the CO 2 released by human activities is far above amounts in the previous 800,000 years. This CO2 is triggering the increase in temperatures we’ve seen.
- Earth is getting warmer by virtually every measure we know, and the temperature has been well above normal for more than 25 years. Although increases of 1.0-1.6°F (0.6-0.9°C) over the last century or so may not sound very threatening, remember that’s a global average. The warming is stronger over land than over oceans and in the higher latitudes than in the tropics.
- [Image 1] Snow and ice reflect the sun’s energy back to space. Without this white cover, more water can evaporate into the atmosphere where it acts as a greenhouse gas, and the ground absorbs more heat. Snow and ice are melting at rates unseen for thousands of years. In Glacier National Park, for example, there were 150 glaciers in 1850. Today, there are 26. [click, Image 2] Sea ice is dwindling too, especially in the Northern Hemisphere. Satellites have seen average Arctic sea ice shrink by 2.7% per decade from 1978 to 2006, with faster melting in summer.
- [Image 1] Snow and ice reflect the sun’s energy back to space. Without this white cover, more water can evaporate into the atmosphere where it acts as a greenhouse gas, and the ground absorbs more heat. Snow and ice are melting at rates unseen for thousands of years. In Glacier National Park, for example, there were 150 glaciers in 1850. Today, there are 26. [click, Image 2] Sea ice is dwindling too, especially in the Northern Hemisphere. Satellites have seen average Arctic sea ice shrink by 2.7% per decade from 1978 to 2006, with faster melting in summer.
- [Image 1] More water vapor held by a warmer atmosphere also leads to heavier rains and more snowfall. Intense precipitation over the U.S. has increased 20% over the last century. [click, Image 2] But as storm tracks shift, it can also mean some areas get drier. A 2004 study by the National Center for Atmospheric Research found that the percentage of Earth’s land experiencing serious drought had more than doubled since the 1970s.
- Increased warmth has also affected living things. For example, the Japanese keep very detailed records on the blossoming of their Tokyo cherry trees, so they know they are blooming 5 days earlier on average than they were 50 years ago. Also mosquitoes, birds, and insects are moving north in the Northern Hemisphere.
- Scientists learn about the past climate conditions from such things as tree ring analysis, fossil evidence, and analysis of patterns and chemical composition in coral skeletons and ice cores.
- We know about the present changes from observations taken at the surface and in the atmosphere. One of the questions often asked is if the warming isn’t an artifact of urban heat islands or changes in how measurements are done. Scientists have looked at this extensively. For example, when a NASA group removed all but 200 true rural sites, the warming pattern persisted. a U.S. National Climatic Data Center study found no statistically significant urban heat island effect in 289 U.S. stations. And finally, even though there are no cities in the oceans, warming has been measured over them too.
- [Image 1] The main tool for both past and present climate analyses are computer climate models. Much like the models used to forecast weather, climate models simulate the climate system with a 3-dimensional grid that extends through the land, ocean, and atmosphere. The grid may have 10 to 60 different levels in the atmosphere and surface grid spacings of about 60 by 90 miles (100 by 150 km)—the size of Connecticut. The models perform trillions of calculations that describe changes in many climate factors in the grid. [click, Image 2] The models project possible climates based on scenarios that cover a range of assumptions about global population, greenhouse gas emissions, technologies, fuel sources, etc. The model results provide a range of possible impacts based on these assumptions.
- [Image 1] The main tool for both past and present climate analyses are computer climate models. Much like the models used to forecast weather, climate models simulate the climate system with a 3-dimensional grid that extends through the land, ocean, and atmosphere. The grid may have 10 to 60 different levels in the atmosphere and surface grid spacings of about 60 by 90 miles (100 by 150 km)—the size of Connecticut. The models perform trillions of calculations that describe changes in many climate factors in the grid. [click, Image 2] The models project possible climates based on scenarios that cover a range of assumptions about global population, greenhouse gas emissions, technologies, fuel sources, etc. The model results provide a range of possible impacts based on these assumptions.
- [Image 1] A common critique of climate predictions is, “If weather model forecasts aren’t reliable more than a week out, how can models predict climate decades in the future?” While weather and climate models are based on similar physics, they are not predicting the same thing. Weather forecasts look at the day-to-day changes on a local level, and subtle chaotic atmospheric variations make short-term weather forecasts difficult beyond 8-10 days. [click, Image 2] Climate predictions are focused on longer-term influences of the sun, oceans, land, and ice on the atmosphere. Instead of predicting a temperature at a particular place at a particular hour, climate modules project an average temperature over a year or longer in a large region or over the entire globe.
- [Image 1] A common critique of climate predictions is, “If weather model forecasts aren’t reliable more than a week out, how can models predict climate decades in the future?” While weather and climate models are based on similar physics, they are not predicting the same thing. Weather forecasts look at the day-to-day changes on a local level, and subtle chaotic atmospheric variations make short-term weather forecasts difficult beyond 8-10 days. [click, Image 2] Climate predictions are focused on longer-term influences of the sun, oceans, land, and ice on the atmosphere. Instead of predicting a temperature at a particular place at a particular hour, climate modules project an average temperature over a year or longer in a large region or over the entire globe.
- Climate models are not only used to look at how climate might change, they’re also used to figure out WHY it’s changing. When models are run with only natural influences from the sun and volcanic eruptions, they say that during the latter half of the 20 th century, we would have expected little change from normal conditions (the blue line). Only the addition of human emissions (greenhouse gases, sulfates, and ozone) produce the model results in red that most closely reproduce the black line of actual observations. So, although they aren’t perfect, climate models can reproduce many of the larger features of climate change in Earth’s distant past, and they replicate the pattern of warming in the last 100+ years. This gives us confidence that they correctly identify that the warming is due to man’s activities, and that projections of future warming are realistic.
- Global average temperatures are expected to increase by about 2-13°F (1-7°C) by the end of the century. That may not sound like a lot, so what’s the big deal? The problem is that small changes in global average temperature can lead to really large changes in the environment. Let’s look at some of the expected changes.
- [Image 1] There will always be natural variability, and some places and some years will be warmer or cooler than average. In general, however, summers will get hotter, not only because of higher temperatures but also because humidities will increase. That means that heat waves, like the one that killed 35,000 people in Europe in 2003, will become more common. [click, Image 2] On the plus side, winters will be warmer in many places, reducing heating bills. And the number of days with frosts is likely to decrease.
- The oceans will continue their rise in the coming century. The IPCC’s best estimates range from a few inches to a few feet by 2100. If the rise is 2 feet, the US could lose 10,000 square miles, If they rise three, they will inundate Miami and most of coastal Florida. Sea-level rise also increases coastal erosion and the loss of coastal wetlands, and saltwater spoils freshwater drinking supplies. Coastal populations become even more vulnerable to storm surge and flooding. Considering that half of the world’s population lives near coasts, sea-level rise is a serious concern. The big unknown in all this is how much the planet’s ice sheets will melt.
- [Image 1] A warming planet means continuing changes in its ecosystems. As the oceans absorb more carbon dioxide, the chemistry of the ocean changes, putting many sea creatures at risk. The IPCC projects that by 2100 the pH of the ocean will drop to its lowest point in at least 20 million years. [click, Image 2] As temperatures get milder, mosquitoes, ticks, rodents, and other disease carriers will expand their range, particularly in developing countries. Here in the U.S., dengue hemorrhagic fever, a tropical, mosquito-borne disease, hit for the first time in modern times in 2005 in the Lower Rio Grande Valley. [click, Image 3] Warmer temperatures will also mean less snow overall at certain latitudes because more will fall as rain, and the snow that does fall will melt faster. This affects people living in areas that depend on snow-fed reservoirs for water. [click, Image 4] The IPCC projects increases of 5-20% in crop yields in the first decades of this century. but the crops will be more prone to failure if climate variability increases and precipitation becomes less dependable. And ironically, with higher temperatures comes an increased potential for killing freezes. This is because plants start growing earlier, making them more vulnerable to sudden spring-time cold spells.
- Nothing in science is 100% certain There are no laboratory experiments that can tell us what the future will be—the planet IS the test tube [click to reveal bullets] What don’t we know? Is there some climate process we don’t know about? So far, research over the years has strengthened the conclusion that humans are adversely influencing climate, but scientific knowledge is still evolving We don’t know how things might change in the future, such as Will alternative energy sources become widely available? How soon? Will some yet-to-be-discovered technology be able to clean CO2 out of the air? How will changing economics, global population, and political processes affect our ability to tackle the problem?
- [Image 1] The International Panel on Climate Change, the group that produces the main reports on climate change, is a scientific intergovernmental body set up by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and by the United Nations Environment Programme in 1988. [click, Image 2] The IPCC process involves hundreds of scientists from about 140 countries, a variety of fields, and a range of views. Their function is to assess the latest peer-reviewed literature, [click Image 3] compare different computer model results from various sources, and to achieve consensus about where the weight of the evidence points and where uncertainties lie. And
- Based on the evidence accumulated over the last 40 years, these are some of their main conclusions. The words in red were very carefully chosen to reflect quantifiable estimates. So Very High Confidence and means the statement has at least a 9 out of 10 chance of being correct, Very Likely means the scientists are more than 90% sure, and Likely means they are more than 66% sure.
- But what about those who disagree? Scientists ALWAYS disagree Although many statements that climate change is bogus are based on false or incomplete information, there have also been some legitimate scientific criticisms of climate change science. It’s important to separate one from the other, particularly since misinformation can be stubbornly persistent, especially on the Internet. The important questions posed by reputable climate scientists who disagree with most of their peers are these: Do we know enough about the drivers of climate to know what causes change? Are we underestimating the Earth system’s complexity ? Are climate models good enough to accurately simulate the complex climate system? Are there processes that will limit warming naturally by producing a negative feedback? Over the last 40 years, various theories have been proposed, components of climate understanding have been questioned, data have been critiqued (and prompted adjustments), but so far no credible competing explanations have been shown to fit the preponderance of evidence.
- Also, there are scientists who disagree with the IPCC—they believe the conclusions are too conservative and that things will be worse than projected. There is some evidence to support their views. Arctic sea ice is melting much faster than scientists predicted. Also, actual fossil fuel emissions in recent years have exceeded all but the highest IPCC projections, growing four times faster than in the 1990s. Some argue that the IPCC near-future assumptions about global energy use are too optimistic. A recent study also concludes that the IPCC estimates were too rosy with regard to how quickly developing countries will be able to afford technologies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Scientists in this camp also say sea levels may rise far more than we anticipate because our calculations aren’t taking into account the unexpectedly large melting of the Greenland and Antarctic Ice Sheets.
- [Image 1] A survey conducted in 2007 by George Mason University of U.S. scientists who have expertise in climate science (not just a scientific background) what they think. 97% of the 489 respondents agreed that “global average temperatures have increased” during the past century. That’s up from 60% in 1991. [click, Image 2] 84% believe human activities are causing the warming, and only 5% disagree. So the survey does indicate the bulk of climate scientists—those most knowledgeable about the field—now agree that human activity contributes to global warming.
- As with all science that affects our lives, we need to be educated consumers. Do your homework, starting with the IPCC reports. All of the reports provide interesting information, although they are lengthy and quite technical. The AR4 Synthesis Report is easy to read and provides a good summary of the other reports. Also look at the work from other authoritative sources such as the National Academies of Science and the U.S. Climate Change Science Program. When looking at information (particularly on the Web), search out contrasting opinions to see what others say about a topic. And evaluate the source—is it someone with real expertise, or just someone with an opinion.
- Reducing our greenhouse gas emissions and our use of fossil fuels will not be easy, but it is doable. Here’s how some researchers at Princeton view it. Our current path is toward doubling CO 2 emissions in the next 50 years, with even greater increases beyond that. In order to get off this path, we need to find ways to keep [8] emissions constant for the next 50 years and then reduce them during the second half of the century. This would [9] limit atmospheric CO 2 to about 570 ppm—still greater than the roughly 380 ppm in the atmosphere today, but enough to avoid the worst predicted consequences. [Image 1] In order to hold carbon emissions constant over the next 50 years, we need to find some combination of ways to cut 8 billion tons of carbon emissions per year. In the graph, the difference between where we are and where we’d like to be forms a triangle with a height of 8 billion tons in 2055.
- [Image 1] This triangle can be divided into 8 wedges representing one billion tons each.
- Here are examples of 8 technologies that could save 8 billion tons, or 8 wedges, of carbon. Some of these we could do right away, while others are based on technologies still being studied, such as capturing and storing carbon. [Details on strategies: Efficient vehicles: Double car fuel efficiency in 2055 from 30 miles per gallon (mpg) to 60 mpg Reduced vehicle use: Halve the miles traveled by the world’s cars in 2055 Efficient buildings: Cut emissions by 25% in all buildings CCS electricity: Capture and store carbon from 800 large coal power plants or 1600 large natural gas power plants Triple the world’s current nuclear capacity Solar electricity: Increase solar capacity 700 times Forest storage: Halve global deforestation and double forest planting in 50 years Soil storage: Apply carbon management strategies to all of the world’s farm fields] This list represents only some of the possible strategies, but choosing strategies will not be easy. However, the longer we wait to reduce emissions, the higher the target will need to be, and the more adaptation will be necessary. In 2004, when the wedges concept was first introduced, the target was only 7 billion tons.
- As you can see, there are many ways society can approach the struggle to reduce carbon emissions, but there is no single solution. Many of the strategies mentioned are the realm of governments. And the ever-growing world population means that we’ll have to work that much harder to reduce global emissions. But on an individual level, there are many things you can do to make a difference. [click to reveal examples] Lots of other ideas are available on the Internet.
- Scientists are still working on the puzzle. The IPCC’s 5 th Assessment Report is planned for 2013-2014. Climate models are being improved, more data is being collected. However, the puzzle is already complete enough to know we need to take action.
