section 4, chapter 9: energy for muscles
•Als PPTX, PDF herunterladen•
4 gefällt mir•3,253 views
Energy sources of muscle contractions
Melden
Teilen
Melden
Teilen
Empfohlen
Empfohlen
Weitere ähnliche Inhalte
Was ist angesagt?
Was ist angesagt? (20)
Biochemistry ii protein (metabolism of amino acids) (new edition)

Biochemistry ii protein (metabolism of amino acids) (new edition)
Andere mochten auch
Andere mochten auch (20)
ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES IN BIOCHEMISTRY AND BIOPHYSICS FOR MACRO MOLECULES 

ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES IN BIOCHEMISTRY AND BIOPHYSICS FOR MACRO MOLECULES
Vasopressin receptor antagonist and therapeutic potential

Vasopressin receptor antagonist and therapeutic potential
Ähnlich wie section 4, chapter 9: energy for muscles
Ähnlich wie section 4, chapter 9: energy for muscles (20)
L3-RS_Aerobic & Anaerobic Metabolism in Muscles_MSK_Block_Dec2013.ppt

L3-RS_Aerobic & Anaerobic Metabolism in Muscles_MSK_Block_Dec2013.ppt
Microsoft power point explain energy source and muscle metabolism

Microsoft power point explain energy source and muscle metabolism
Energy systems in human body by arianaacardiorespiratory

Energy systems in human body by arianaacardiorespiratory
Mehr von Michael Walls
Mehr von Michael Walls (20)
Kürzlich hochgeladen
Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? webinar
Thursday 2 May 2024
A joint webinar created by the APM Enabling Change and APM People Interest Networks, this is the third of our three part series on Making Communications Land.
presented by
Ian Cribbes, Director, IMC&T Ltd
@cribbesheet
The link to the write up page and resources of this webinar:
https://www.apm.org.uk/news/making-communications-land-are-they-received-and-understood-as-intended-webinar/
Content description:
How do we ensure that what we have communicated was received and understood as we intended and how do we course correct if it has not.Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...

Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...Association for Project Management
Kürzlich hochgeladen (20)
Basic Civil Engineering first year Notes- Chapter 4 Building.pptx

Basic Civil Engineering first year Notes- Chapter 4 Building.pptx
UGC NET Paper 1 Mathematical Reasoning & Aptitude.pdf

UGC NET Paper 1 Mathematical Reasoning & Aptitude.pdf
Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...

Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...
Micro-Scholarship, What it is, How can it help me.pdf

Micro-Scholarship, What it is, How can it help me.pdf
ICT role in 21st century education and it's challenges.

ICT role in 21st century education and it's challenges.
Mixin Classes in Odoo 17 How to Extend Models Using Mixin Classes

Mixin Classes in Odoo 17 How to Extend Models Using Mixin Classes
Asian American Pacific Islander Month DDSD 2024.pptx

Asian American Pacific Islander Month DDSD 2024.pptx
section 4, chapter 9: energy for muscles
- 1. Chapter 9, Section 4 Energy Sources for Contraction
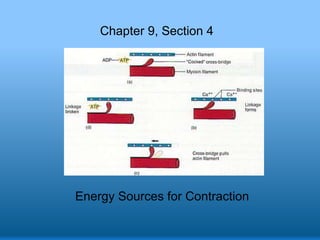
- 2. Energy Sources for Contraction ATP provides the energy to power the interaction between actin & myosin filaments. • However, ATP is quickly spent and must be replenished New ATP molecules are synthesized by 1. Hydrolysis of Creatine Phosphate 2. Glycolysis (anaerobic respiration) 3. Aerobic Respiration
- 3. Creatine Phosphate Creatine Phosphate can be hydrolyzed into Creatine, releasing energy that is used to make new ATP. The energy from creatine phosphate hydrolysis cannot be used to directly power muscles. Instead, it’s used to produce new ATP.
- 4. Creatine Phosphate…continued When cellular ATP is abundant, creatine phosphate can be replenished by phosphorylating creatine. Creatine Phosphate provides energy for only about 10 seconds of a high intensity muscle contraction.
- 5. Glycolysis Anaerobic respiration (glycolysis) occurs in the cytosol of the cell and does not require oxygen. Glucose molecules are partially broken down producing just 2 ATP for each glucose. If there isn’t sufficient oxygen available, glycolysis produces lactic acid as a byproduct.
- 6. Oxygen debt of glycolysis Exercise and strenuous activity depends on anaerobic respiration for ATP supplies. During exercise anaerobic respiration causes lactic acid to accumulate in the cells. After exercise, when oxygen is available the O2 is used to convert lactic acid back to glucose in the liver. Oxygen debt is the amount of oxygen needed by liver cells to convert accumulated lactic acid back to glucose.
- 7. Oxygen debt
- 8. Aerobic Respiration Aerobic respiration (uses oxygen) occurs in the mitochondria and it includes the citric acid cycle & electron transport chain. Aerobic respiration is a slower reaction than glycolysis, but it produces the most ATP. Myoglobin Oxygen binding protein (similar to hemoglobin) within muscles -Provides additional oxygen supply to muscles
- 9. Aerobic Respiration Aerobic respiration is used primarily at rest or during light exercise. Muscles that rely on aerobic respiration have plenty of mitochondria and a good blood supply.
- 10. Energy Sources for Contraction Figure 9.13. The oxygen required for aerobic respiration is carried in the blood and stored in myoglobin. In the absence of oxygen, anaerobic respiration uses pyruvic acid to produce lactic acid.
- 11. Muscle Fatigue • Muscle Fatigue = Inability for the muscle to contract • Several factors can cause muscle fatigue: • Decreased blood flow • Ion imbalances across the sarcolemma • Lactic acid accumulation – (greatest cause of fatigue) • Cramp: • A cramp is a sustained, involuntary, and painful muscle contraction • It’s due to electrolyte imbalance surrounding muscle
- 12. Heat Production • Heat is produced as a by-product of cellular respiration • Muscle cells are major source of body heat • Blood transports heat throughout body core End of Chapter 9, Section