Dichotomous Key, Classification Lesson PowerPoint, Biology, Idetification Plants
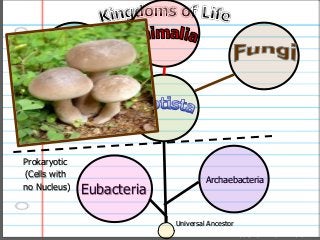
- 1. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Eubacteria Archaebacteria Eukaryotic (Cells with Nucleus) Prokaryotic (Cells with no Nucleus) Universal Ancestor
- 3. Dichotomous key: A tool that allows the user to determine the identity of items in the natural world. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 4. Dichotomous key: A tool that allows the user to determine the identity of items in the natural world. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 5. Dichotomous key: A tool that allows the user to determine the identity of items in the natural world. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 6. Dichotomous key: A tool that allows the user to determine the identity of items in the natural world. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 7. Dichotomous key: A tool that allows the user to determine the identity of items in the natural world. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 8. Dichotomous key: A tool that allows the user to determine the identity of items in the natural world. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 9. Dichotomous key: A tool that allows the user to determine the identity of items in the natural world. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 10. Dichotomous key: A tool that allows the user to determine the identity of items in the natural world. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 11. Dichotomous key: A tool that allows the user to determine the identity of items in the natural world. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 12. Dichotomous key: A tool that allows the user to determine the identity of items in the natural world. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 13. Dichotomous key: A tool that allows the user to determine the identity of items in the natural world. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 14. • Taxonomy and Classification Available Sheet. – Follows slideshow for classwork.
- 15. • Please use the key to answer the questions below. – I have no feathers but legs?___________ – I have feathers but don’t swim?________ – I have no feathers or legs?______ – I have feathers and swim?____________ Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 16. • Please use the key to answer the questions below. – I have no feathers but legs? Lizard – I have feathers but don’t swim?________ – I have no feathers or legs?______ – I have feathers and swim?____________ Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 17. • Please use the key to answer the questions below. – I have no feathers but legs? Lizard – I have feathers but don’t swim?________ – I have no feathers or legs?______ – I have feathers and swim?____________ Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 18. • Please use the key to answer the questions below. – I have no feathers but legs? Lizard – I have feathers but don’t swim? Hen – I have no feathers or legs?______ – I have feathers and swim?____________ Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 19. • Please use the key to answer the questions below. – I have no feathers but legs? Lizard – I have feathers but don’t swim? Hen – I have no feathers or legs?______ – I have feathers and swim?____________ Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 20. • Please use the key to answer the questions below. – I have no feathers but legs? Lizard – I have feathers but don’t swim? Hen – I have no feathers or legs? Snake – I have feathers and swim?____________ Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 21. • Please use the key to answer the questions below. – I have no feathers but legs? Lizard – I have feathers but don’t swim? Hen – I have no feathers or legs? Snake – I have feathers and swim?____________ Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 22. • Please use the key to answer the questions below. – I have no feathers but legs? Lizard – I have feathers but don’t swim? Hen – I have no feathers or legs? Snake – I have feathers and swim? Duck Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 23. Based on characteristics and uses process of comparison and elimination. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 24. • Which shark fin fits the following description? – Tail not separated into a top and bottom fin. End of tail is blunt instead of pointy? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 25. • Which shark fin fits the following description? – Tail not separated into a top and bottom fin. End of tail is blunt instead of pointy? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 26. • Answer! Which shark fin fits the following description? – Tail not separated into a top and bottom fin. End of tail is blunt instead of pointy? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 27. • Answer! Which two shark fins fit the following description? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 28. • Answer! Which two shark fins fit the following description? – Upper part of tail extends far beyond the bottom. Tip of top tail fin curved. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 29. • Answer! Which two shark fins fit the following description? – Upper part of tail extends far beyond the bottom. Tip of top tail fin curved. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 30. • Which two shark fins fit the following description? – Trunk before tail fin has small fin. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 31. • Which two shark fins fit the following description? – Trunk before tail fin has small fin. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 32. • Use constant characteristics rather than ones that disappear or vary with the season or other environmental factor. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 33. • Use constant characteristics rather than ones that disappear or vary with the season or other environmental factor. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 34. • Use characteristics which can be directly observed. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 35. • Use characteristics which can be directly observed. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Black and White color with orange around neck…
- 36. • Use characteristics which can be directly observed. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy And they love each other…
- 37. • Use characteristics which can be directly observed. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy And they love each other…
- 38. • Use characteristics which can be directly observed. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy And they love each other… “They form mating pairs is a better description.”
- 39. • What is a big insect to you?
- 40. • What is a big insect to you?
- 41. • What is a big insect to you?
- 42. • Use quantitative (numbered) measurements with an amount or dimension rather than vague terms like… Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 43. • Use quantitative (numbered) measurements with an amount or dimension rather than vague terms like… "big" and "small." Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 44. • Use quantitative (numbered) measurements with an amount or dimension rather than vague terms like… "big" and "small." Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 45. • Use quantitative (numbered) measurements with an amount or dimension rather than vague terms like… "big" and "small." Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 46. • Use quantitative (numbered) measurements with an amount or dimension rather than vague terms like… "big" and "small." Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 47. • Use quantitative (numbered) measurements with an amount or dimension rather than vague terms like… "big" and "small." Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy “OH?” “That’s not very Big.”
- 48. • Rules to Follow When Using a Dichotomous Key – Always read both choices, even if the first seems to be the logical. – Understand the meaning of the terms involved in the key. – When measurements are given, use a scale to measure the specimen. Do not guess at a measurement. – Living things are always variable, so do not base your organism identification in the field on a single observation. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 49. • Rules to Follow When Using a Dichotomous Key – Always read both choices, even if the first seems to be the logical. – Understand the meaning of the terms involved in the key. – When measurements are given, use a scale to measure the specimen. Do not guess at a measurement. – Living things are always variable, so do not base your organism identification in the field on a single observation. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 50. • Rules to Follow When Using a Dichotomous Key – Always read both choices, even if the first seems to be the logical. – Understand the meaning of the terms involved in the key. – When measurements are given, use a scale to measure the specimen. Do not guess at a measurement. – Living things are always variable, so do not base your organism identification in the field on a single observation. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 51. • Rules to Follow When Using a Dichotomous Key – Always read both choices, even if the first seems to be the logical. – Understand the meaning of the terms involved in the key. – When measurements are given, use a scale to measure the specimen. Do not guess at a measurement. – Living things are always variable, so do not base your organism identification in the field on a single observation. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 52. • Rules to Follow When Using a Dichotomous Key – Always read both choices, even if the first seems to be the logical. – Understand the meaning of the terms involved in the key. – When measurements are given, use a scale to measure the specimen. Do not guess at a measurement. – Living things are always variable, so do not base your organism identification in the field on a single observation. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 53. • Activity! Guess Who / 7 Questions? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 54. • Activity! Guess Who / 7 Questions? –Create a series of questions to find the three secret members of the class that I have selected and put their names on the card. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 55. • Activity! Guess Who / 7 Questions? –Create a series of questions to find the three secret members of the class that I have selected and put their names on the card. –Use yes / no questions based on characteristics. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 56. • Activity! Wacky People. – Use a dichotomous key to find the names for various humanoids. – Assignment is to correctly identify each character with the correct name. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 57. • Activity – EEK Dichotomous Key – http://www.dnr.state.wi.us/org/caer/ce/eek/veg/ treekey/treestart.htm Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Collect a leaf and use the online dichotomous key at… http://oregonstate.edu/trees/dichotomous_key.html
- 58. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 59. • Leaf for EEK Dichotomous key. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 60. • You should be close to page 4/5 in your bundle.
- 61. Classification uses… Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 62. Homology: Similarities between organisms Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 63. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 64. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 65. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 66. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 67. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 68. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 69. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 70. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 71. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 72. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 73. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 74. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 75. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 76. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 77. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 78. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 79. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 80. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 81. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 82. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 83. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 84. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 85. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 86. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 87. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 88. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 89. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 90. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 91. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 92. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 93. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 94. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 95. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 96. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 97. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 98. • Embryonic homology Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 99. • Which of the following is a blastula (early embryo) of a sea urchin, starfish, frog, and human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 100. • Which of the following is a blastula (early embryo) of a sea urchin, starfish, frog, and human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 101. • Which of the following is a blastula (early embryo) of a sea urchin, starfish, frog, and human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 102. • Which of the following is a blastula (early embryo) of a sea urchin, starfish, frog, and human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 103. • Which of the following is a blastula (early embryo) of a sea urchin, starfish, frog, and human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 104. • Which of the following is a blastula (early embryo) of a sea urchin, starfish, frog, and human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 105. • Which of the following is a blastula (early embryo) of a sea urchin, starfish, frog, and human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 106. • Which of the following is a blastula (early embryo) of a sea urchin, starfish, frog, and human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 107. • Which of the following is a blastula (early embryo) of a sea urchin, starfish, frog, and human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 108. • Which of the embryos below is a human, chicken, fish, and cat? Human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 109. • Which of the embryos below is a human, chicken, fish, and cat? Human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 110. • Which of the embryos below is a human, chicken, fish, and cat? Human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 111. • Which of the embryos below is a human, chicken, fish, and cat? Human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 112. • Which of the embryos below is a human, chicken, fish, and cat? Human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 113. • Which of the embryos below is a human, chicken, fish, and cat? Human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 114. • Which of the embryos below is a human, chicken, fish, and cat? Human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 115. • Which of the embryos below is a human, chicken, fish, and cat? Human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 116. • Which of the embryos below is a human, chicken, fish, and cat? Human Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Learn more about homology at… http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/article/lines_04
- 117. DNA: Similar genes aid in classification Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 118. • DNA provides insight into how similar and how different organisms are. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 119. • DNA provides insight into how similar and how different organisms are. This allows taxonomist to classify organisms more accurately. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 120. • DNA provides insight into how similar and how different organisms are. This allows taxonomist to classify organisms more accurately. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 121. • Humans and Chimpanzee share 94% of the same genes. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 122. • Humans and Chimpanzee share 94% of the same genes. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 123. • Humans and Chimpanzee share 94% of the same genes. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 124. • Humans and Chimpanzee share 94% of the same genes. – We can get a blood transfusion from a chimp. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 125. • Red Pandas
- 126. • Red Pandas and Giant Pandas
- 127. • Red Pandas and Giant Pandas both eat bamboo.
- 128. • Red Pandas and Giant Pandas both eat bamboo. – Giant Pandas are more closely related to…
- 129. • Red Pandas and Giant Pandas both eat bamboo. – Giant Pandas are more closely related to… – Red Pandas more closely related to…
- 130. • Red Pandas and Giant Pandas both eat bamboo. – Giant Pandas are more closely related to… – Red Pandas more closely related to…
- 131. • Red Pandas and Giant Pandas both eat bamboo. – Giant Pandas are more closely related to… – Red Pandas more closely related to…
- 132. • Red Pandas and Giant Pandas both eat bamboo. – Giant Pandas are more closely related to… – Red Pandas more closely related to…
- 133. • Red Pandas and Giant Pandas both eat bamboo. – Giant Pandas are more closely related to… – Red Pandas more closely related to…
- 134. • Red Pandas and Giant Pandas both eat bamboo. – Giant Pandas are more closely related to… – Red Pandas more closely related to…
- 135. • Can these two mate? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 136. • Horse zebra hybrid (sterile), called a Zebroid. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 137. • Horse zebra hybrid (sterile), called a Zebroid. – Zebras and horses have a different number of genes. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 138. • Horse zebra hybrid (sterile), called a Zebroid. – Zebras and horses have a different number of genes. A sterile offspring is usually the result after breeding. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 139. • Horse zebra hybrid (sterile), called a Zebroid. – Zebras and horses have a different number of genes. A sterile offspring is usually the result after breeding. A horse and zebra are closely related but both different species. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 141. • Activity Worksheet! Salamander (Order Caudata) Dichotomous Key. – Use a dichotomous key to identify salamanders Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 142. The 3 Domains of Life. All life is either… Archaeabacteria Eubacteria Eukarya Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 143. The 3 Domains of Life. All life is either… Archaeabacteria Eubacteria Eukarya Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 144. The 3 Domains of Life. All life is either… Archaeabacteria Eubacteria Eukarya Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 145. The 3 Domains of Life. All life is either… Archaeabacteria Eubacteria Eukarya Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 146. The 3 Domains of Life. All life is either… Archaeabacteria Eubacteria Eukarya Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Learn more about the Domains of Life at… http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/alllife/threedomains.html
- 147. • Humans are Eukarya, Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 148. • Humans are Eukarya, the other domains are forms of bacteria. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 149. “Excuse Me” “Does anyone know where I can find some good food.”
- 150. The Kingdoms of life. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 151. The Kingdoms of life. All life belongs to one of these. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 152. The Kingdoms of life. All life belongs to one of these. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 153. The Kingdoms of life. All life belongs to one of these. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 154. The Kingdoms of life. All life belongs to one of these. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 155. The Kingdoms of life. All life belongs to one of these. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 156. The Kingdoms of life. All life belongs to one of these. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 157. The Kingdoms of life. All life belongs to one of these. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Monera
- 158. The Kingdoms of life. All life belongs to one of these. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Monera
- 159. The Kingdoms of life. All life belongs to one of these. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Monera
- 160. The Kingdoms of life. All life belongs to one of these. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Monera
- 161. The Kingdoms of life. All life belongs to one of these. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Monera
- 162. The Kingdoms of life. All life belongs to one of these. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Monera Learn more about the six Kingdoms of Life at… http://biology.about.com/od/evolution/a/aa091004a.htm
- 163. “I’m dressed as King Phillip.” “Am I late for the spaghetti dinner?”
- 164. • Taxonomy and Classification Available Sheet. – Follows slideshow for classwork.
- 165. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 166. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 167. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 168. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 169. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 170. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 171. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 172. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 173. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 174. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 175. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Universal Ancestor
- 176. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Universal Ancestor
- 177. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Universal Ancestor
- 178. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Eubacteria Universal Ancestor
- 179. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Eubacteria Universal Ancestor
- 180. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Eubacteria Prokaryotic (Cells with no Nucleus) Universal Ancestor
- 181. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Eubacteria Prokaryotic (Cells with no Nucleus) Universal Ancestor
- 182. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Eubacteria Archaebacteria Prokaryotic (Cells with no Nucleus) Universal Ancestor
- 183. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Eubacteria Archaebacteria Prokaryotic (Cells with no Nucleus) Universal Ancestor
- 184. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Eubacteria Archaebacteria Prokaryotic (Cells with no Nucleus) Universal Ancestor
- 185. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Eubacteria Archaebacteria Eukaryotic (Cells with Nucleus) Prokaryotic (Cells with no Nucleus) Universal Ancestor
- 186. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Eubacteria Archaebacteria Eukaryotic (Cells with Nucleus) Prokaryotic (Cells with no Nucleus) Universal Ancestor
- 187. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Eubacteria Archaebacteria Eukaryotic (Cells with Nucleus) Prokaryotic (Cells with no Nucleus) Universal Ancestor
- 188. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Eubacteria Archaebacteria Eukaryotic (Cells with Nucleus) Prokaryotic (Cells with no Nucleus) Universal Ancestor
- 189. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Eubacteria Archaebacteria Eukaryotic (Cells with Nucleus) Prokaryotic (Cells with no Nucleus) Universal Ancestor
- 190. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Eubacteria Archaebacteria Eukaryotic (Cells with Nucleus) Prokaryotic (Cells with no Nucleus) Universal Ancestor
- 191. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Eubacteria Archaebacteria Eukaryotic (Cells with Nucleus) Prokaryotic (Cells with no Nucleus) Universal Ancestor
- 192. • Until recently (1984), scientists believed all life got its energy from the sun. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 193. • Until recently (1984), scientists believed all life got its energy from the sun. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 194. • Until recently (1984), scientists believed all life got its energy from the sun. A whole new system existed on the ocean floor. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 195. • Until recently (1984), scientists believed all life got its energy from the sun. A whole new system existed on the ocean floor. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 196. • Until recently (1984), scientists believed all life got its energy from the sun. A whole new system existed on the ocean floor. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy 12H2S + 6CO2 → C6H12O6 (=carbohydrate) + 6H2O + 12S Learn more about the differences between chemosynthesis and photosynthesis at... http://oceanexplorer.noaa.gov/facts/photochemo.html
- 197. • Archaebacteria can create energy without light at the bottom of the ocean under enormous pressures, Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 198. • Archaebacteria can create energy without light at the bottom of the ocean under enormous pressures, hot and cold temperatures and without light. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 199. • Archaebacteria can create energy without light at the bottom of the ocean under enormous pressures, hot and cold temperatures and without light. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 200. • Video Link! Hydrothermal Vents. – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BXGF3XS-yAI – without light. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 201. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 202. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Learn more about archaeabacteria at… http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/archaea/archaea.html
- 203. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 204. • These bacteria can also be found in extreme places. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 205. • These bacteria can also be found in extreme places. – Many scientists think this type of life may be found in the harsh environments on other planets. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 206. • These bacteria can also be found in extreme places. – Many scientists think this type of life may be found in the harsh environments on other planets. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Their cell membrane is a bit different from Eubacteria which allow them to survive in harsh places.
- 207. • Video Link! Archaeabacteria – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W25nI9kpxtU Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 208. “By the way, I really enjoy eating Spaghetti.”
- 209. Domains and Kingdoms
- 210. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies
- 211. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies
- 212. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies
- 213. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies
- 214. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies
- 215. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies
- 216. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies
- 217. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Gets Energy from..
- 218. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Gets Energy from..
- 219. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Cell Wall Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Cell Wall Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Cell Wall Varies Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Cell Wall Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Cell Wall (Chitin) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) No Cell Wall Single or Multi- Cellular Gets Energy from..
- 220. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Gets Energy from..
- 221. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Most are Unicellular) Some are multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies
- 222. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Auto / Hetero Varies Auto / Hetero Varies Auto / Hetero Sunlight Autotrophic Absorbs Hetero- trophic Consumes Hetero- trophic
- 223. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Auto / Hetero Varies Auto / Hetero Varies Auto / Hetero Sunlight Autotrophic Absorbs Hetero- trophic Consumes Hetero- trophic Autrophic: Can make its own food (chemo or photsynthesis
- 224. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Auto / Hetero Varies Auto / Hetero Varies Auto / Hetero Sunlight Autotrophic Absorbs Hetero- trophic Consumes Hetero- trophic Heterotrophic: Must consume food (eat or absorb)
- 225. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food
- 226. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I’m a multicellular organism that absorbs its food?
- 227. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Hetero- trophic Consumes Food I’m a multicellular organism that absorbs its food? Fungi (Heterotrophs)
- 228. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I’m a single celled organism that has a nucleus?
- 229. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I’m a single celled organism that has a nucleus? Protista
- 230. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I’m a multicellular organism that can make it own food?
- 231. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Auto- trophic Absorbs Consumes Food I’m a multicellular organism that can make it own food? Plantae (Autotroph)
- 232. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I’m a unicellular organism without a nucleus?
- 233. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I’m a unicellular organism without a nucleus? Eubacteria or Archaebacteria
- 234. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I’m a multicellular organism that eats other organisms?
- 235. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Hetero- trophic I’m a multicellular organism that eats other organisms?
- 236. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I’m a multicellular organism?
- 237. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I’m a multicellular organism? Plantae, Fungi, and Animalia
- 238. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I’m an autroph?
- 239. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I’m an autroph? Eubacteria, Archaebacteria, some Protista, and Plantae (Varies)
- 240. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I’m only a heterotroph?
- 241. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I’m only a heterotroph? Fungi and Animalia, they must eat or absorb food.
- 242. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I’m heterotrophic?
- 243. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Single (Unicellular) Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I’m heterotrophic? Fungi and Animalia, and Eubacteria, Archaebacteria, Protista (Varies)
- 244. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Varies Multicellular Cell Wall Multicellular Cell Wall (Chitin) Multicellular No Cell Wall Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I don’t have a cell wall?
- 245. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Varies Multicellular Cell Wall Multicellular Cell Wall (Chitin) Multicellular No Cell Wall Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I don’t have a cell wall? Animalia
- 246. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Varies Multicellular Cell Wall Multicellular Cell Wall (Chitin) Multicellular No Cell Wall Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I have a cell wall but it’s made of chitin?
- 247. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Varies Multicellular Cell Wall Multicellular Cell Wall (Chitin) Multicellular No Cell Wall Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I have a cell wall but it’s made of chitin? Fungi
- 248. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Varies Multicellular Cell Wall Multicellular Cell Wall (Chitin) Multicellular No Cell Wall Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I have a cell wall made of peptidoglycan?
- 249. Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archae- bacteria Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Prokaryotic (No nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Eukaryotic (Nucleus) Single or Multi- Cellular Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Single (Unicellular) Cell Wall Varies Multicellular Cell Wall Multicellular Cell Wall (Chitin) Multicellular No Cell Wall Gets Energy from.. Varies Varies Varies Sunlight Absorbs Consumes Food I have a cell wall made of peptidoglycan? Eubacteria
- 250. • Video Link! Hank Explains Eubacteria, Archaeabacteria, and Protists – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vAR47-g6tlA Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 251. “Can I come over for good spaghetti”
- 252. • Taxonomy and Classification Available Sheet. – Follows slideshow for classwork.
- 253. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 254. • Does anyone know King Phillip? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 255. • Does anyone know King Phillip? – Will someone invite him over for dinner? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 256. • Does anyone know King Phillip? – Will someone invite him over for dinner? – He likes spaghetti? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 257. • Does anyone know King Phillip? – Will someone invite him over for dinner? – He likes spaghetti? – Make sure the spaghetti is good, King Phillip only likes top quality pasta. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 258. The 8 Taxonomic ranks. All living things have 8 names. 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 259. Domain - Did Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 260. Kingdom - King Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 261. Phylum - Phillip Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 262. Class - Come Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 263. Order - Over Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 264. Family - For Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 265. Genus - Good Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 266. Species – Spaghetti Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 267. • What does “Did King Phillip Come Over For Good Spaghetti” stand for? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 268. • Answer! – 1) Domain - Did – 2) Kingdom - King – 3) Phylum - Phillip – 4) Class – Come – 5) Order - Over – 6) Family - For – 7) Genus - Good – 8) Species – Spaghetti Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 269. • Carlos Linnaeus created a system that uses binominal nomenclature (two names):
- 270. • Carlos Linnaeus created a system that uses binominal nomenclature (two names): – Every organism gets a genus and species name.
- 271. • Carlos Linnaeus created a system that uses binominal nomenclature (two names): – Every organism gets a genus and species name. – The names are usually based in Latin
- 272. • Carlos Linnaeus created a system that uses binominal nomenclature (two names): – Every organism gets a genus and species name. – The names are usually based in Latin Brachypelma smithi Grammostola rosea
- 273. • Carlos Linnaeus created a system that uses binominal nomenclature (two names): – Every organism gets a genus and species name. – The names are usually based in Latin Brachypelma smithi Grammostola rosea
- 274. • Carlos Linnaeus created a system that uses binominal nomenclature (two names): – Every organism gets a genus and species name. – The names are usually based in Latin Brachypelma smithi Grammostola rosea
- 275. • Carlos Linnaeus created a system that uses binominal nomenclature (two names): – Every organism gets a genus and species name. – The names are usually based in Latin Brachypelma smithi Grammostola rosea
- 276. Genus name is Capitalized, species name is not. They are both italicized. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 277. Genus name is Capitalized, species name is not. They are both italicized. Ex) Armadillidium vulgare Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 278. Genus name is Capitalized, species name is not. They are both italicized. Ex) Armadillidium vulgare Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 279. Genus name is Capitalized, species name is not. They are both italicized. Ex) Armadillidium vulgare Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 280. • Two or more groups can sometimes be found to be more closely related than thought.
- 281. • Two or more groups can sometimes be found to be more closely related than thought. – If the organism is more connected than originally though the species can be connected with a super put on the name “Supergroups”.
- 282. • Two or more groups can sometimes be found to be more closely related than thought. – If the organism is more connected than originally though the species can be connected with a super put on the name “Supergroups”. – If less connected than originally thought the species may be a subspecies.
- 283. • The wolf Canus lupus is not endangered. Canus lupus lupus
- 284. • The wolf Canus lupus is not endangered. – Canus lupus has 39 subspecies. Some of these subspecies are threatened. Canus lupus lupus
- 285. • The wolf Canus lupus is not endangered. – Canus lupus has 39 subspecies. Some of these subspecies are threatened. Canus lupus lupus Canis lupus albus Canis lupus arabs
- 286. • The wolf Canus lupus is not endangered. – Canus lupus has 39 subspecies. Some of these subspecies are threatened. Canus lupus lupus Canis lupus arctos Canis lupus baileyi
- 287. • The wolf Canus lupus is not endangered. – Canus lupus has 39 subspecies. Some of these subspecies are threatened. Canus lupus lupus Canis lupus crassodon Canis lupus dingo
- 288. • The wolf Canus lupus is not endangered. – Canus lupus has 39 subspecies. Some of these subspecies are threatened. Canus lupus lupus Canis lupus familaris Canis lupus dingo Domestic Dog
- 289. • The wolf Canus lupus is not endangered. – Canus lupus has 39 subspecies. Some of these subspecies are threatened. Canus lupus lupus Canis lupus familaris Canis lupus dingo Domestic Dog Not threatened
- 297. • Which of the following organisms below are not of the Kingdom Animalia?
- 298. • Answer – Which are not of Phylum Chordata?
- 299. • Answer – Which are not in the Order Mammalia?
- 300. • Answer – Which are not in the Order Rodentia?
- 301. • Answer – Which are not in the Family Sciuridae?
- 302. • Answer – Which are not in the Genus Scuirus?
- 303. • Answer – Which are not in the Class vulgaris?
- 304. • Answer – Sciurus vulgaris
- 305. • Taxanomic Name: • Domain -Eukarya • Kingdom -Animalia • Class -Chordata • Phylum –Mammalia • Order –Rodentia • Family –Sciuridae • Genus –Sciurus • Species -vulgaris
- 306. • Taxanomic Name: • Domain -Eukarya • Kingdom -Animalia • Class -Chordata • Phylum –Mammalia • Order –Rodentia • Family –Sciuridae • Genus –Sciurus • Species -vulgaris
- 307. • Taxanomic Name: • Domain -Eukarya • Kingdom -Animalia • Class -Chordata • Phylum –Mammalia • Order –Rodentia • Family –Sciuridae • Genus –Sciurus • Species -vulgaris
- 308. • Taxanomic Name: • Domain -Eukarya • Kingdom -Animalia • Class -Chordata • Phylum –Mammalia • Order –Rodentia • Family –Sciuridae • Genus –Sciurus • Species -vulgaris
- 309. • Taxanomic Name: • Domain -Eukarya • Kingdom -Animalia • Class -Chordata • Phylum –Mammalia • Order –Rodentia • Family –Sciuridae • Genus –Sciurus • Species -vulgaris
- 310. • Taxanomic Name: • Domain -Eukarya • Kingdom -Animalia • Class -Chordata • Phylum –Mammalia • Order –Rodentia • Family –Sciuridae • Genus –Sciurus • Species -vulgaris
- 311. • Taxanomic Name: • Domain -Eukarya • Kingdom -Animalia • Class -Chordata • Phylum –Mammalia • Order –Rodentia • Family –Sciuridae • Genus –Sciurus • Species -vulgaris
- 312. • Taxanomic Name: • Domain -Eukarya • Kingdom -Animalia • Class -Chordata • Phylum –Mammalia • Order –Rodentia • Family –Sciuridae • Genus –Sciurus • Species -vulgaris
- 313. • Taxanomic Name: • Domain -Eukarya • Kingdom -Animalia • Class -Chordata • Phylum –Mammalia • Order –Rodentia • Family –Sciuridae • Genus –Sciurus • Species -vulgaris
- 314. • Activity! Wearing a “Hello, My name is…” name tag for the rest of today and tomorrow until class.
- 315. • Activity! Wearing a “Hello, My name is…” name tag for the rest of today and tomorrow until class. Your real name goes here…
- 317. Eukarya,
- 318. Eukarya, Animalia,
- 320. Eukarya, Animalia, Chordata, Sub Phylum Vertebrata,
- 321. Eukarya, Animalia, Chordata, Sub Phylum Vertebrata, Mammalia,
- 322. Eukarya, Animalia, Chordata, Sub Phylum Vertebrata, Mammalia, Primate,
- 323. Eukarya, Animalia, Chordata, Sub Phylum Vertebrata, Mammalia, Primate, Hominidae,
- 324. Eukarya, Animalia, Chordata, Sub Phylum Vertebrata, Mammalia, Primate, Hominidae, Homo sapien sapien
- 325. Eukarya, Animalia, Chordata, Sub Phylum Vertebrata, Mammalia, Primate, Hominidae, Homo sapien sapienSubspecies
- 326. Humans Taxonomic Classification - - - - - - - - Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 327. Domain - Eukarya Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 328. Kingdom - Animalia Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 329. Phylum - Chordata Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 330. Sub-Phylum is vertebrata. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 331. • Sub-Phylum is vertebrata. – Vertebrata have backbone, some primitive organisms in Chordata have a notochord. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 332. Class - Mammalia Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 333. Order – Primate Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 334. Family - Hominidae Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 335. Genus - Homo Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 336. Species – sapien sapien Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 337. Species – sapien sapien subspecies Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 338. Species – sapien sapien subspecies Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Homo sapien means wise man, or knowing man in Latin.
- 348. Note: We get another sapiens so we are Homo sapiens sapiens. It means we are a bit different (sub species) from our 250,000 year old ancestors. Not that much different however (less robust and some differences in the skull and slightly larger brain size). We could still mate with them? That would be a bit awkward I imagine.
- 349. Note: We get another sapiens so we are Homo sapiens sapiens. It means we are a bit different (sub species) from our 250,000 year old ancestors. Not that much different however (less robust and some differences in the skull and slightly larger brain size). We could still mate with them? That would be a bit awkward I imagine.
- 350. • Video Link! (Optional) Khan Academy • Tree of Life (Advanced) • http://www.khanacademy.org/video/taxono my-and-the-tree-of-life?playlist=Biology
- 351. • Video Link! Taxonomy and Classification Crash Course. – Optional and Advanced. – Preview for language. – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=F38BmgPcZ_I
- 352. • Try Again! Try to guess the mystery picture beneath the boxes. – Raise your hand when you think you know. You only get one guess. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 353. “Did you know that I really like good spaghetti.”
- 354. “Did you know that I really like good spaghetti.”
- 360. “If you guessed a guy dressed up as King Phillip than you are right.”
- 361. • You should be close to page 4/5 in your bundle.
- 363. • This PowerPoint is one small part of my Taxonomy and Classification Unit. • A Seven Part 3,000+ Slide PowerPoint full of engaging activities, critical class notes, review opportunities, question, answers, games, and much more. • 19 Page bundled homework that chronologically follows the slideshow for nightly review. Modified version provided as well as answer keys. • 24 pages of unit notes with visuals for students and support professionals. • 2 PowerPoint Review Games with Answer Key • Rubrics, videos, templates, materials list, First Day PowerPoint, guide, and much more. • http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Taxonomy_Classification_Unit. html
- 365. Areas of Focus within The Taxonomy and Classification Unit: Taxonomy, Classification, Need for Taxonomy vs. Common Names, What is a Species?, Dichotomous Keys, What does Classification Use?, The Domains of Life, Kingdoms of Life,The 8 Taxonomic Ranks, Humans Taxonomic Classification, Kingdom Monera, Prokaryotic Cells, Types of Eubacteria, Bacteria Classification, Gram Staining,Bacterial Food Borne Illnesses, Penicillin and Antiseptic, Oral Hygiene and Plaque, Bacterial Reproduction (Binary Fission), Asexual Reproduction, Positives and Negatives of Bacteria, Protista, Plant-like Protists, Animal-like Protists, Fungi-like Protists, Animalia, Characteristics of Animalia, Animal Symmetry, Phylums of Animalia (Extensive), Classes of Chordata, Mammals, Subclasses of Mammals, Characteristics of Mammals, Classes of Fish, Fashion a Fish Project, Animal Poster Project, Fungi, Positives and Negatives of Fungi, Divisions of Fungi (Extensive), Parts of a Mushroom, 3 Roles of Fungi, Fungi Reproduction, Mold Prevention, Plant Divisions, Photosynthesis, Plant Photo Tour, Non Vascular Plants, Algae, Lichens, Bryophytes, Seedless Vascular Plants, Cone Bearing Plants, Flowering Plants, Monocotyledons, Dicotyledons and much more. Full Unit can be found at… http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Taxonomy_Classification_Unit.html
- 368. • Please visit the links below to learn more about each of the units in this curriculum – These units take me about four years to complete with my students in grades 5-10. Earth Science Units Extended Tour Link and Curriculum Guide Geology Topics Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Geology_Unit.html Astronomy Topics Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Astronomy_Unit.html Weather and Climate Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Weather_Climate_Unit.html Soil Science, Weathering, More http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Soil_and_Glaciers_Unit.html Water Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Water_Molecule_Unit.html Rivers Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/River_and_Water_Quality_Unit.html = Easier = More Difficult = Most Difficult 5th – 7th grade 6th – 8th grade 8th – 10th grade
- 369. Physical Science Units Extended Tour Link and Curriculum Guide Science Skills Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Science_Introduction_Lab_Safety_Metric_Methods. html Motion and Machines Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Newtons_Laws_Motion_Machines_Unit.html Matter, Energy, Envs. Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Energy_Topics_Unit.html Atoms and Periodic Table Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Atoms_Periodic_Table_of_Elements_Unit.html Life Science Units Extended Tour Link and Curriculum Guide Human Body / Health Topics http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Human_Body_Systems_and_Health_Topics_Unit.html DNA and Genetics Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/DNA_Genetics_Unit.html Cell Biology Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Cellular_Biology_Unit.html Infectious Diseases Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Infectious_Diseases_Unit.html Taxonomy and Classification Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Taxonomy_Classification_Unit.html Evolution / Natural Selection Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Evolution_Natural_Selection_Unit.html Botany Topics Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Plant_Botany_Unit.html Ecology Feeding Levels Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Ecology_Feeding_Levels_Unit.htm Ecology Interactions Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Ecology_Interactions_Unit.html Ecology Abiotic Factors Unit http://sciencepowerpoint.com/Ecology_Abiotic_Factors_Unit.html
- 370. • More Units Available at… Earth Science: The Soil Science and Glaciers Unit, The Geology Topics Unit, The Astronomy Topics Unit, The Weather and Climate Unit, and The River Unit, The Water Molecule Unit. Physical Science: The Laws of Motion and Machines Unit, The Atoms and Periodic Table Unit, The Energy and the Environment Unit, and The Introduction to Science / Metric Unit. Life Science: The Diseases and Cells Unit, The DNA and Genetics Unit, The Life Topics Unit, The Plant Unit, The Taxonomy and Classification Unit, Ecology: Feeding Levels Unit, Ecology: Interactions Unit, Ecology: Abiotic Factors, The Evolution and Natural Selection Unit and The Human Body Systems and Health Topics Unit. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 371. • Thank you for your time and interest in this curriculum tour. Please visit the welcome / guide on how a unit works and link to the many unit previews to see the PowerPoint slideshows, bundled homework, review games, unit notes, and much more. Thank you for your interest and please feel free to contact me with any questions you may have. Best wishes. • Sincerely, • Ryan Murphy M.Ed • ryemurf@gmail.com
