Renal regulation of metabolic acidosis and alkalosis
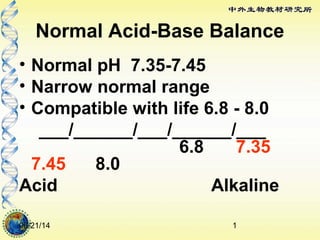
- 1. 06/21/14 1 Normal Acid-Base Balance • Normal pH 7.35-7.45 • Narrow normal range • Compatible with life 6.8 - 8.0 ___/______/___/______/___ 6.8 7.35 7.45 8.0 Acid Alkaline
- 3. 06/21/14 3 Acid & Base • Acid: • An acid is "when hydrogen ions accumulate in a solution" • It becomes more acidic • [H+] increases = more acidity • CO2 is an example of an acid. Base: A base is chemical that will remove hydrogen ions from the solution Bicarbonate is an example of a base.
- 4. 06/21/14 4 Acid and Base Containing Food: • To maintain health, the diet should consist of 60% alkaline forming foods and 40% acid forming foods. To restore health, the diet should consist of 80% alkaline forming foods and 20% acid forming foods. • Generally, alkaline forming foods include: most fruits, green vegetables, peas, beans, lentils, spices, herbs,seasonings,seeds and nuts. • Generally, acid forming foods include: meat, fish, poultry, eggs, grains, and legumes.
- 5. 06/21/14 5 Citric Acid And Lactic Acid Although both citric acid and lactic acid are acids BUT Citric acid leads to Alkalosis while Lactic acid to Acidosis due to metabolism
- 6. 06/21/14 6 Acidoses & Alkalosis • An abnormality in one or more of the pH control mechanisms can cause one of two major disturbances in Acid-BaseAcid-Base balance – AcidosisAcidosis – AlkalosisAlkalosis
- 7. 06/21/14 7 Acidosis • Acidosis is excessive blood acidity caused by an overabundance of acid in the blood or a loss of bicarbonate from the blood (metabolic acidosis), or by a buildup of carbon dioxide in the blood that results from poor lung function or slow breathing (respiratory acidosis). • Blood acidity increases when people ingest substances that contain or produce acid or when the lungs do not expel enough carbon dioxide.
- 8. 06/21/14 8 Metabolic Acidosis • Bicarbonate deficit - blood concentrations of bicarb drop below 22mEq/L • Causes: –Loss of bicarbonate through diarrhea or renal dysfunction –Accumulation of acids (lactic acid or ketones) which may occur in starvation or high fever. –Failure of kidneys to excrete H+
- 9. 06/21/14 9 Metabolic Acidosis(Cont) - metabolic balance before onset of acidosis pH 7.4 metabolic acidosis pH 7.1 HCO3 - decreases because of excess presence of ketones, chloride or organic ions - body’s compensation- hyperactive breathing to “ blow off ” CO2 - kidneys conserve HCO3 - and eliminate H+ ions in acidic urine -therapy required to restore metabolic balance
- 10. 06/21/14 10 Alkalosis • Alkalosis is excessive blood alkalinity caused by an overabundance of bicarbonate in the blood or a loss of acid from the blood (metabolic alkalosis), or by a low level of carbon dioxide in the blood that results from rapid or deep breathing (respiratory alkalosis).
- 11. 06/21/14 11 Metabolic alkalosis • Metabolic alkalosis is due to the gain of base or the loss of acid. The primary abnormality is an increased HCO3. • Cause • Caused from an increase in bicarbonate in the blood because of ingestion of excess bicarbonate in the form of an antacid (Tums), eating excess fruits (vegetarian diets and fat diets), loss of acid from vomiting, or loss of potassium from diuretics.
- 12. 06/21/14 12 Metabolic alkalosis(contd) - metabolic balance before onset of alkalosis - pH = 7.4 metabolic alkalosis pH = 7.7 - HCO3 - increases because of loss of chloride ions or excess ingestion of NaHCO3 - body’s compensation - breathing suppressed to hold CO2 - kidneys conserve H+ ions and eliminate HCO3 - in alkaline urine - therapy required to restore metabolic balance
- 13. 06/21/14 13 Effects Of Ph Change On Cell : • Acidosis and alkalosis are not diseases but rather are the results of a wide variety of disorders • pH changes have dramatic effects on normal cell function – 1)1) Changes in excitability of nerve and muscle cells – 2)2) Influences enzyme activity – 3)3) Influences KK++ levels
- 14. 06/21/14 14 RESPONSES TO ACIDOSIS AND ALKALOSIS • Mechanisms protect the body against life- threatening changes in hydrogen ion concentration are – 1) Buffering Systems in Body Fluids1) Buffering Systems in Body Fluids – 2) Respiratory Responses2) Respiratory Responses – 3) Renal Responses3) Renal Responses – 4) Intracellular Shifts of Ions4) Intracellular Shifts of Ions
- 15. 06/21/14 15 RESPONSES TO ACIDOSIS AND ALKALOSIS • Buffer system: temporary solution • ~Respiratory mechanism provide short time regulation • ~Renal mechanism : permanent solution
- 16. 06/21/14 16 • RENAL REGULATION OF METABOLIC ACIDOSIS AND ALKALOSIS
- 17. 06/21/14 17 Renal Regulation (Contd): • Only the kidneys can rid the body of acids generated by cellular metabolism (nonvolatile or fixed acids) • The kidney in response: – To AcidosisTo Acidosis • Retains bicarbonate ions and eliminates hydrogen ions – To AlkalosisTo Alkalosis • Eliminates bicarbonate ions and retains hydrogen ions
- 18. 06/21/14 18 Renal Regulation (Contd): • To maintain normal pH, the kidneys must perform 2 physiologic functions. • 1.Reabsorb all the filtered HCO3: • A function principally of the proximal tubule. • 2. To excrete the daily H+ load: • A function of the collecting duct.
- 19. 06/21/14 19 Renal Regulation (Contd): • Chemical buffers can tie up excess acids or bases, but they cannot eliminate them from the body • The lungs can eliminate carbonic acid by eliminating carbon dioxide • Only the kidneys can rid the body of metabolic acids (phosphoric, uric, and lactic acids and ketones) and prevent metabolic acidosis • The ultimate acid-base regulatory organs are the kidneys • The most important renal mechanisms for regulating acid-base balance are conserving (reabsorbing) or generating new bicarbonate ions and excreting bicarbonate ions • Losing a bicarbonate ion is the same as gaining a hydrogen ion; reabsorbing a bicarbonate ion is the same as losing a hydrogen ion
- 20. 06/21/14 20 Renal Regulation (Contd): Reabsorption of Bicarbonate: • Plasma bicarbonate is freely filtered at the glomerulus. • Carbonic acid formed in filtrate dissociates to release carbon dioxide and water • Carbon dioxide then diffuses into tubule cells, where it acts to trigger further hydrogen ion secretion • For each hydrogen ion secreted, a sodium ion and a bicarbonate ion are reabsorbed by the PCT cells • Secreted hydrogen ions form carbonic acid • Thus, bicarbonate disappears from filtrate at the same rate that it enters the peritubular capillary blood
- 21. 06/21/14 21 Reabsorption of Bicarbonate Ions:
- 22. 06/21/14 22 Renal Regulation (Contd): • Generating New Bicarbonate Ions: • Two mechanisms carried out by tubule cells generate new bicarbonate ions • Both involve renal excretion of acid via secretion and excretion of hydrogen ions or ammonium ions (NH4+)
- 23. 06/21/14 23 Renal Regulation (Contd): Excretion Of Buffered H Ions: Alpha intercalated cells of the renal tubules can synthesize new bicarbonate ions while excreting more hydrogen ions.
- 24. 06/21/14 24 Excretion Of Buffered H+:(Cont) • In response to acidosis hydrogen ions must be counteracted by generating new bicarbonate • Kidneys generate bicarbonate ions and add them to the blood • An equal amount of hydrogen ions are added to the urine • Dietary:The excreted hydrogen ions must bind to buffers (phosphate buffer system) in the urine and excreted • Bicarbonate generated is then moved into the interstitial space via a cotransport system • Passively moved into the peritubular capillary blood
- 25. 06/21/14 25 Synthesis Of New Bicarbonate & Excretion Of Buffered H+:
- 26. 06/21/14 26 Renal Regulation (Contd): Excretion Of Ammonium Ion : • Ammonium ions are weak acids. • This method uses ammonium ions produced by the metabolism of glutamine in PCT cells • Each glutamine metabolized produces two ammonium ions and two bicarbonate ions • Bicarbonate moves to the blood and ammonium ions are excreted in urine
- 28. 06/21/14 28 ACIDIFICATION OF URINE BY EXCRETION OF AMMONIA Capillar y Distal Tubule Cells Tubular urine to be excreted NH2 H + NH3 NH2 H + NH3 WHAT HAPPENS NEXT?
- 29. 06/21/14 29 Capillar y Distal Tubule Cells Tubular Urine NH3 Na + Cl- + H2CO 3 HCO3 - + NaCl NaHCO3 Click Mouse to Start Animation NaHCO3 NH3Cl- H + NH4Cl Click Mouse to See Animation Again Notice the H+ - Na+ exchange to maintain electrical neutrality ACIDIFICATION OF URINE BY EXCRETION OF AMMONIA Dissociation of carbonic acid
- 30. 06/21/14 30 Renal Regulation (Contd): • Bicarbonate Ion Secretion • When the body is in alkalosis, tubular cells secrete bicarbonate ions and reclaim hydrogen ions and acidify the blood • This mechanism is the opposite of bicarbonate ion reabsorption process
- 31. 06/21/14 31 Bicarbonate Ion Secretion
- 32. 06/21/14 32 Daily Reabsorption of HCO-3 By Kidney: • 85% HCO-3 reabsorption (H+ Secretion) occurs in PCT (proximal convuluted tubule) • 10% HCO-3 reabsorption (H+ secretion) occurs in thick ascending LOH • 4.9% (approx 5%) reabsorption (H+ secretion) occurs in DCT & CT. • For each HCO3 reabsorbed, there must be one H+ ion secreted.
- 33. 06/21/14 33
