Male Reproductive System
- 1. Anatomy ASSIGNMENT MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM NAME: TOOBA REHMAN CLASS: FIRST PROF. YEAR ROLL NO. : 100 Group: 16 (B) COURSE NAME: ANATOMY COURSE CODE: 317 COURSE INCHARGE: dr. safoora tariq
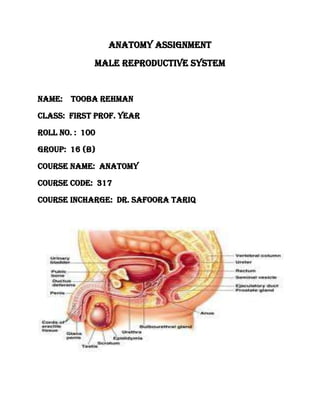
- 2. INTRODUCTION REPRODUCTION The process in which one or two parent organisms form a new individual is called reproduction and the organs involve in reproduction are collectively called reproductive system. MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Genital organs of a male body include in reproductive system are collectively called male reproductive system. Male reproductive system consist of f0llowing organs named below. 1) Testes 2) Scrotum 3) Seminal vesical 4) Prostate gland 5) Cowper’s gland 6) Epididymis 7) Vas deferens 8) Spermatic cord 9) Urinogenital duct 10) Penis
- 3. EXPLANATION TESTES (singular=Testis) Testes are r0ugh egg like in shape and about 3 cm long contain a mass of semineferous tubules that manufacture the male sperm cell called Spermatozoa. The testes (TES-te¯z), or testicles, are paired oval glands in the scrotum measuring about 5 cm long and 2.5 cm in diameter . Each testis (singular) has a mass of 10–15 grams. The testes develop near the kidneys, in the posterior portion of the abdomen, and they usually begin their descent into the scrotum through the inguinal canals (passage-ways in the anterior abdominal wall;) during the latter half of the seventh month of fetal development.A serous membrane called the tunica vaginalis (tunica sheath), which is derived from the peritoneum and forms during the descent of the testes, partially covers the testes. A collection of serous fluid in the tunica vaginalis is called a hydrocele. SCROTUM The scrotum(SKRO-tum = bag), the supporting structure for the testes, consists of loose skin and underlying subcutaneous layer that hangs from the root (attached portion) of the penis .Externally, the scrotum looks like a single pouch of skin separated into lateral portions by a median ridge called the raphe (RA—fe= seam). Internally, the scrotal septumdivides the scro-tum into two sacs, each containing a single testis .The septum is made up of a subcutaneous layer and muscle tissue called the dartos muscle (DAR-tos =skinned), which is composed of bundles of smooth muscle fibers. The dartos muscle is also found in the subcutaneous layer of the scrotum. Associated with each testis in the scrotum is the cremaster muscle(kre-MAS-ter = suspender), a series of small bands of skeletal muscle that descend as an extension of the internal oblique muscle through the spermatic cord to surround the testes.
- 4. SEMINAL VESICAL The paired seminal vesicles(VES-i-kuls) or seminal glandsare convoluted pouchlike structures, about 5 cm in length, lying posterior to the base of the urinary bladder and anterior to the rectum. Seminal vesical produces much of the seminal fluid and lies lateral to the ductus on the posterior wall of the bladder with its upper end just below the p0int of enterance of ureter into the bladder. The very short duct leaves the l0wer end to join the ductus deference at the edge of the prostate gland and form the ejaculat0ry duct. PROSTATE GLAND The prostate (PROS-ta t) is a single, doughnut-shaped gland about the size of a golf ball. It measures about 4 cm from side to side, about 3 cm from top to bottom, and about 2 cm from front to back. It is inferior to the urinary bladder and surrounds the prostatic urethra . The prostate slowly increases in size from birth to puberty. It then expands rapidly until about age 30, after which time its size typically remains stable until about age 45, when further enlargement may occur. Prostate consist of glands embedded in a mass of connective tissues and smooth muscle. It secrets about 30% of seminal fluid. COWPER’s GLAND The paired bulbourethral glands (bul-bo -u -RE--thral), or Cowper’s glands are about the size of peas. They are located inferior to the prostate on either side of the membranous urethra within the deep muscles of the perineum, and their ducts open into the spongy urethra .
- 5. EPIDIDYMIS The epididymis(ep-i-DID-i-mis; epi- above or over; -didymis=testis) is a comma-shaped organ about 4 cm long that lies along the posterior border of each testis.The plural is epididymides (ep-i-did-IM-i-des). Each epi-didymis consists mostly of the tightly coiled ductus epididymis. The efferent ducts from the testis join the ductus epididymis at the larger, superior portion of the epididymis called the head. The bodyis the narrow midportion of the epididymis, and the tail is the smaller, inferior portion. At its distal end, the tail of the epididymis continues as the ductus (vas) deferens .The ductus epididymis would measure about 6 m in length if it were uncoiled. It is lined with pseudostratified columnar epithelium and encircled by layers of smooth muscle. The free surfaces of the columnar cells contain stereocilia, which despite their name are long, branching microvilli (not cilia) that increase the surface area for the reabsorption of degenerated sperm. Connective tissue around the muscle layer attaches the loops of the ductus epididymis and carries blood vessels and nerves. VAS (DUCTUS) DEFERENS Within the tail of the epididymis, the ductus epididymis becomes less convoluted, and its diameter increases. Beyond this point, the duct is known as the ductus deferens 0R vas deferens.The ductus deferens, which is about 45 cm long, ascends along the posterior border of the epididymis through the spermatic cord and then enters the pelvic cavity. There it loops over the ureter and passes over the side and down the posterior surface of the urinary bladder. The dilated terminal portion of the ductus deferens is the ampulla (am-PUL-la = little jar). The mucosa of the ductus deferens consists of pseudostratified columnar epithelium and lamina propria (areolar connective tissue). The muscularis is composed of three layers of smooth muscle; the inner and outer layers are longitudinal, and the middle layer is circular.
- 6. SPERMATIC CORD The collective name f0r the ductus deferens, the testicular and 0ther vessels and nerves and various connective tissue c0verings derived from the abd0minal musculature that f0rm the inguinal canal. The spermatic cordis a supporting structure of the male repro-ductive system that ascends out of the scrotum. It consists of the ductus (vas) deferens as it ascends through the scrotum, the testicular artery, veins that drain the testes and carry testosterone into circulation (the pampiniform plexus), autonomic nerves, lymphatic vessels, and the cremaster muscle. The spermatic cord and ilioinguinal nerve pass through the inguinal canal (IN-gwin-al =groin), an oblique passageway in the anterior abdominal wall just superior and parallel to the medial half of the inguinal ligament. The canal, which is about 4–5 cm long, originates at the deep (abdominal) inguinal ring,a slit like opening in the aponeurosis of the transversus ab-dominis muscle; the canal ends at the superficial (subcutaneous) inguinal ring, a somewhat triangular opening in the aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle. In females, the round ligament of the uterus and ilioinguinal nerve pass through the inguinal canal.
- 7. URINOGENITAL DUCT In males, the urethrais the shared terminal duct of the reproductive and urinary systems; so it is also kn0wn as urinogenital duct. It serves as a passageway for both semen and urine. About 20 cm long, it passes through the prostate, the deep muscles of the perineum, and the penis, and is subdivided into three parts . The prostatic urethrais 2–3 cm long and passes through the prostate. As this duct continues inferiorly, it passes through the deep muscles of the perineum, where it is known as the membranous urethra.The membranous urethra is about 1 cm in length. As this duct passes through the corpus spongiosum of the penis, it is known as the spongy (penile) urethra,which is about 15–20 cm long. The spongy urethra ends at the external urethral orifice. PENIS The peniscontains the urethra and is a passageway for the ejaculation of semen and the excretion of urine . It is cylindrical in shape and consists of a body, glans penis, and a root. The body of the penisis composed of three cylindrical masses of tissue, each surrounded by fibrous tissue called the tunica albuginea . The two dorsolateral masses are called the corpora cavernosa penis(corpora=main bod-ies; cavernosa =hollow). The smaller midventral mass, the corpus spongiosum penis, contains the spongy urethra and keeps it open during ejaculation. Skin and a subcutaneous layer enclose all three masses, which consist of erectile tissue. Erectile tissue is composed of numerous blood sinuses (vascular spaces) lined by endothelial cells and surrounded by smooth muscle and elastic connective tissue.
- 8. BLOOD SUPPLY TO THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE ORGANS :FOR TESTES AND EPIDIDYMIS: Internal to the tunica albuginea is the tunica vasculosa, containing a plexus of blood vessels and connective tissue. Bilateral testicular arteries originating from the aorta, just inferior to the renal arteries, provide arterial supply to the testes. The testicular arteries enter the scrotum in the spermatic cord via the inguinal canal and split into two branches at the posterosuperior border of the testis. Additionally, the testes receive blood from the cremasteric branch of the inferior epigastric artery and the artery to the ductus deferens. The pampiniform plexus drains both the testis and epididymis before coalescing to form the testicular vein, usually above the spermatic cord formation at the deep inguinal ring. The tenth and eleventh thoracic spinal nerves supply the testes via the renal and aortic autonomic plexuses. Blood supply for epididymis is same as for testes. FOR PROSTATE GLAND: The arterial supply to the prostate gland is derived from the inferior vesical artery and branches of the middle rectal artery. Venous drainage of the prostate forms the prostatic plexus, which eventually drains into the internal iliac vein FOR SEMINAL VESICLES AND COWPER’s GLAND: Arterial blood supply to the seminal vesicles includes branches from the inferior vesical and middle rectal arteries, while venous accompanies these arteries. The inferior division of the hypogastric plexus provides innervation to the seminal vesicles. Blood supply for cowper’s gland is same as for seminal vesicles. FOR DUCTUS DEFERENS AND URINOGENITAL DUCT: Each ductus deferens has an artery usually derived from the superior vesical artery (artery to the ductus), with venous drainage to the pelvic venous plexus. Same blood supplying process for urinogenital duct.
- 9. FOR PENIS: The vasculature of the penis is extensive. The perineal artery (a branch of the internal pudendal artery) together with the posterior scrotal artery and the inferior rectal artery supply tissues from the bulb of the penis to the anus. The artery of the bulb of the penis, from the internal pudendal, penetrates the penile bulb and subsequently supplies the corpus spongiosum. The deep artery of the penis is one of two terminal branches of the internal pudendal artery; it enters the crus of the penis and continues through the length of the bilateral corpus cavernosum. The other terminal branch of the internal pudendal artery is the dorsal artery of the penis running along the dorsal surface of the penis supplying the penile skin and the glans penis. The venous drainage of the penis includes the veins draining the corpora cavernosa, which subsequently drains into the circumflex veins. These veins receive venous blood from the corpus spongiosum on the ventral aspect of the penis and wrap around the penis to drain into the deep dorsal vein. The superficial dorsal vein drains the penile skin and prepuce before draining via the superficial external pudendal vein into the external pudendal veins. The deep dorsal vein further drains blood from the glans penis and corpora cavernosa before joining the prostatic venous plexus.
