Capital structure theories notes
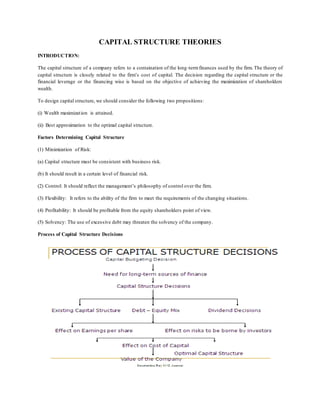
- 1. CAPITAL STRUCTURE THEORIES INTRODUCTION: The capital structure of a company refers to a containation of the long-termfinances used by the firm. The theory of capital structure is closely related to the firm’s cost of capital. The decision regarding the capital structure or the financial leverage or the financing wise is based on the objective of achieving the maximization of shareholders wealth. To design capital structure, we should consider the following two propositions: (i) Wealth maximization is attained. (ii) Best approximation to the optimal capital structure. Factors Determining Capital Structure (1) Minimization of Risk: (a) Capital structure must be consistent with business risk. (b) It should result in a certain level of financial risk. (2) Control: It should reflect the management’s philosophy of control over the firm. (3) Flexibility: It refers to the ability of the firm to meet the requirements of the changing situations. (4) Profitability: It should be profitable from the equity shareholders point of view. (5) Solvency: The use of excessive debt may threaten the solvency of the company. Process of Capital Structure Decisions
- 2. THEORIES OF CAPITAL STRUCTURE: Equity and debt capital are the two major sources of long-term funds for a firm. The theories on capital structure suggest the proportion of equity and debt in the capital structure. Assumptions i. There are only two sources of funds, i.e., the equity and the debt, having a fixed interest. ii. The total assets of the firm are given and there would be no change in the investment decisions of the firm. iii. EBIT (Earnings before Interest & Tax)/NOP (Net Operating Profits) of the firm are given and is expected to remain constant. iv. Retention Ratio is NIL, i.e., total profits are distributed as dividends. [100% dividend pay-out ratio] v. The firm has a given business risk which is not affected by the financing wise. vi. There is no corporate or personal tax. vii. The investors have the same subjective probability distribution of expected operating profits of the firm. viii. The capital structure can be altered without incurring transaction costs. In discussing the theories of capital structure, we will consider the following notations: E = Market value of the Equity D = Market value of the Debt V = Market value of the Firm = E +D I = Total Interest Payments T = Tax Rate EBIT/NOP = Earnings before Interest and Tax or Net Operating Profit PAT = Profit after Tax D0 = Dividend at time 0 (i.e. now) D1 = Expected dividend at the end of Year 1. Po = Current Market Price per share P1 = Expected Market Price per share at the end of Year 1. Kd = Cost of Debt after Tax [ I (1 – T)/D] Ke = Cost of Equity [D0/P] K0 = Overall cost of capital i.e., WACC D E D E KdD + KeE EBIT = Kd ( -------- ) + Ke ( -------- ) = Kd ( ---- ) + Ke ( ------ ) = --------------- = --------- D + E D + E V V V V Different Theories of Capital Structure (1) Net Income (NI) approach (2) Net Operating Income (NOI) Approach (3) Traditional Approach (4) Modigliani-Miller Model a. without taxes b. with taxes. Net Income Approach As suggested by David Durand, this theory states that there is a relationship between the Capital Structure and the value of the firm. Assumptions (1) Total Capital requirement of the firm are given and remain constant (2) Kd < Ke (3) Kd and Ke are constant (4) Ko decreases with the increase in leverage.
- 3. Illustration: Firm A Firm B Earnings Before Interest of Tax (EBIT) 2,00,000 2,00,000 Interest - 50,000 Equity Earnings (E) 2,00,000 1,50,000 Cost of Equity (Ke) 12% 12% Cost of Debt (Kd) 10% 10% E Market Value of Equity = ----- Ke 16,66,667 12,50,000 I Market Value of Debt = ------- Ke Nil 5,00,000 Total Value of the Firm [E+D] 16,66,667 17,50,000 EBIT Overall cost of capital (K0) = ----------------- E + D 12% 11.43% Net Operating Income (NOI) Approach According to David Durand, under NOI approach, the total value of the firmwill not be affected by the composition of capital structure. Assumptions (1) K0 and Kd is constant. (2) Ke will change with the degree of leverage. (3) There is no tax. ke ko kd Debt Cost kd ke, ko
- 4. Illustration A firm has an EBIT of Rs. 5,00,000 and belongs to a risk class of 10%. What is the cost of Equity if it employs 8% debt to the extent of 30%, 40% or 50% of the total capital fund of Rs. 20,00,000? Solution: 30% 40% 50% Debt (Rs.) 6,00,000 8,00,000 10,00,000 Equity (Rs.) 14,00,000 12,00,000 10,00,000 EBIT (Rs.) 5,00,000 5,00,000 5,00,000 Ko 10% 10% 10% Value of the Firm (V) (Rs.) (EBIT/Ko) 50,00,000 50,00,000 50,00,000 Value of Equity (E) (Rs.) (V–D) 44,00,000 42,00,000 40,00,000 Interest @ 6% (Rs.) 36,000 48,000 60,000 Net Profit (EBIT–Int.) (Rs.) 4,64,000 4,52,000 4,40,000 Ke (NP/E) 10.545% 10.76% 11% Traditional Approach: It takes a mid-way between the NI approach and the NOI approach. Assumptions (i) The value of the firm increases with the increase in financial leverage, upto a certain limit only. (ii) Kd is assumed to be less than Ke. ke ko kd Debt Cost
- 5. Ke Cost of Capital Ko (%) Kd O Optimal Leverage Part I Capital (Degree) Structure Ke Cost of Capital Ko (%) Kd O P Range of Optimal Leverage Part II Capital (Degree) Structure Traditional viewpoint on the Relationship between Leverage, Cost of Capital and the Value of the Firm Modigliani – Miller (MM) Hypothesis The Modigliani – Miller hypothesis is identical with the net operating Income approach. Modigliani and Miller argued that, in the absence of taxes the cost of capital and the value of the firm are not affected by the changes in capital structure. In other words, capital structure decisions are irrelevant and value of the firm is independent of debt – equity mix. Basic Propositions M - M Hypothesis can be explained in terms of two propositions of Modigliani and Miller. They are: i. The overall cost of capital (KO) and the value of the firm are independent of the capital structure. The total market value of the firm is given by capitalizing the expected net operating income by the rate appropriate for that risk class. ii. The financial risk increases with more debt content in the capital structure. As a result cost of equity (Ke) increases in a manner to offset exactly the low – cost advantage of debt. Hence, overall cost of capital remains the same.
- 6. Assumptions of the MM Approach 1. There is a perfect capital market. Capital markets are perfect when i) investors are free to buy and sell securities, ii) they can borrow funds without restriction at the same terms as the firms do, iii) they behave rationally, iv) they are well informed, and v) there are no transaction costs. 2. Firms can be classified into homogeneous risk classes.All the firms in the same risk class will have the same degree of financial risk. 3. All investors have the same expectation of a firm’s net operating income (EBIT). 4. The dividend payout ratio is 100%, which means there are no retained earnings. 5. There are no corporate taxes. This assumption has been removed later. Preposition I According to M – M, for the firms in the same risk class, the total market value is independent of capital structure and is determined by capitalizing net operating income by the rate appropriate to that risk class. Proposition I can be expressed as follows: X NO I V = S +D = -------- = ---------- Ko Ko Where, V = the market value of the firm S = the market value of equity D = the market value of debt According the proposition I the average cost of capital is not affected by degree of leverage and is determined as follows: X K o = ---- V According to M –M, the average cost of capital is constant as shown in the following Figure. ko Debt Cost MM's Proposition I
- 7. Arbitrage Process According to M –M, two firms identical in all respects except their capital structure cannot have different market values or different cost of capital. In case, these firms have different market values, the arbitrage will take place and equilibrium in market values is restored in no time. Arbitrage process refers to switching of investment from one firm to another. When market values are different, the investors will try to take advantage of it by selling their securities with high market price and buying the securities with low market price. The use of debt by the investors is known as personal leverage or homemade leverage. Because of this arbitrage process, the market price of securities in higher valued market will come down and the market price of securities in the lower valued market will go up, and this switching process is continued until the equilibrium is established in the market values. So, M –M, argue that there is no possibility of different market values for identical firms. Reverse Working of Arbitrage Process Arbitrage process also works in the reverse direction. Leverage has neither advantage nor disadvantage. If an unlevered firm (with no debt capital) has higher market value than a levered firm (with debt capital) arbitrage process works in reverse direction. Investors will try to switch their investments from unlevered firmto levered firm so that equilibrium is established in no time. Thus, M – M proved in terms of their proposition I that the value of the firm is not affected by debt-equity mix. Proposition II M – M’s proposition II defines cost of equity. According to them, for any firm in a given risk class, the cost of equity is equal to the constant average cost of capital (Ko) plus a premium for the financial risk, which is equal to debt – equity ratio times the spread between average cost and cost of debt. Thus, cost of equity is: D Ke = Ko + (Ko – Kd) x ------ S Where, Ke = cost of equity D/S = debt – equity ratio M – M argue that Ko will not increase with the increase in the leverage, because the low – cost advantage of debt capital will be exactly offset by the increase in the cost of equity as caused by increased risk to equity shareholders. The crucial part of the M – M Thesis is that an excessive use of leverage will increase the risk to the debt holders which results in an increase in cost of debt (Ko). However, this will not lead to a rise in Ko. M – M maintains that in such a case Ke will increase at a decreasing rate or even it may decline. This is because of the reason that at an increased leverage, the increased risk will be shared by the debt holders. Hence Ko remain constant. This is illustrated in the Figure given below: Ke Ko Cost of Capital (percent) Kd O Leverage X
- 8. Criticism of M M Hypothesis The arbitrage process is the behavioural and operational foundation for M M Hypothesis. But this process fails the desired equilibrium because of the following limitations. 1. Rates of interest are not the same for the individuals and firms. The firms generally have a higher credit standing because of which they can borrow funds at a lower rate of interest as compared to individuals. 2. Home – Made leverage is not a perfect substitute for corporate leverage. If the firm borrows, the risk to the shareholder is limited to his shareholding in that company. But if he borrows personally, the liability will be extended to his personal property also. Hence, the assumption that personal or home – made leverage is a perfect substitute for corporate leverage is not valid. 3. The assumption that transaction costs do not exist is not valid because these costs are necessarily involved in buying and selling securities. 4. The working of arbitrage is affected by institutional restrictions, because the institutional investors are not allowed to practice home – made leverage. 5. The major limitation of M – M hypothesis is the existence of corporate taxes. Since the interest charges are tax deductible, a levered firm will have a lower cost of debt due to taxadvantage when taxes exist. M – M Hypothesis Corporate Taxes Modigliani and Miller later recognized the importance of the existence of corporate taxes. Accordingly, they agreed that the value of the firm will increase or the cost of capital will decrease with the use of debt due to taxdeductibility of interest charges. Thus, the optimum capital structure can be achieved by maximising debt component in the capital structure. According to this approach, value of a firm can be calculated as follows: EBIT Value of Unlevered firm (Vu) = --------(I - t) Ko Where, EBIT = Earnings before interest and taxes Ko = Overall cost of capital t = Tax rate. I = Interest on debt capital
