Raw 2009 -THE ROLE OF LATEST FIXATIONS ON ONGOING VISUAL SEARCH A MODEL TO EVALUATE THE SELECTION MECHANISM
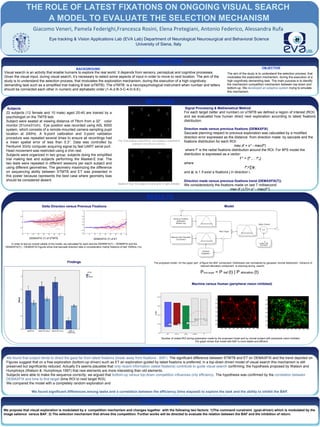
- 1. DISCUSSION CONCLUSION INTRODUCTION BACKGROUND OBJECTIVE METHODS Signal Processing & Mathematical Method For each target (letter and number) on sTMTB we defined a region of interest (ROI) and we evaluated how human direct next exploration according to latest fixations distribution. Direction made versus previous fixations (DEMAXFIX) Saccade planning respect to previous exploration was calculated by a modified direction error expressed as the distance from direction made by saccade and the fixations distribution for each ROI: max df = o* - max(f*) where f* is the radial fixations distribution around the ROI. For 8PS model the distribution is expressed as a vector: F* = {f*1… f*8} where f*i=∑ϕj i and ϕj i is 1 if exist a fixations j in direction i. Direction made versus previous fixations trend (DEMAXFIX(T)) We consideredonly the fixations made on last T millisecond: max df (∆T)= o* - max(F*) Subjects 22 subjects (12 female and 10 male) aged 25-40 are trained by a psychologist on the TMTB test. Subject were seated at viewing distance of 78cm from a 32” color monitor (51cmx31cm). Eye position was recorded using ASL 6000 system, which consists of a remote-mounted camera sampling pupil location at 240Hz. A 9-point calibration and 3-point validation procedure was repeated several times to ensure all recordings had a mean spatial error of less than 0.3°. Data was controlled by Pentium4 3GHz computer acquiring signal by fast UART serial port. Head movement was restricted using a chin rest. Subjects were organized in two group: subjects doing the simplified trial making test and subjects performing the Masket-E trial. The two tests were repeated in different sessions per each subject and using different geometries. The geometry maximizing the difference on sequencing ability between STMTB and ET was presented in this poster because represents the best case where geometry bias should be considered absent. RESULTS Eye tracking & Vision Applications Lab (EVA Lab) Department of Neurological Neurosurgical and Behavioral Science University of Siena, Italy THE ROLE OF LATEST FIXATIONS ON ONGOING VISUAL SEARCH A MODEL TO EVALUATE THE SELECTION MECHANISM Giacomo Veneri, Pamela Federighi,Francesca Rosini, Elena Pretegiani, Antonio Federico, Alessandra Rufa Visual search is an activity that enable humans to explore the real world. It depends from sensory, perceptual and cognitive processes. Given the visual input, during visual search, it’s necessary to select some aspects of input in order to move to next location. The aim of the study is to understand the selection process, that modulates the exploration mechanism, during the execution of a high cognitively demanding task such as a simplified trial making B test (sTMTB). The sTMTB is a neuropsychological instrument when number and letters should be connected each other in numeric and alphabetic order (1-A-2-B-3-C-4-D-5-E). The aim of the study is to understand the selection process, that modulates the exploration mechanism, during the execution of a high cognitively demanding task. The main purpose is to identify the mechanism competition mechanism between top-down and bottom-up. We developed an adaptive system trying to emulate this mechanism. Delta Direction versus Previous Fixations Model Machine versus Human (peripheral vision inhibited) Findings We found that subject tends to direct the gaze far from latest fixations (break away from fixations - BAF). The significant difference between STMTB and ET on DEMAXFIX and the trend depicted on Figures suggest that on a free exploration (bottom-up driven) such as ET an exploration guided by latest fixations is preferred; in a top-down driven model of visual search this mechanism is still preserved but significantly reduced. Actually it’s seems plausible that only recent information (latest fixations) contribute to guide visual search confirming, the hypothesis proposed by Watson and Humphreys (Watson & Humphreys 1997) that new elements are more interesting than old elements. Subjects were able to make the sequence correctly; we argued that bottom-up versus top-down competition influences only efficiency. The hypothesis was confirmed by the correlation between DEMAXFIX and time to find target (time ROI to next target ROI). We compared the model with a completely random exploration and We found significant differences among tasks and a correlation between the efficiency (time elapsed) to explore the task and the ability to inhibit the BAF. We propose that visual exploration is modulated by a competition mechanism and changes together with the following two factors: 1)The command constraint (goal-driven) which is modulated by the image salience versus BAF. 2) The selection mechanism that drives this competition. Further works will be directed to evaluate the relation between the BAF and the inhibition of return. Pnext target = P baf (t) | P allocation (t) The Trial making Task Part B : the subject is required to connect 1-A-2-B-3-C-4-D-5-E. Masket E trial: the subject is looking for E right oriented. The proposed model. On the upper part of figure the BAF component. Distribution are normalized by gaussian normal distribution. Variance of relevant allocation component is reducing during search. DEMAXFIX (T) of STMTB DEMAXFIX (T) of ET In order to test an overall validity of the model, we calculated for each test the DEMINFIX(T) – DEMINFIX and the DEMAXFIX(T) – DEMAXFIX.Figures show that saccade direction take in consideration mainly fixations of last 1000ms (1s). 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 Number of visited ROI during exploration made by the proposed model and by normal subject with peripheral vision inhibited. The graph shows that model with BAF is more stable and efficient.
