Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
5. convolution and correlation of discrete time signals 

5. convolution and correlation of discrete time signals
Ec8491 Communication Theory-Unit 1 - Amplitude Modulation

Ec8491 Communication Theory-Unit 1 - Amplitude Modulation
Viewers also liked
Viewers also liked (19)
Similar to Electronics noise
Similar to Electronics noise (20)
5000 Integrated circuits power audio amplifiers data book.pdf

5000 Integrated circuits power audio amplifiers data book.pdf
Electronics noise
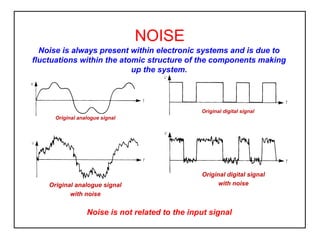
- 1. NOISE Noise is always present within electronic systems and is due to fluctuations within the atomic structure of the components making up the system. Original digital signal Original analogue signal Original analogue signal with noise Original digital signal with noise Noise is not related to the input signal
- 2. COMMON TYPES of NOISE Thermal (Johnson) Noise: Caused by heat generated due to the random movement of atoms within the components. Has an infinite bandwidth with equal noise power. Flicker Noise: Caused by random variations in the diffusion of charge carriers within devices, transistors especially and is a low frequency noise. Shot Noise: Caused by uneven distribution of charge carriers due to the granular nature of semiconductor materials as a result of fluctuations in the diffusion process. Pink Noise: A low frequency noise similar to flicker noise also known as 1/f noise since its power spectrum is inversely proportional to frequency. White Noise: Similar to thermal noise, having noise components at all frequencies with equal noise power across the spectrum.
- 3. SIGNAL to NOISE RATIO The signal-to-noise ratio (S/N ratio) is a quantitative method of describing the quality of a signal in terms of its corruption by noise. That is, the ratio of the magnitude of the signal to that of the noise, usually expressed as the ratio of signal power (Ps) to the noise power (Pn). Ps S N ratio = 10 log10 Pn dB The signal-to-noise ratio within a given system varies with the magnitude of the signal. If the signal becomes very small, the relative size of the noise will increase causing the S/N ratio to decrease, (remember the noise level is independent of signal). Manufacturers of audio equipment often like to quote the signal-to-noise ratio as a selling point for their equipment.