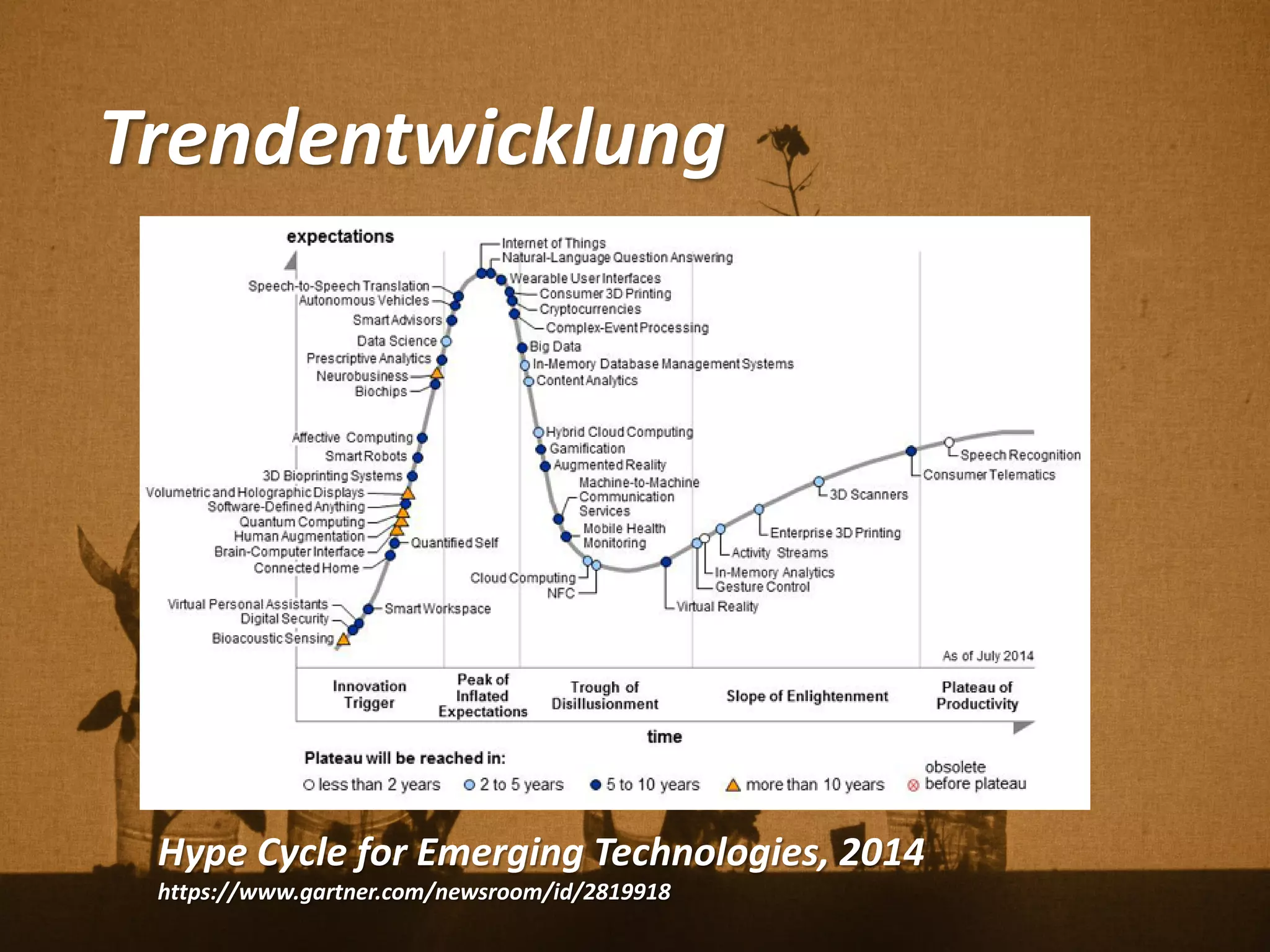
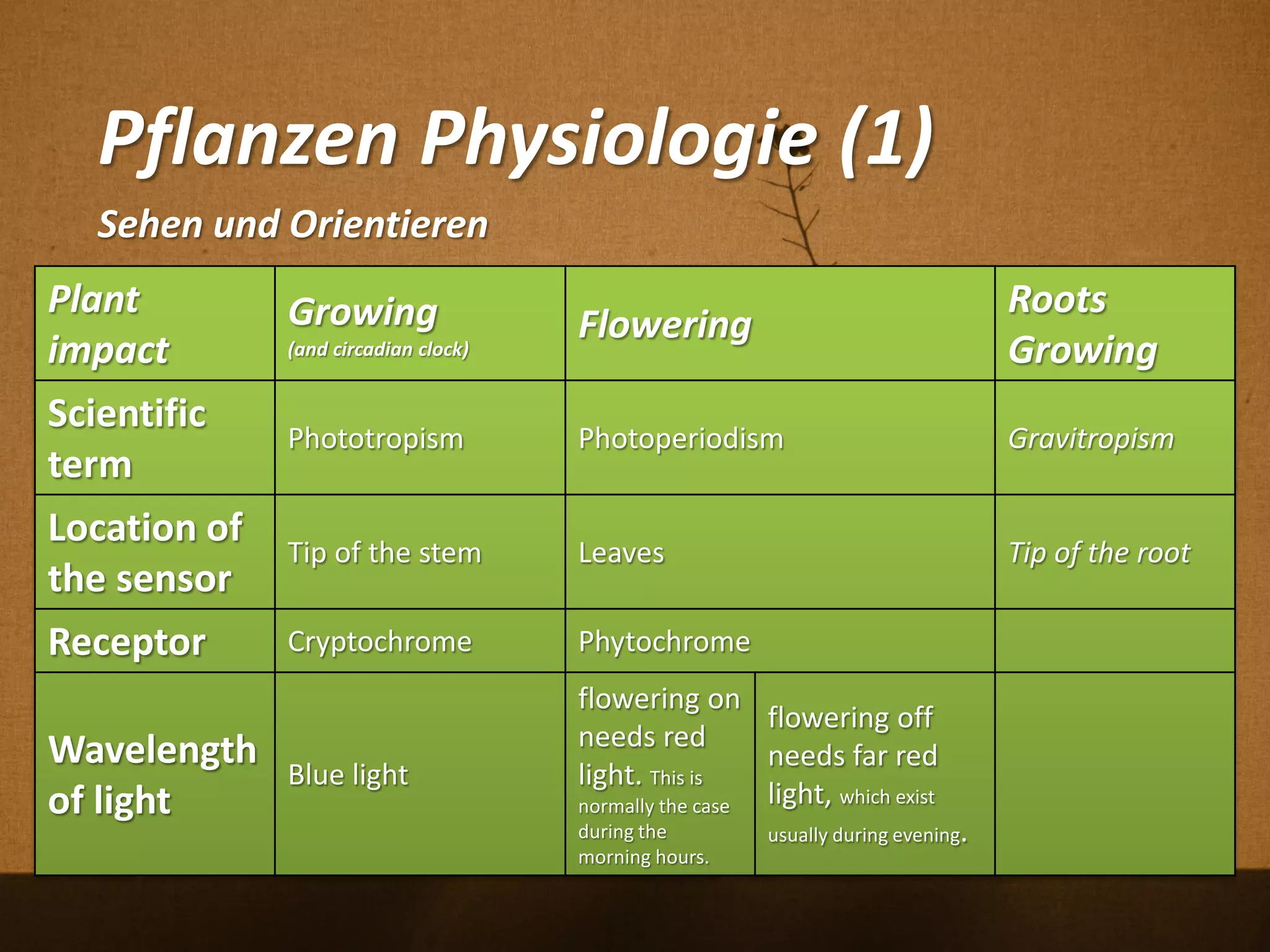
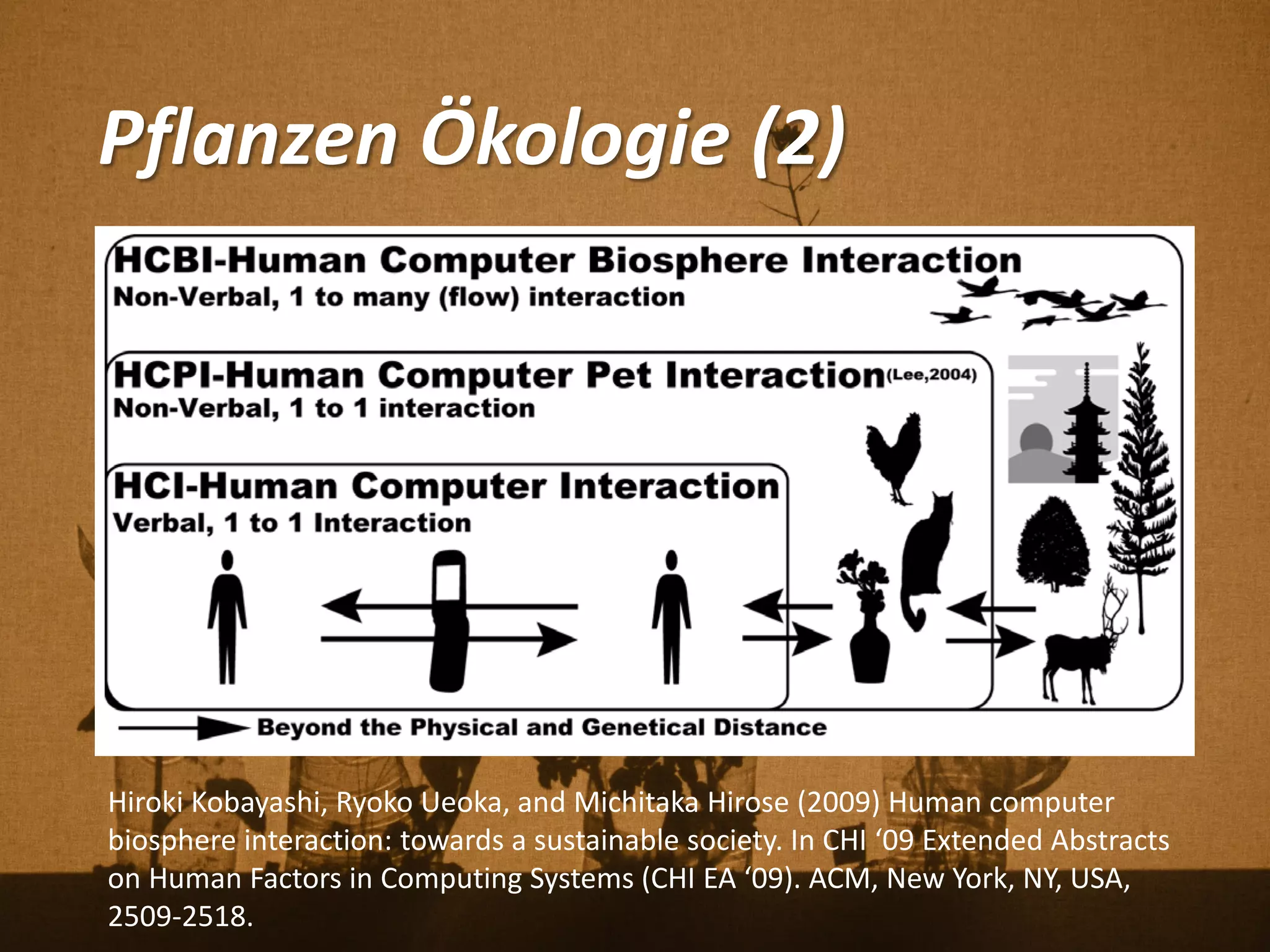
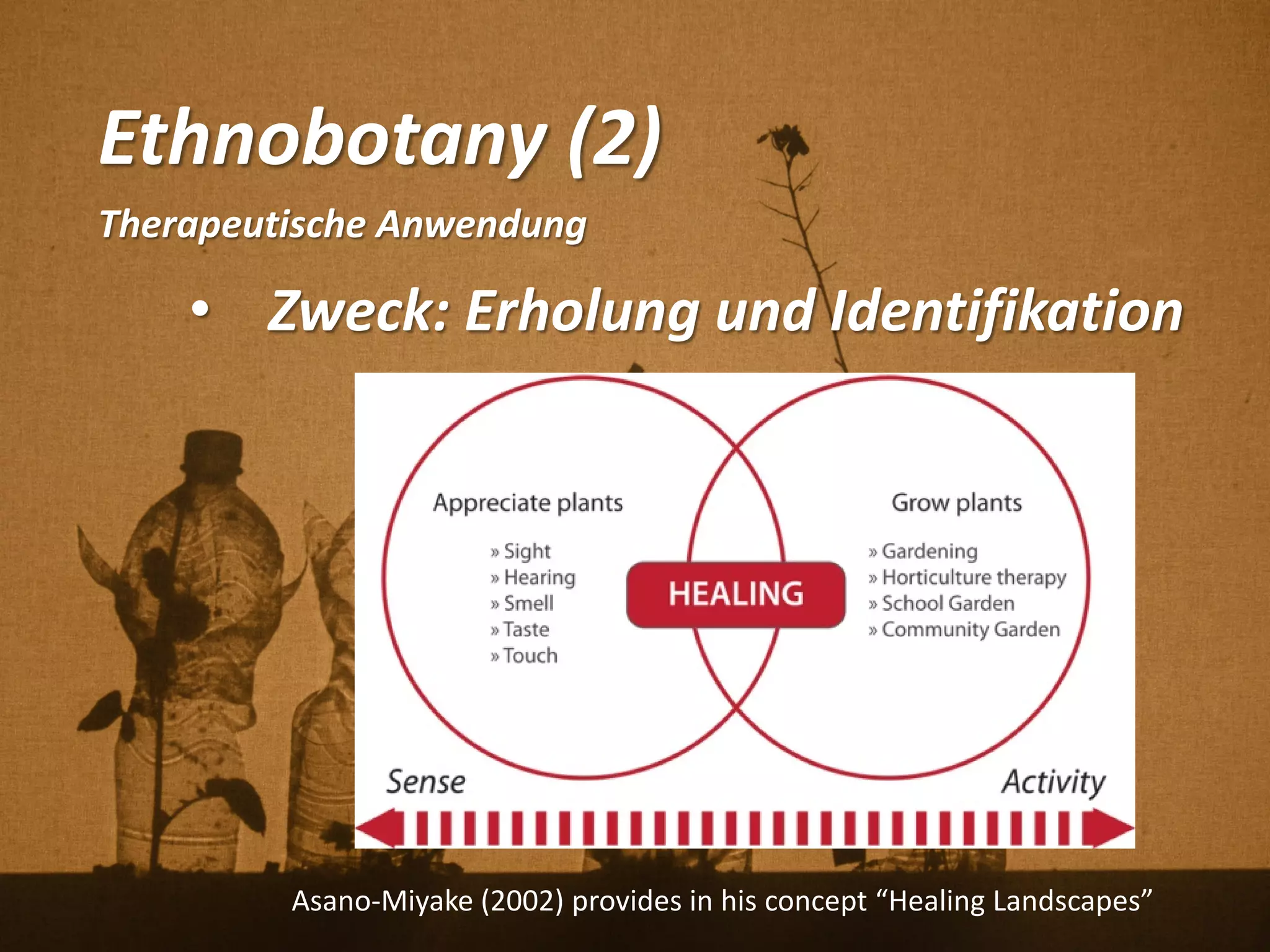
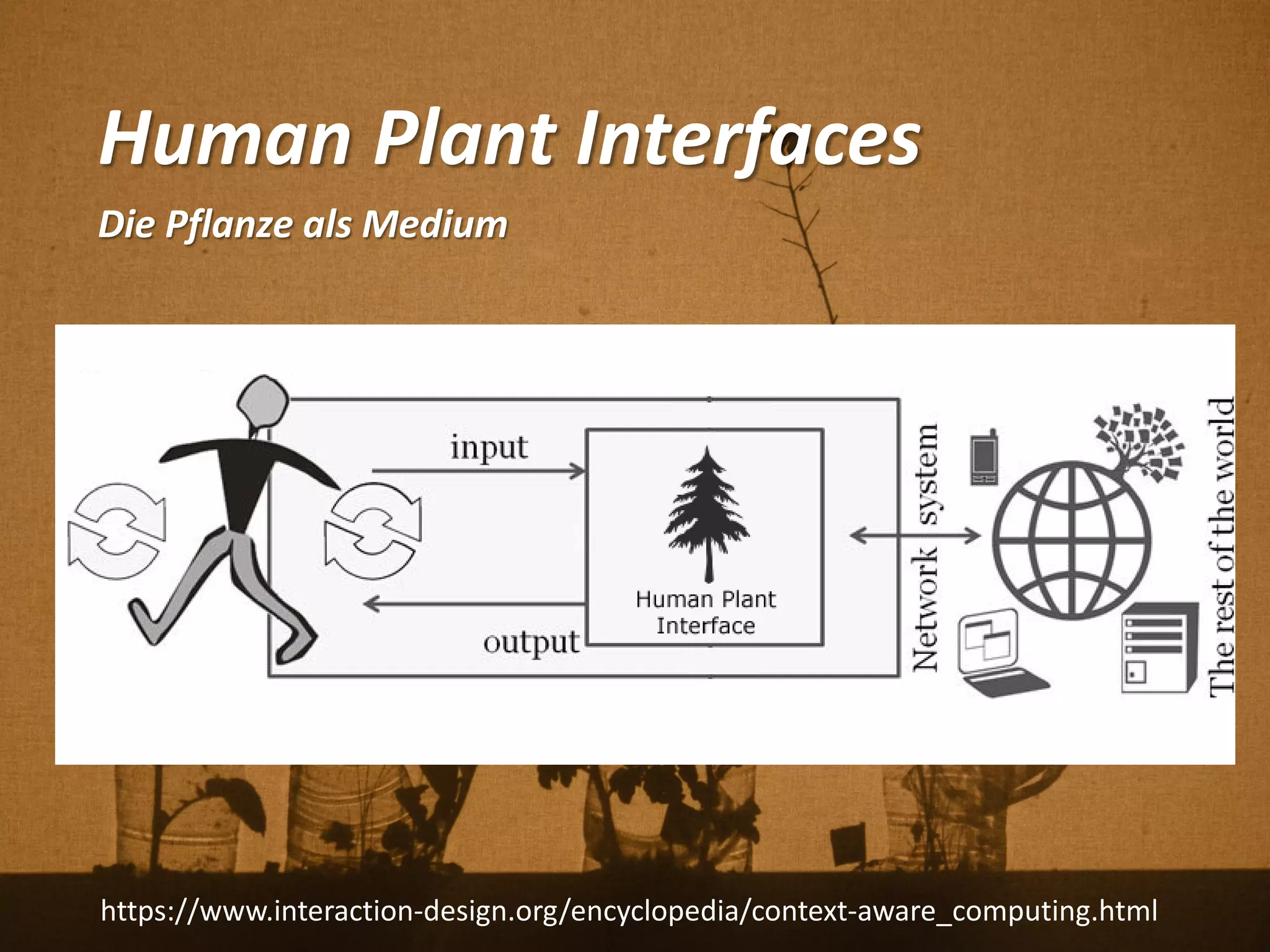
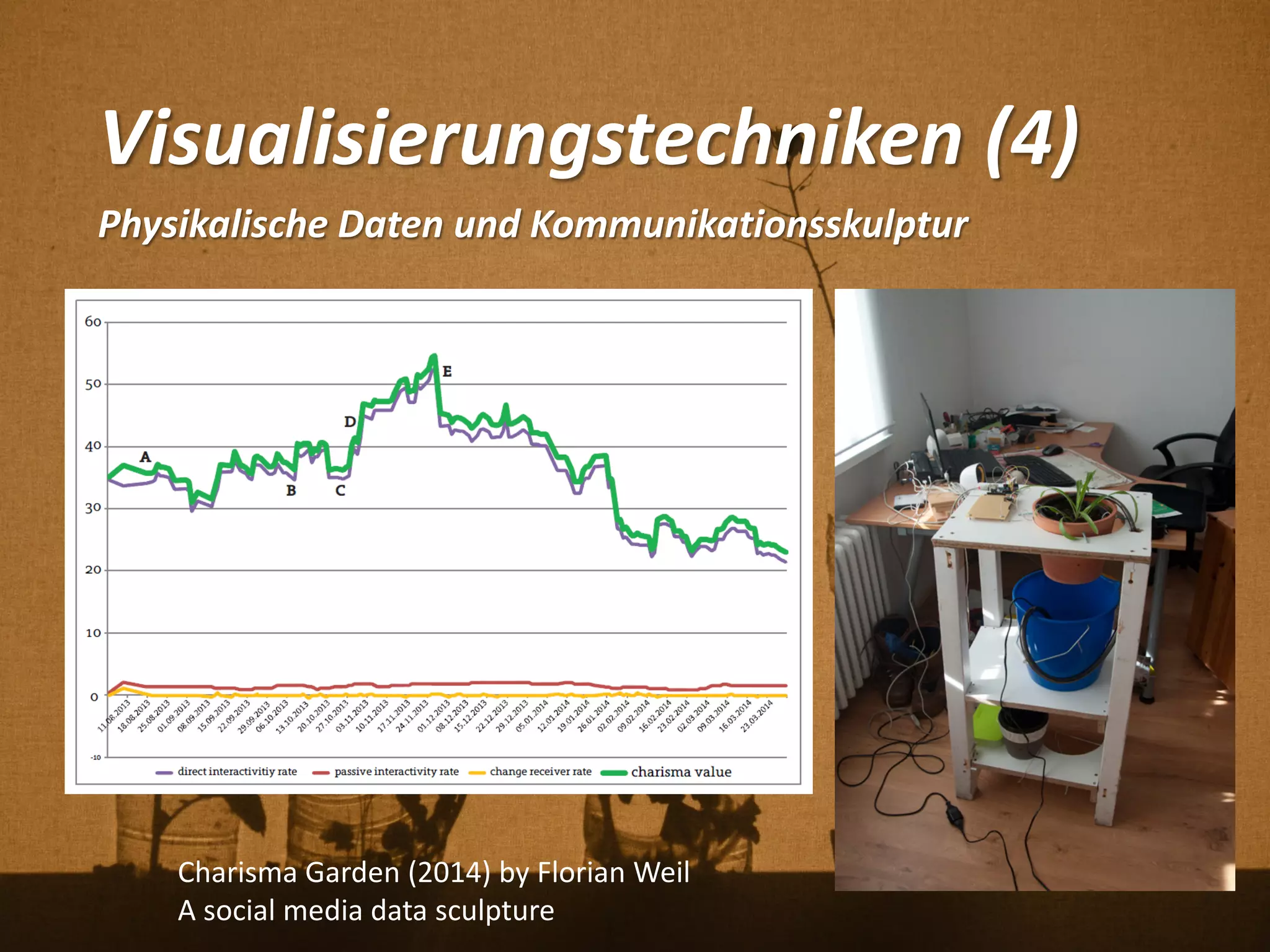
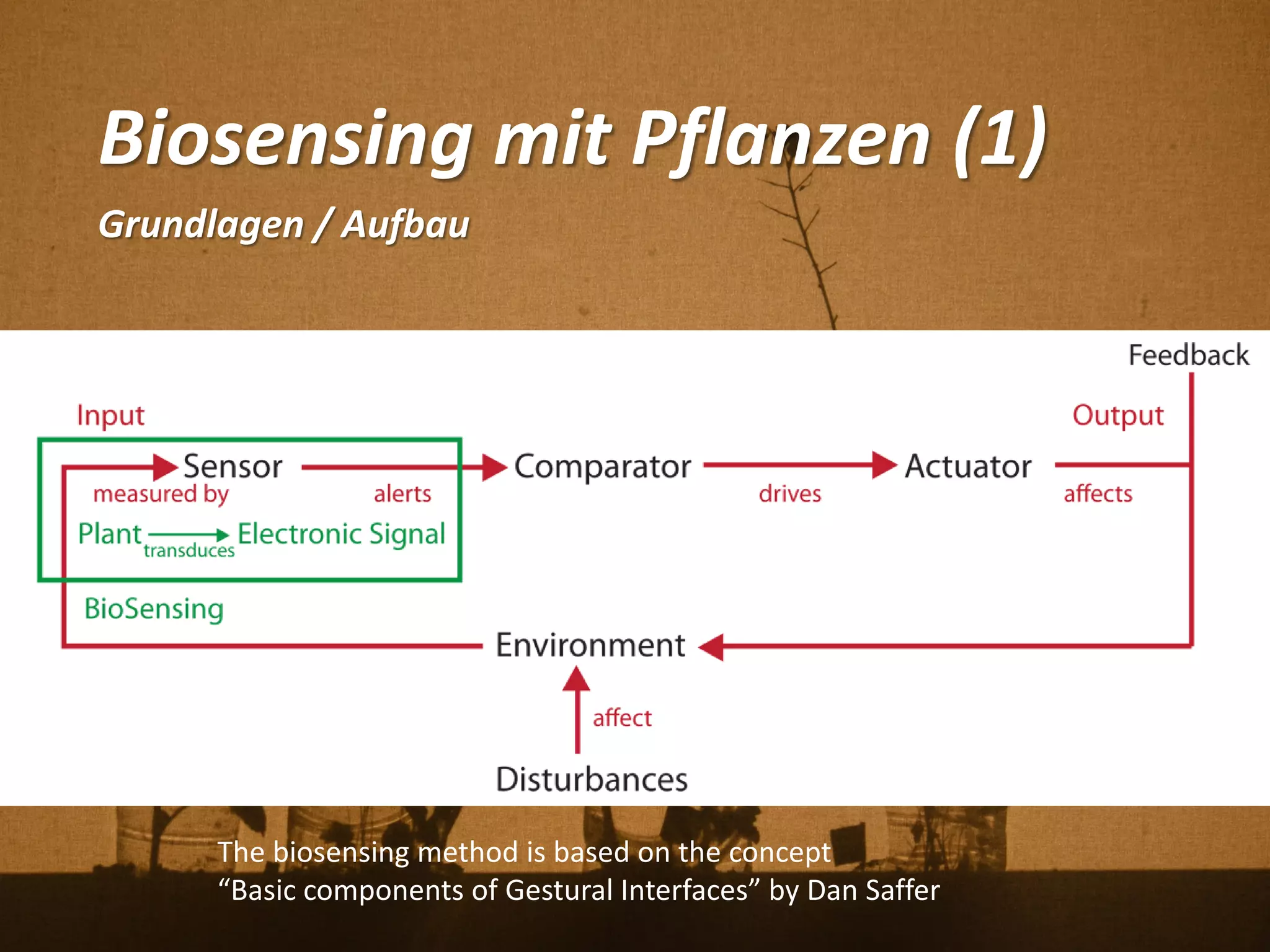
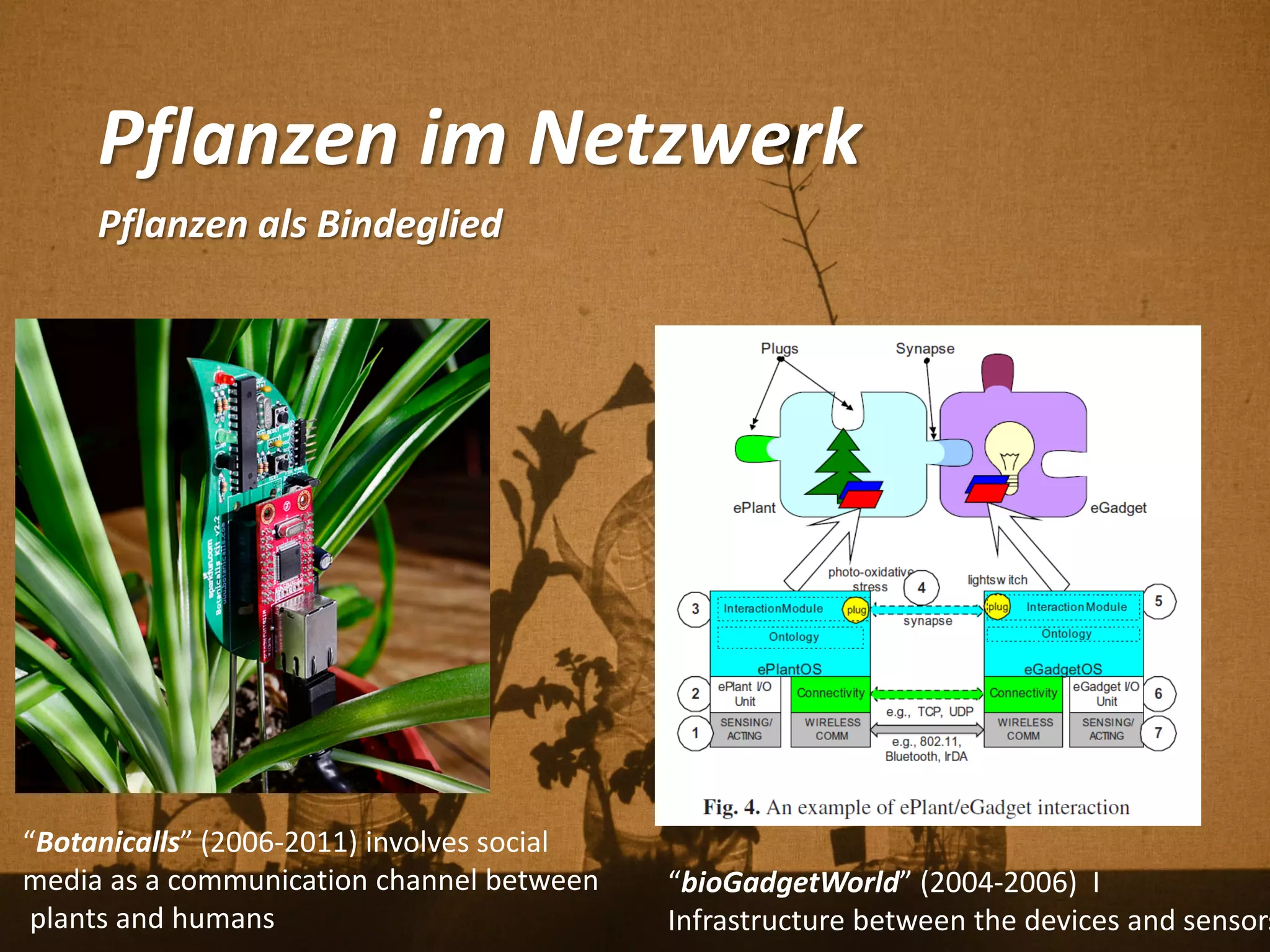
Florian Weil spricht in seiner Gastvorlesung über 'Human Plant Interfaces', eine interdisziplinäre Forschungsrichtung, die physische, soziale und kulturelle Interaktionen zwischen Menschen und Pflanzen untersucht. Er betont die Bedeutung von Pflanzen für das menschliche Wohlbefinden und diskutiert verschiedene Aspekte der Botanik, Ökologie und Ethnobotanik, während er innovative Projekte und Technologien vorstellt, die Pflanzen als Kommunikationsmedium nutzen. Der Vortrag schließt mit einem praxisorientierten Workshop, der Experimente mit Pflanzen und Sensoren umfasst.