Ethernet - Networking presentation
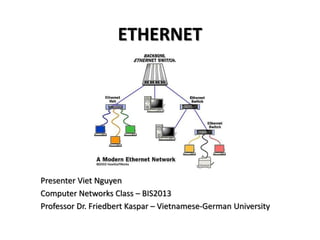
- 1. ETHERNET Presenter Viet Nguyen Computer Networks Class – BIS2013 Professor Dr. Friedbert Kaspar – Vietnamese-German University
- 2. Ethernet – IEEE 802.3 • Introduction – An overview of Ethernet – Network topologies and Switched LAN • Ethernet technology – Ethernet technologies and cable types – Ethernet frame • Ethernet devices – Link-layer switch – Switches vs. Routers • Ethernet applications – Firewall – IP Spoofing • Summary – Ethernet and its future – References Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 2
- 3. INTRODUCTION Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 3
- 4. Overview • Move Beyond Your LAN with Ethernet Services • Ethernet is a family of computer networking technologies for local area networks (LANs). Ethernet was commercially introduced in 1980 and standardized in 1983 as IEEE 802.3.[1] Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies such as token ring, FDDI, and ARCNET. Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 4
- 5. Overview (2) • "Switching and 100Mbps speeds make 16Mbps technology obsolete" – the time when Token Ring technology was replaced by Ethernet. (http://www.techrepublic.com/blog/classics-rock/does-anyone-actually- still-use-token-ring/) Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 5 1000BASE-T http://www.sld.co.uk/products/comms/IPPBX_schematic.jpg 10BASE5
- 6. Network Topologies Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 6 http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/9/96/NetworkTopologies.png
- 7. Network Topologies (2) Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 7 Star bus - Probably the most common network topology in use today, star bus combines elements of the star and bus topologies to create a versatile network environment. Nodes in particular areas are connected to hubs (creating stars), and the hubs are connected together along the network backbone (like a bus network). Quite often, stars are nested within stars http://computer.howstuffworks.com/lan-switch2.htm
- 8. Switched Local Area Networks Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 8
- 9. TECHNOLOGY Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 9
- 10. Ethernet Technologies Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 10 Designation Supported Media Maximum Segment Length Transfer Speed Topology 100Base-TX Category5 UTP 100m 100Mbps Star,using either simple repeater hubs or Ethernet switches 100Base-FX Fiber-optic- two strands of multimode 62.5/125 fiber 412m(Half-Duplex) 2000m(full-duplex) 100 Mbps (200 Mb/s full-duplex mode) Star(often only point-to- point) 1000Base-SX Fiber-optic- two strands of multimode 62.5/125 fiber 260m 1Gbps Star, using buffered distributor hub (or point-to- point) 1000Base-LX Fiber-optic- two strands of multimode 62.5/125 fiber or monomode fiber 440m(multimode) 5000m(single- mode) 1Gbps Star,using buffered distributor hub (or point-to-point) 1000Base-CX Twinax,150-Ohm- balanced, shielded, specialty cable 25m 1Gbps Star(or point-to-point) 1000Base-T Category5 100m 1Gbps Star
- 11. Ethernet Cable Types Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 11 http://www.directron. com/cableguide.html http://academy.delmar. edu/Courses/ITNW2313 /1Essentials.html
- 12. Ethernet Frame • A data packet on an Ethernet link is called an Ethernet packet, which transports an Ethernet frame as payload. Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 12 802.3 Ethernet packet and frame structure Layer Preamble Start of frame delimiter MAC destination MAC source 802.1Q tag (optional) Ethertype (E thernet II) or length (IEEE 802.3) Payload Frame check sequence(3 2-bit CRC) Interpacket gap 7 octets 1 octet 6 octets 6 octets (4 octets) 2 octets 46(42)[b]– 1500 octets 4 octets 12 octets Layer 2 Ethernet frame ← 64–1518(1522) octets → Layer 1 Ethernet packet ← 72–1526(1530) octets → The internal structure of an Ethernet frame is specified in IEEE 802.3-2012 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ethernet_frame
- 13. Ethernet Frame (2) • Ethernet II framing (The most common Ethernet Frame format, type II) defines the two-octet EtherType field in an Ethernet frame that identifies an upper layer protocol encapsulating the frame data. An EtherType value of 0x0800 signals that the frame contains an IPv4 datagram. An EtherType of 0x0806 indicates an ARP frame, 0x8100 indicates an IEEE 802.1Q frame and 0x86DD indicates an IPv6 frame. Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 13 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ethernet_frame
- 14. IPDatagram Encapsulation Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 14 http://www.tcpipguide.com/free/t_IPDatagramEncapsulation.htm
- 15. Sublayers of the data link layer • Logical link control sublayer: – Multiplexing protocols transmitted over the MAC layer (when transmitting) and decoding them (when receiving). – Providing node-to-node flow and error control • Media access control (MAC) sublayer – provides addressing and channel access control mechanisms – The hardware that implements the MAC is referred to as a medium access controller. – The MAC layer emulates a full-duplex logical communication channel in a multi-point network. This channel may provide unicast, multicast or broadcast communication service. Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 15 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_link_layer
- 16. Logical Link Control Services • Ethernet • Since bit errors are very rare in wired networks, Ethernet does not provide flow control or automatic repeat request (ARQ), incorrect packets are detected but only cancelled, not retransmitted, retransmissions rely on higher layer protocols. • As the EtherType in an Ethernet frame using Ethernet II framing is used to multiplex different protocols on top of the Ethernet MAC header it can be seen as an LLC identifier. However, Ethernet frames lacking an EtherType have no LLC identifier in the Ethernet header, and, instead, use an IEEE 802.2 LLC header after the Ethernet header to provide the protocol multiplexing function. • Wireless LAN: In wireless communications, bit errors are very common. In wireless networks such as IEEE 802.11, flow control and error management is part of the CSMA/CA MAC protocol, and not part of the LLC layer. The LLC sub layer follows the IEEE 802.2 standard. • HDLC (High-Level Data Link Control): Some non-IEEE 802 protocols can be thought of as being split into MAC and LLC layers. For example, while HDLC specifies both MAC functions (framing of packets) and LLC functions (protocol multiplexing, flow control, detection, and error control through a retransmission of dropped packets when indicated), some protocols such as Cisco HDLC can use HDLC-like packet framing and their own LLC protocol. Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 16 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Logical_Link_Control
- 17. Media access control Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 17 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Media_access_control According to IEEE Std 802-2001 section 6.2.3 "MAC sublayer", the primary functions performed by the MAC layer are: •Frame delimiting and recognition •Addressing of destination stations (both as individual stations and as groups of stations) •Conveyance of source-station addressing information •Transparent data transfer of LLC PDUs, or of equivalent information in the Ethernet sublayer •Protection against errors, generally by means of generating and checking frame check sequences •Control of access to the physical transmission medium In the case of Ethernet, according to 802.3-2002 section 4.1.4, the functions required of a MAC are: •receive/transmit normal frames •half-duplex retransmission and backoff functions •append/check FCS (frame check sequence) •interframe gap enforcement •discard malformed frames •append(tx)/remove(rx) preamble, SFD (start frame delimiter), and padding •half-duplex compatibility: append(tx)/remove(rx) MAC address
- 18. DEVICES Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 18
- 19. Link-Layer Switches • A switch receives incoming link-layer frames, filters and forwards them onto outgoing links. Switch filtering and forwarding are done with a switch table. • A switch has self-learning property (particularly for the already-overworked network administrator) that its table is built automatically, dynamically, and autonomously. • Switches are plug-and-play devices and require no intervention from a network administrator or user. Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 19
- 20. Switches vs. Routers Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 20 A router in that it forwards packets using MAC addresses (layer- 2) whereas a router is a layer-3 packet switch.
- 21. Switches vs. Routers (2) Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 21 Switches Routers switches are plug-and-play not plug-and-play. their IP addresses need to be configured Switches can also have relatively high filtering and forwarding rates since switches have to process frames only up through layer 2, whereas routers have to process datagrams up through layer 3 larger per-packet processing time than switches, because they have to process up through the layer-3 fields routers do not have the spanning tree restriction, they have allowed the Internet to be built with a rich topology to prevent the cycling of broadcast frames, the active topology of a switched network is restricted to a spanning tree. packets are not restricted to a spanning tree and can use the best path between source and destination No firewall integrated provide firewall protection against layer-2 broadcast storms
- 22. Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 22 Hub vs. Switch vs. Router http://thamarai-stor.blogspot.com/2010/05/ikkks-switch-vs-router-vs-hub.html
- 23. Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 23 http://www.cisco1900router.com/t utorial-of-differences-between-hub- bridge-switch-and-router.html a bridge is a product that connects a local area network (LAN) to another local area network that uses the same protocol. Having a single incoming and outgoing port and filters traffic on the LAN by looking at the MAC address, bridge is more complex than hub. Bridge looks at the destination of the packet before forwarding unlike a hub. It restricts transmission on other LAN segment if destination is not found. A bridge works at the data-link (physical network) level of a network, copying a data frame from one network to the next network along the communications path.
- 24. APPLICATIONS Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 24
- 25. Firewalls Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 25 http://www.vicomsoft.com/learning-center/firewalls/ Social engineering involves skills not unlike those of a confidence trickster. People are tricked into revealing sensitive information. A firewall filters both inbound and outbound traffic. "There are management solutions to technical problems, but no technical solutions to management problems"
- 26. Figure 9: Stateful Multilayer Inspection FirewallFigure 8: Application level Gateway Figure 6: Packet Filtering Firewall Figure 7: Circuit level Gateway Firewalls (2) Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 26
- 27. IP Spoofing Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 27 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:IP_spoofing_en.svg Any router that implements ingress filtering checks the source IP field of IP packets it receives, and drops packets if the packets don't have an IP address in the IP address block that the interface is connected to
- 28. SUMMARY Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 28
- 29. The Ethernet Summary • The Introduction covered the market use of Ethernet and its related to the Network Layer. • The Technology and Devices sections dive deeper to the software and supported hardware for the Ethernet: Ethernet Frame, cable types, routers and switches. • The Application gave an example of a real world use from Ethernet knowledge. Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 29
- 30. Ethernet and its future Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 30 Report from The Future of Ethernet – Technology Exploration Forum on October 15, 2013 - October 16, 2013 at Santa Clara, CA – Interconnectedness and the Future of Ethernet http://www.enterprisenetworkingplanet.com/netsp/interconnectedness-and-the-future-of-ethernet-1.html http://www.enterprisenetworkingplanet.com/netsp/interconnectedness-and-the-future-of-ethernet-2.html
- 31. Ethernet and its future (2) • Vehicular Ethernet, the Internet of Things, and the Industry as an Ecosystem – From enhanced traffic management and traffic alerts drawn from live video feeds broadcast from individual vehicles to the ability to tax cars based on their miles driven, the possible applications are endless. • Standardizing software defined networking for interoperability – "In the past, people have talked about SDN more on an individual basis. But the Ethernet Alliance is supporting 802 in the standardization effort, which means we really want to be able to take Vendor A, plug it into Vendor B, plug that into Vendor C, and have it all work," • Energy Efficient Ethernet – As networks grow and evolve, their power consumption may rise, creating additional cost issues. The Energy Efficient Ethernet (EEE) standard for twisted pair and backplane Ethernet aims to counter that by reducing power consumption as activity drops. • Interconnectedness and the importance of consensus-building – Addressing both the main themes D'Ambrosia mentioned—interoperability and cost concerns—will require a general consensus and interconnectedness among diverse segments of the networking community. Other TEF 2013 panels bear this out, from the panel session that pulled leaders from 802.1, 802.3, and 802.11 up onto a stage with the chair of 802, to sessions that focused on the synergy between wired and wireless technologies and on photonic integration. Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 31
- 32. References • Computer Networking A Top-Down Approach – Kurose and Ross – A product of PEASON. • http://www.omnisecu.com/basic- networking/index.php • http://www.ccse.kfupm.edu.sa/~marwan/COE 344_T062/ • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ethernet • The INTERNET Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 32
- 33. THANK YOU! The end Ethernet – Viet Nguyen Prof. Dr. F. Kaspar – Computer Networking – BIS2013 – Vietnamese-German University Slide 33
Editor's Notes
- http://www.business.att.com/content/mixedmedia/EthernetServices-ATT.mp4 (from http://www.business.att.com/enterprise/Family/network-services/ethernet/ )
- The Ethernet standards comprise several wiring and signaling variants of the OSI physical layer in use with Ethernet. The original 10BASE5 Ethernet used coaxial cable as a shared medium. Later the coaxial cables were replaced with twisted pair and fiber optic links in conjunction with hubs or switches. Data rates were periodically increased from the original 10 megabits per second to 100 gigabits per second.
- Preamble and start frame delimiter An Ethernet frame starts following a 7-octet preamble and 1-octet start frame delimiter (SFD), both of which are part of the Ethernet packet enveloping the frame.[c] Prior to Fast Ethernet, the on-the-wire bit pattern for this portion of the frame is 10101010 10101010 10101010 10101010 10101010 10101010 10101010 10101011.[4]:sections 4.2.5 and 3.2.2 Since octets are transmitted least-significant bit first, the corresponding hexadecimal representation is 0x55 0x55 0x55 0x55 0x55 0x55 0x55 0xD5.
- Filtering is the switch function that determines whether a frame should be forwarded to some interface or should just be dropped. Forwarding is the switch function that determines the interfaces to which a frame should be directed, and then moves the frame to those interfaces. Self-learning 1. The switch table is initially empty. 2. For each incoming frame received on an interface, the switch stores in its table (1) the MAC address in the frame’s source address field, (2) the interface from which the frame arrived, and (3) the current time. 3. The switch deletes an address in the table if no frames are received with that address as the source address after some period of time (the aging time). In this manner, if a PC is replaced by another PC (with a different adapter), the MAC address of the original PC will eventually be purged from the switch table. Properties Elimination of collisions: In a LAN built from switches (and without hubs), there is no wasted bandwidth due to collisions! The switches buffer frames and never transmit more than one frame on a segment at any one time. As with a router, the maximum aggregate throughput of a switch is the sum of all the switch interface rates. Thus, switches provide a significant performance improvement over LANs with broadcast links. Heterogeneous links: Because a switch isolates one link from another, the different links in the LAN can operate at different speeds and can run over different media. For example, the uppermost switch in Figure 5.22 might have three 1 Gbps 1000BASE-T copper links, two 100 Mbps 100BASE-FX fiber links, and one 100BASE-T copper link. Thus, a switch is ideal for mixing legacy equipment with new equipment. Management: 1. if an adapter malfunctions and continually sends Ethernet frames (called a jabbering adapter), a switch can detect the problem and internally disconnect the malfunctioning adapter 2. A cable cut disconnects only that host that was using the cut cable to connect to the switch 3. switches also gather statistics on bandwidth usage, collision rates, and traffic types, and make this information available to the network manager
- • Hub – repeats signal on bit level • Switch – link-layer device • store, forward Ethernet frames • examine incoming frame’s MAC address, selectively forward frame to one-or-more outgoing links when frame is to be forwarded on segment • uses CSMA/CD to access segment – transparent • hosts are unaware of presence of switches – plug-and-play, self-learning • switches do not need to be configured
- 2. What does a firewall do? A firewall examines all traffic routed between the two networks to see if it meets certain criteria. If it does, it is routed between the networks, otherwise it is stopped. A firewall filters both inbound and outbound traffic. It can also manage public access to private networked resources such as host applications. It can be used to log all attempts to enter the private network and trigger alarms when hostile or unauthorized entry is attempted. Firewalls can filter packets based on their source and destination addresses and port numbers. This is known as address filtering. Firewalls can also filter specific types of network traffic. This is also known as protocol filtering because the decision to forward or reject traffic is dependent upon the protocol used, for example HTTP, ftp or telnet. Firewalls can also filter traffic by packet attribute or state.
- Stateful multilayer inspection firewalls combine the aspects of the other three types of firewalls. They filter packets at the network layer, determine whether session packets are legitimate and evaluate contents of packets at the application layer. They allow direct connection between client and host, alleviating the problem caused by the lack of transparency of application level gateways. They rely on algorithms to recognize and process application layer data instead of running application specific proxies. Stateful multilayer inspection firewalls offer a high level of security, good performance and transparency to end users. They are expensive however, and due to their complexity are potentially less secure than simpler types of firewalls if not administered by highly competent personnel. (See Figure 8).
- In computer networking, IP address spoofing or IP spoofing is the creation of Internet Protocol (IP) packets with a source IP address, with the purpose of concealing the identity of the sender or impersonating another computing system.[1] Defense against spoofing attacks Packet filtering is one defense against IP spoofing attacks. The gateway to a network usually performs ingress filtering, which is blocking of packets from outside the network with a source address inside the network. This prevents an outside attacker spoofing the address of an internal machine. Ideally the gateway would also perform egress filtering on outgoing packets, which is blocking of packets from inside the network with a source address that is not inside. This prevents an attacker within the network performing filtering from launching IP spoofing attacks against external machines. It is also recommended to design network protocols and services so that they do not rely on the IP source address for authentication. ingress filtering & egress filtering Any router that implements ingress filtering checks the source IP field of IP packets it receives, and drops packets if the packets don't have an IP address in the IP address block that the interface is connected to. This may not possible if the end host is multi-homed and also sends transit network traffic. In computer networking, egress filtering is the practice of monitoring and potentially restricting the flow of information outbound from one network to another. Typically it is information from a private TCP/IPcomputer network to the Internet that is controlled.
- Ethernet: Frame structure, service model (unreliable, connectionless), media access control protocol, i.e. CSMA/CD (carrier sense multiple access with collision detection). Varieties like media types and bandwidths. Wireshark demo.
