Acid base imbalance in medicine
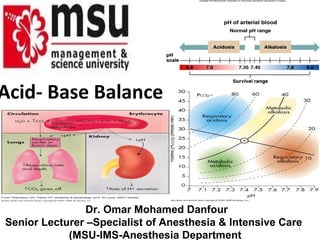
- 1. Acid- Base Balance Dr. Omar Mohamed Danfour Senior Lecturer –Specialist of Anesthesia & Intensive Care 1 (MSU-IMS-Anesthesia Department
- 2. pH Review • PH = - log [H+] • H+ is really a proton • If [H+] is high, the solution is acidic pH • If [H+] is low, the solution is basic or alkaline pH • Acids are H+ donors. • Bases are H+ acceptors, or give up OH- in solution. • Acids and bases can be: – Strong – dissociate completely in solution • HCl, NaOH – Weak – dissociate only partially in solution • Lactic acid, carbonic acid 2
- 3. Acid Base -Basic Concepts • Hydrogen Ion [H+] is tightly controlled • [H+] is determined by the balance between PaCO2 and serum HCO3 (bicarbonate), {normal ratio is 20 (Hco3) : 1(H2Co3)} Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation [H+] = 24 (PaCO2 / HCO3-) Normal Values – [H+] = 40 nEq/L – pH = 7.40 (7.35-7.45) – PaCO2 = 40 mm Hg (35-45) – HCO3 = 24 mEq/L (22-26) – < 6.8 or > 8.0 death occurs 3
- 4. [H+] pH pH = 6.1 + log ([PaCO2] / [0.03 x HCO3-]) pH [H+] pH [H+] 7.80 16 7.30 50 7.75 18 7.25 56 7.70 20 7.20 63 7.65 22 7.15 71 7.60 25 7.10 79 7.55 28 7.00 89 7.50 32 6.95 100 7.45 35 6.90 112 7.40 40 6.85 141 7.35 45 6.80 159 4
- 5. Keep It Simple • PaCO2 = Acid – PaCO2 = pH (Acidemia) – PaCO2 = pH (Alkalemia) • HCO3 = Base – HCO3 = pH (Alkalemia) – HCO3 = pH (Acidemia) • Acidosis: pH < 7.35 – Respiratory PaCO > 40 mmHg – Metabolic HCO3 < 24 mEq/L • Alkalosis: pH > 7.45 – Respiratory PaCO2 < 40 mmHg 5
- 6. The Body and pH 6
- 7. Simple Acid-Base Disorders Type of Disorder pH PaCO2 [HCO3] Metabolic Acidosis ↓ ↓ ↓ Metabolic Alkalosis ↑ ↑ ↑ Acute Respiratory Acidosis ↓ ↑ ↑ Chronic Respiratory Acidosis ↓ ↑ ↑↑ Acute Respiratory Alkalosis ↑ ↓ ↓ Chronic Respiratory Alkalosis ↑ ↓ ↓↓ 7
- 8. Small changes in pH can produce major disturbances • Most enzymes function only with narrow pH ranges • Acid-base balance can also affect electrolytes (Na+, K+, Ca++, Cl-) • Can also affect hormones • The body produces more acids than bases • Acids take in with foods • Acids produced by metabolism of lipids and proteins • Cellular metabolism produces CO2. • CO2 + H20 ↔ H2CO3 ↔ H+ + HCO3- 8
- 9. Control of Acids 1. Buffer systems Take up H+ or release H+ as conditions change Buffer pairs – weak acid and a base Exchange a strong acid or base for a weak one Results in a much smaller pH change CO2 + H20 ↔ H2CO3 ↔ H+ + HCO3- Bicarbonate buffer • Sodium Bicarbonate (NaHCO3) and carbonic acid (H2CO3) • Maintain a 20:1 ratio : HCO3- : H2CO3 HCl strong Acid + NaHCO3 weak Base ↔ H2CO3 weak acid + NaCl 9
- 10. Phosphate buffer • Major intracellular buffer • H+(acid) + HPO42- ↔ H2PO4- (titratable acids eliminated in urine) • OH-(Base) + H2PO4-acid ↔ H2O + H2PO42- Protein Buffers • Hemoglobin is rich in histidine which is an effective buffer from PH5.7 to 7.7.(Hb in RBCs in equilibrium as a weak acid(HHB) and a potassium salt (KHb) • Carboxyl group gives up H+ • Amino Group accepts H+ • Side chains that can buffer H+ are present on 27 10
- 11. 2. Respiratory mechanisms • Exhalation of carbon dioxide • Powerful, but only works with volatile acids • Doesn’t affect fixed acids like lactic acid • CO2 + H20 ↔ H2CO3 ↔ H+ + HCO3- • Body pH can be adjusted by changing rate and depth of breathing 3. Kidney excretion • Can eliminate large amounts of acid • Can also excrete base • Can conserve and produce bicarb ions • Most effective regulator of pH • If kidneys fail, pH balance fails 11
- 12. Rates of correction • Buffers function almost instantaneously (rapid) • Respiratory mechanisms take several minutes to hours • Renal mechanisms may take several hours to days 12
- 13. 13
- 14. Acid-Base Imbalances • pH< 7.35 acidosis • pH > 7.45 alkalosis • The body response to acid-base imbalance is called compensation • May be complete if brought back within normal limits • Partial compensation if range is still outside normals • If underlying problem is metabolic, hyperventilation or hypoventilation can help : respiratory compensation. • If problem is respiratory, renal mechanisms can bring about metabolic compensation 14
- 15. 15
- 16. Respiratory Acidosis • Carbonic acid excess caused by blood levels of CO2 above 45 mm Hg. • Hypercapnia – high levels of CO2 in blood Causes: • Chronic conditions: – Depression of respiratory center in brain that controls breathing rate – drugs or head trauma – Paralysis of respiratory or chest muscles – COPD, pneumonia & obesity CO2 + H20 ↔ H2CO3 ↔ H+ + HCO3- 16
- 17. Respiratory Acidosis • Acute conditons: – Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome – Pulmonary edema – Pneumothorax – Pulmonary emboli – Aspiration pneumonia – Increased CO2 production (Malignant hyperthermia & thyroid storm) 17
- 18. Signs and Symptoms of Respiratory Acidosis • Breathlessness • Restlessness • Lethargy and disorientation • Tremors, convulsions, coma • Respiratory rate rapid, then gradually depressed • Skin warm and flushed due to vasodilation caused by excess CO2 18
- 19. Compensation for Respiratory Acidosis • This is accomplished via two mechanisms; a) rapid cell buffering and • In this setting, carbonic acid (H2CO3 ) can only be buffered by the limited intracellular buffers (primarily hemoglobin and proteins). H2CO3 + Hb- → HHb + HCO3- b) an increase in net acid excretion. • Kidneys eliminate hydrogen ion and retain bicarbonate ion (Chronic state) 19
- 20. 20
- 21. Treatment of Respiratory Acidosis • Restore & improve alveolar ventilation • IV lactate solution (converted to bicarbonate ions in the liver). • Treat underlying dysfunction or disease e.g. pul odema, Res depression 21
- 22. Respiratory Alkalosis • Carbonic acid deficit • pCO2 less than 35 mm Hg (hypocapnea) • Most common acid-base imbalance • Primary cause is hyperventilation CO2 + H20 ↔ H2CO3 ↔ H+ + HCO3- 22
- 23. Respiratory Alkalosis • Conditions that stimulate respiratory center: – Oxygen deficiency at high altitudes – Pulmonary disease and Congestive heart failure – caused by hypoxia – Acute anxiety & pain – Fever, anemia – Early salicylate intoxication – Cirrhosis – Gram-negative sepsis – Iatrogenic (ventilator induced) 23
- 24. Signs and Symptoms of Respiratory Alkalosis • Alkalosis causes over excitability of the central and peripheral nervous systems. • Numbness • Light headedness • It can cause : – Nervousness – muscle spasms or tetany – Convulsions – Loss of consciousness – Death 24
- 25. Compensation of Respiratory Alkalosis • There are two mechanisms responsible for this compensation to respiratory alkalosis; 1) Rapid cell buffering and 2) Decrease in net renal acid excretion. • hydrogen ions move from the cells into the extracellular fluid, where they combine with [HCO3- to form carbonic acid in the following reaction: H+ + HCO3- → H2CO3 (CA) • In acute respiratory alkalosis, for every 10 mmHg decrease in the PCO2, there is a 2meq/L decrease in the plasma HCO3- concentration. • In chronic state renal compensation result in a 4 meq/L reduction in plasma [HCO3-] for every 10 mmHg reduction in PCO2. 25
- 26. 26
- 27. Treatment of Respiratory Alkalosis • Treat underlying cause • Breathe into a paper bag ??? • IV Chloride containing solution (hydrochloric acid, arginine chloride & ammonium chloride), Cl- ions replace lost bicarbonate ions 27
- 28. Metabolic Acidosis • Bicarbonate deficit - blood concentrations of bicarb drop below 22mEq/L • Occurs when pH falls below 7.35 • Causes: – Loss of bicarbonate through diarrhea or renal dysfunction – Accumulation of acids (lactic acid or ketones) – Failure of kidneys to excrete H+ [H+] = 24 ×(PCO2 / [HCO3-]) CO2 + H20 ↔ H2CO3 ↔ H+ + HCO3- 28
- 29. Two types of Metabolic Acidosis – High Anion Gap = net gain of acid – Normal anion gap = loss of bicarbonate Anion Gap Calculation • [Na+ + K+] – [Cl + HCO3] (Normal = 12 + 2) E.g :- Na 140, k 4 , CL 114, HCO3 18 (140 + 4) – (114 + 18) 144 – 132 = 12 normal E.g:- Na 140 , Cl 104, K 4.0, HCO3 10 (144) – (114) = 30 = High anion gap 29
- 30. Normal Anion Gap High Anion Gap Differential (USED CARP) (MUDPILES) • Ureterostomy • Methanol • Small bowel fistula • Uremia • Extra Chloride • DKA • Diarrhea • Paraldehyde • Carbonic anhydrase • Inborn inhibitors Errors • Addison’s disease • Lactic • Renal tubular acidosis Acidosis • Pancreatic fistulas • Ethylene Glycol Treatment: Replace • Salicylates 30
- 31. Symptoms of Metabolic Acidosis • Headache, lethargy • Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea • Coma • Death Compensation for Metabolic Acidosis • Increased ventilation • Renal excretion of hydrogen ions if possible • K+ exchanges with excess H+ in ECF ( H+ into cells, K+ out of cells) CO2 + H20 ↔ H2CO3 ↔ H+ + HCO3- 31
- 32. Compensation • Respiratory compensation results in a 1.2 mmHg reduction in PCO2 for every 1.0 meq/L reduction in the plasma HCO3- concentration down to a minimum PCO2 of 10 to 15mmHg. For example, if an acid load lowers the plasma HCO3- concentration to 9 meq/L, then: Degree of HCO3- reduction is 24 (optimal value) – 9 = 15. Therefore, PCO2 reduction should be 15 × 1.2 = 18. Then PCO2 measured should be 40 (optimal value) – 18 = 22mmHg. 32
- 33. 33
- 34. Treatment of Metabolic Acidosis • Treat the causes • Improve renal perfusion & acid excretion • NaHCO3, Dose = (weight Kg x base deficit x 0.3) • Ensure adequate ventilation 34
- 35. Metabolic Alkalosis • Characterized by – Primary ↑ in HCO3 concentration greater than 26 mEq/ L – Compensatory ↑ in PaCO2 • Classified according to urinary chloride – Chloride responsive – Chloride resistant 35
- 36. Metabolic Alkalosis Chloride Responsive Urine Cl- < 20 mEq/L Causes • Volume Contraction: – Nasogastric suctioning, Gastric fistula – Vomiting , pyloric stenosis • Post Hypercapnia • Low chloride intake • Hypomagnesemia • Penicillin • Cystic fibrosis (sweat) • Alkali therapy (NaHCO3, Antacid abuse) • Chloride depletion (Diarrhoea & Diuretics 36
- 37. Metabolic Alkalosis Chloride Unresponsive (resistant) Urine Cl- > 20 mEq/L • Mineralcorticoid excess e.g Hyperaldosteronism • Exogenous steroids, Cushing’s disease • Alkali Ingestion • Licorice ingestion • Too much wine • Tobacco chewers • Bartter’s Syndrome 37
- 38. Symptoms of Metabolic Alkalosis • Respiration slow and shallow • Hyperactive reflexes ; tetany • Often related to depletion of electrolytes • Dysrhythmias Compensation for Metabolic Alkalosis • Alkalosis most commonly occurs with renal dysfunction, so can’t count on kidneys • Alkali load • Acid loss - vomiting • Respiratory compensation difficult (hypoventilation limited by hypoxia) 38
- 39. Compensation contn. • The development of alkalemia is sensed by central and peripheral chemoreceptors, resulting in a reduction in the rate of ventilation and a reduction in tidal volume and thus an elevation in the pCO2. pCO2 rises 0.7 mmHg for every 1.0 meq/L increment in the plasma [HCO3-]. For example, if an alkali load raises the the plasma HCO3- concentration to 34 meq/L, then: Degree of HCO3- elevation is 34 – 24 (optimal value)= 10. Therefore, PCO2 elevation should be 0.7 × 10 = 7 Then PCO2 measured should be 40 (optimal value) +7 = 47mmHg. 39
- 40. 40
- 41. Treatment of Metabolic Alkalosis • Electrolytes to replace those lost • Treat underlying disorder • IV chloride containing solution e.g saline (Chloride Responsive) • Aldosterone antagonist (Chloride resistant) 41
- 42. Miscellaneous 1 Arterial pH is related to the ratio of PCO2 to HCO3, both pulmonary & renal compensatory mechanism are always such that PCO2 and HCO3 change in the same direction. the exception occurs when there is a mixed acid base disorder. In that situation, multiple acid base processes coexisting may lead to a normal pH or a mixed picture especially when PCO2 & HCO3 moves in opposite direction If the compensatory response is more or less than expected, by definition a mixed acid-base disorder 42 exist.
- 43. An Alternative Approach An Alternative Approach that is rapid but perhaps less precise is to correlate changes in Ph with changes in CO2 or HCO3. • For a respiratory disturbance, every 10mmHg changes in CO2 should change arterial PH by approximately 0.08 U in the opposite direction. • During metabolic disturbance, every 6mEq change in HCO3 also changes arterial PH by 0,1 in the same direction. • If the change in pH exceed or is less than predicted, a mixed acid-base disorder is likely to be present. • If the Arterial pH is relatively normal and the PCO2 and/or HCO3 are abnormal, one can assume that a mixed 43
- 44. Miscellaneous 2 • The Delta Ratio (∆/∆) • Assessment of elevated anion gap metabolic acidosis to determine if a mixed acid base disorder is present. Delta ratio = ∆ Anion gap/∆ [HCO3-] or ↑anion gap/ ↓ [HCO3-] = Measured anion gap – Normal anion gap Normal [HCO3-] – Measured [HCO3-] = (AG – 12) (24 - [HCO3-]) 44
- 45. Miscellaneous cont Delta ratio Assessment Guidelines < 0.4 Hyperchloremic normal anion gap acidosis <1 High AG & normal AG acidosis 1 to 2 Pure Anion Gap Acidosis Lactic acidosis: average value 1.6 DKA more likely to have a ratio closer to 1 due to urine ketone loss High AG acidosis and a concurrent metabolic alkalosis >2 or a pre-existing compensated respiratory acidosis45
- 46. Compensation Primary Disorder Compensatory Mechanism Metabolic acidosis Increased ventilation Metabolic alkalosis Decreased ventilation Respiratory acidosis Increased renal reabsorption of HCO3- in the proximal tubule Increased renal excretion of H in the distal tubule Respiratory alkalosis Decreased renal reabsorption of HCO3- in the proximal tubule Decreased renal excretion of H+ in the 46
- 47. Compensator Compensatory Initial Expected level Primary y chemical disorder change compensation Mechanism response PCO2 = (1.5 × [HCO3-]) + ± 2 Metabolic ↓HCO3- ↓PCO2 Hyperventilation ↓PCO2 = 1.2 ×∆ [HCO3-] Acidosis PCO2 = (0.9 × [HCO3-]) + Metabolic 16 ± 2 ↑HCO3- ↑PCO2 Hypoventilation Alkalosis ↑PCO2 = 0.7 × ∆ [HCO3-] Respiratory ↑PCO2 ↑HCO3- Acidosis Intracellular Buffering ↑[HCO3-] = 1 mEq/L for Acute (hemoglobin, every 10 mm Hg ∆PCO2 intracellular proteins) Generation of new HCO3- due to the ↑[HCO3-] = 3.5 mEq/L for Chronic increased excretion every 10 mm Hg ∆PCO2 of ammonium. Respiratory ↓PCO2 ↓HCO3- Alkalosis Intracellular ↓[HCO3-] = 2 mEq/L for Acute Buffering every 10 mm Hg ∆PCO2 Decreased reabsorption of 47 ↓[HCO3-] =4 mEq/L for
- 48. Acidemia (PH<7.35) PCO2 Normal High Or low Incompatible Normal [HCO3] [HCO3] or high Low Low High Normal Mixed Chronic Acute respiratory respiratory respiratory and metabolic Metabolic acidosis acidosis acidosis acidosis 48
- 49. ↓ Plasma [HCO3] Anion gap Normal Increased High anion gap Plasma [K] metabolic acidosis Low Normal High Respiratory Hyperkalemic Hypokalemic alkalosis hyperchloremic hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis metabolic acidosis 49
- 50. Alkalemia (PH>7.45) PCO2 Low HighNormal Normal [HCO3] Incompatible or [HCO3] Low High High Low Normal Mixed Acute Chronic Metabolic respiratory and respiratory respiratory alkalosis metabolic alkalosis alkalosis alkalosis 50
- 51. ↑ Plasma [HCO3] Metabolic alkalosis Respiratory acidosis Spot urine [Cl] >20mmolL <20mmolL Saline Saline responsive unresponsive metabolic alkalosis metabolic alkalosis 51
- 52. Example • A patient is in intensive care because he suffered a severe myocardial infarction 3 days ago. The lab reports the following values from an arterial blood sample: – pH 7.3 – HCO3- = 20 mEq / L ( 22 - 26) – pCO2 = 32 mm Hg (35 - 45) Diagnosis • Metabolic acidosis • With partial compensation 52
- 53. CASE 1 • A 44 year old moderately dehydrated man was admitted with a two day history of acute severe diarrhea. Electrolyte results: Na+ 134, K+ 2.9, Cl- 108, HCO3- 16, • Urea 31, Cr 1.5. • ABG: pH 7.31 pCO2 33 mmHg HCO3 16 pO2 93 mmHg 53
- 54. CASE 2 • A 22 year old female with type I DM, presents to the emergency department with a 1 day history of nausea, vomiting, polyuria, polydypsia and vague abdominal pain. P.E. noted for deep sighing breathing, orthostatic hypotension, and dry mucous membranes. • Labs: Na 132 , K 6.0, Cl 93, HCO3- 11 glucose 720, Urea 38, Cr 2.6. UA: pH 5, SG 1.010, ketones negative, glucose positive . Plasma ketones trace. ABG: pH 7.27 HCO3- 10 PCO2 23 • What is the acid base disorder? 54
- 55. CASE 3 • A 70 year old man with history of CHF presents with increased shortness of breath and leg swelling. ABG: pH 7.24, PCO2 60 mmHg, PO2 52 HCO3- 27 • What is the acid base disorder? 55
Hinweis der Redaktion
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
- 1/13/2012
