23204958
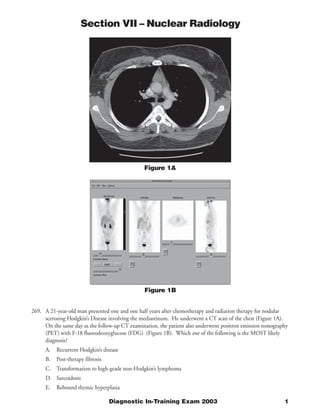
- 1. Section VII – Nuclear Radiology Figure 1A Figure 1B 269. A 21-year-old man presented one and one half years after chemotherapy and radiation therapy for nodular scerosing Hodgkin’s Disease involving the mediastinum. He underwent a CT scan of the chest (Figure 1A). On the same day as the follow-up CT examination, the patient also underwent positron emission tomography (PET) with F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) (Figure 1B). Which one of the following is the MOST likely diagnosis? A. Recurrent Hodgkin’s disease B. Post-therapy fibrosis C. Transformation to high-grade non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma D. Sarcoidosis E. Rebound thymic hyperplasia Diagnostic In-Training Exam 2003 1
- 2. Section VII – Nuclear Radiology Question #269 Findings: The CT scan of the chest at the time of presentation (Figure 1A) demonstrates a small soft tissue mass in the anterior mediastinum in the midline, anterior to the great vessels. The repeat CT obtained 15 months later (Figure 1B) appears essentially unchanged, with a persistent soft tissue mass in the anterior mediastinum. The FDG PET scan performed at the time of the follow-up CT (Figure 1C) is normal, without evidence of lymphadenopathy in the neck, chest, abdomen, or pelvis. In particular, there is no increased FDG uptake in the region of the anterior mediastinal mass noted on the CT studies. Rationales: A) Incorrect. In the case of Hodgkin’s disease resistant to chemotherapy, persistent and/or more extensive lymphadenopathy within the chest would be anticipated, as well as possible other new sites of involvement. None of these findings are evident in the current case, in which the PET scan is normal. B) Correct. A residual soft tissue mass on CT secondary to post-treatment fibrosis is the most likely explanation for the findings in this case. FDG PET imaging is more specific than CT for the detection of recurrence in lymphoma. The absence of increased FDG uptake in the patient’s persistent anterior mediastinal mass is strong evidence against the presence of residual or recurrent active disease C) Incorrect. De-differentiation into anaplastic lymphoma is not common in Hodgkin’s disease in young adults, and represents a far less likely explanation for the findings in this case than post-treatment fibrosis and scarring. D) Incorrect. The findings in this case are not suggestive of active sarcoidosis. Like other forms of granulomatous disease, sarcoidosis is a potential cause for a false positive FDG PET scan, not a false negative study. Therefore, if the mediastinal mass on the CT studies was due to sarcoidosis, then a focal area of increased FDG uptake in this region would be expected. Furthermore, the distribution of adenopathy on the CT studies is not typical for sarcoidosis, which usually involves the paratracheal and hilar regions, and may affect the pulmonary parenchyma. E) Incorrect. Thymic hypertrophy can occur following treatment for lymphoma of the chest, particularly in young adult patients. The location of the CT findings is reasonable for thymic hypertrophy, although the configuration of the soft tissue mass is not classic in appearance. Furthermore, in such cases there is commonly mild to moderate increased FDG uptake within the thymus gland, a finding not present in this case. Thus, while not excluded, thymic hypertrophy is a less likely etiology for the findings in this case than post-treatment fibrosis and scarring. Citations: Jerusalem G, et. al.: Blood 1999;94:429-433. 2 American College of Radiology
- 3. Section VII – Nuclear Radiology Figure 2 270. A 44-year-old woman underwent I-131 whole body imaging, 7 days following administration of a therapeutic dose of I-131 sodium iodide for a well-differentiated thyroid carcinoma (Figure 2). Based upon the appear- ance of the scan, which one of the following is CORRECT? A. The tumor most likely is a follicular carcinoma B. The patient has diffuse hepatic metastases C. The therapeutic I-131 dose should have been 30 mCi. D. The patient is a candidate for adjunct chemotherapy E. A follow-up whole body I-131 scan should be obtained in 3 years Diagnostic In-Training Exam 2003 3
- 4. Section VII – Nuclear Radiology Question #270 Findings: Post-therapy whole body I-131 images demonstrate multiple foci of functioning thyroid tissue in the thyroid bed, as well as an additional focus located more superiorly in the neck, to the left of midline. Additional foci of uptake consistent with skeletal metastases are noted in the region of the right shoulder, both proximal femora (right > left) and in the mid-thoracic and lower lumbar spine. Small foci of abnormal tracer uptake are noted in the soft tissue superolateral to the right hip and in the lower abdomen, to the right of midline posteriorly. These latter lesions could also represent additional skeletal metastases. Rationales: A) Correct. The patient has evidence of widely metastatic well-differentiated thyroid carcinoma, involving the thyroid bed, cervical lymph nodes, and skeleton. Statistically, the most likely histologic type to produce these findings is follicular carcinoma. Papillary and mixed papillary-follicular carcinoma is more common, but less commonly metastasizes to the skeleton. Anaplastic and medullary carcinoma are less well differentiated, and are unlikely to accumulate I-131. B) Incorrect. The scan demonstrates mild diffuse hepatic uptake. This finding is typically seen on post-therapy imaging, especially in patients with significant amounts of residual functioning thyroid tissue present. It is most often secondary to hepatic uptake of iodinated thyroid hormone, a normal metabolic process. Hepatic metastases are uncommon in well-differentiated thyroid carcinoma, and when present, are more likely to demonstrate an irregular or focal distribution, which is not evident in this case. C) Incorrect. The patient has definite evidence of skeletal metastases, indicative of advanced Stage IV disease. This study is not consistent with Stage I disease. D) Incorrect. Most authorities agree that patients with well-differentiated thyroid carcinoma and evidence of residual or recurrent disease should be treated with I-131 sodium iodide as long as there is evidence of I-131 uptake by the lesions, which indicates the potential for cure or at least significant reduction in the extent of disease. This recommendation is particularly true in patients with widespread disease, as in the current case. I-131 is not only efficacious in such patients, but is also associated with significantly lower morbidity than external beam radiotherapy. I-131 therapy can also be efficacious in patients with well-differentiated thyroid carcinoma and negative diagnostic I-131 whole body scans, but elevated serum thyroglobulin levels. In such patients, I-131 uptake by metastases may be evident only on post-therapy images. External beam radiotherapy is appropriately reserved for patients whose lesions do not actively take up I-131, who have undifferentiated histologic types of thyroid cancer or who demonstrate evidence of de-differentiation of the tumor. E) Incorrect. In general, patients are maintained on thyroid hormone replacement, followed up with repeat diagnostic whole body I-131 scans annually and monitored by serum thyroglobulin levels between scans. Treating no more frequently than annually is usually sufficient for disease control, and reduces the likelihood of hematologic or pulmonary toxicity. In cases in which there is clinical evidence of rapidly progressive disease, the interval between scans can be reduced to 6 months. In a patient with widespread metastases, such as the present case, a three-year follow-up interval is far too long, and would be inappropriate, potentially permitting significant disease progression. Citations: Mettler FA, Jr. and Guiberteau MJ: Essentials of Nuclear Medicine Imaging, 4th ed., W. B. Saunders Co., Philadelphia, 1998, pp. 121-125. 4 American College of Radiology
- 5. Section VII – Nuclear Radiology Figure 3A Figure 3B 271. A 20-year-old woman had massive intracranial bleeding during surgery for resection of a craniopharyngioma, and is now comatose. Radionuclide flow studies and delayed brain imaging using Tc-99m glucoheptonate were performed following surgery (Figures 3A and 3B) and repeated the following day (Figures 3C and 3D). Based upon these images, which one of the following is CORRECT? A. Both studies demonstrate findings consistent with brain death B. Neither study demonstrates findings consistent with brain death C. Radionuclide findings of brain death are present only on the second study D. Both studies are indeterminate for the presence of brain death E. Follow-up magnetic resonance imaging is necessary to confirm the presence of brain death Diagnostic In-Training Exam 2003 5
- 6. Section VII – Nuclear Radiology Figure 3C Figure 3D 6 American College of Radiology
- 7. Section VII – Nuclear Radiology Question #271 Findings: The first study (Figures 3A and 3B) demonstrates severely reduced intracerebral perfusion, with no visualization of the intracerebral vessels and only questionable visualization of the sagittal sinus on the flow study. However, the delayed static images demonstrate definite visualization of the sagittal and both transverse sinuses. The repeat study performed the following day (Figures 3C and 3D) demonstrates interval deterioration in cerebral perfusion. The flow study again demonstrates no definite evidence of intracerebral perfusion, now without visualization of the intracerebral vessels or the dural sinuses. A “hot nose” sign is also present, another indirect indication of severely reduced perfusion of the internal carotid circulation as compared to the external carotid circulation. A focal area of increased uptake is noted in the posterior scalp region on the static images, most likely secondary to inflammation and dependent edema in this region. There has been interval disappearance of sagittal and transverse sinus visualization, with only questionable faint activity noted in the region of the posterior aspect of the sagittal sinus. Rationales: A) Incorrect. While cerebral perfusion is significantly impaired on both studies, the visualization of the dural sinuses on the first study is not consistent with the radionuclide diagnosis of brain death. B) Incorrect. As noted above, the first study is not diagnostic of brain death. However, the second study demonstrates no evidence of intracerebral vessel visualization nor definite visualization of the dural sinuses, and demonstrates the corroborative “hot nose” sign. Thus, the 2nd study is consistent with brain death. C) Correct. As discussed in A and B above, the second study is consistent with brain death, representing an interval change compared to the study performed on the previous day. D) Incorrect. The second study is consistent with brain death. The findings of the radionuclide brain scan are correlated with other clinical data (physical findings, EEG, etc.) in order to make a final determination of clinical brain death. E) Incorrect. Confirmation of brain death is done by correlating the brain scan findings with other clinical data, primarily physical findings, and the EEG. Magnetic resonance imaging is not a sensitive indicator of brain death. Citations: Sandler MP, Coleman RE, Wackers FJTh, Patton JA, Gottschalk A and Hoffer PB (eds.): Diagnostic Nuclear Medicine, 3rd Ed., Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, 1996, pp. 1091-1097. Diagnostic In-Training Exam 2003 7
- 8. Section VII – Nuclear Radiology Figure 4A Figure 4B 272. A 60-year-old woman presented with hypercalcemia and a history of a renal calculus. Tc-99m sestamibi images of the neck and mediastinum were obtained at 30 minutes and 3 hours post-injection, including (clockwise from upper left) anterior neck, anterior neck with “cold” sternal notch marker, anterior neck and chest, pinhole neck, left anterior oblique neck and chest and right anterior oblique neck and chest (Figures 4A and 4B). Which one of the following is the LEAST likely etiology for the findings in this case? A. Thyroid adenoma B. Parathyroid hyperplasia C. Parathyroid adenoma D. Papillary carcinoma of the thyroid E. Colloid goiter 8 American College of Radiology
- 9. Section VII – Nuclear Radiology Question #272 Findings: Tc-99m sestamibi images of the neck and mediastinum demonstrate normal uptake by the thyroid and salivary glands on the initial 30-minute post-injection images (Figure 4A). Normal left ventricular myocardial activity and hepatic activity are also evident. There is a superimposed focal area of increased tracer uptake noted overlying the left lower pole of the thyroid. The 3 hour delayed images (Figure 4B) demonstrate substantial washout of activity from the thyroid, with a persistent focus of increased uptake overlying the left lower pole region. Rationales: A) Incorrect. A focal thyroid adenoma is a common cause of a false positive radionuclide parathyroid scan. In this clinical setting, a parathyroid adenoma is more likely, but a thyroid adenoma cannot be excluded based on the imaging findings in this case alone. B) Incorrect. Parathyroid hyperplasia typically produces multiple foci of less striking increased tracer uptake in the neck, in the expected locations of the parathyroid glands, with the intensity of uptake usually less than is present in this case. Nonetheless, it is definitely in the differential diagnosis for focally increased sestamibi uptake in the neck, especially in a patient with clinical evidence of hyperparathyroidism. C) Incorrect. The findings in this case are classic for a focal parathyroid adenoma, which is in fact the most likely diagnosis in this case. A solitary parathyroid adenoma is found to be the cause of primary hyperparathyroidism in approximately 85% of cases. D) Incorrect. Papillary carcinoma of the thyroid is another cause for false positive Tc-99m sestamibi parathyroid scintigraphy studies. The clinical setting of the case again is more suggestive of parathyroid adenoma, but a thyroid malignancy cannot entirely be excluded. E) Correct. Of all the choices indicated, colloid goiter is the least likely cause for the findings in this case. A colloid goiter is typically a multifocal process, associated with thyroid enlargement and inhomogeneous uptake on early images. In addition, colloid goiter is unlikely to be associated with focal area(s) of significantly increased sestamibi uptake, as is present in this case. Citations: Sandler MP, Coleman RE, Wackers FJTh, Patton JA, Gottschalk A and Hoffer PB (eds.): Diagnostic Nuclear Medicine, 3rd Ed., Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, 1996, pp. 998-1011. Diagnostic In-Training Exam 2003 9
- 10. Section VII – Nuclear Radiology Figure 5 273. A 55-year-old woman presented with abdominal pain and weight loss. You are presented with 48-hour anterior and posterior whole body In-111 pentetreotide images (Figure 5). Which one of the following is the MOST likely diagnosis? A. Pheochromocytoma B. Carcinoid tumor of the small bowel C. Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma D. Islet cell carcinoma E. Adenocarcinoma of the colon 10 American College of Radiology
- 11. Section VII – Nuclear Radiology Question #273 Findings: Forty-eight hour whole body In-111 pentetreotide images demonstrate multiple focal areas of increased tracer uptake within both lobes of the liver, consistent with multiple focal neuroendocrine tumor hepatic metastases. There is also a large focal area of increased uptake in the epigastric region, just to the right of midline, in the expected location of the body of the pancreas. No other focal lesions are demonstrated in the abdomen or in the chest. Rationales: A) Incorrect. Pheochromocytoma is a neoplasm that may demonstrate increased uptake of octreotide analogs, and the focal lesion in the right upper quadrant could conceivably represent a right adrenal lesion. However, widespread hepatic metastases are not as common as in carcinoid, islet cell carcinoma, or small cell lung carcinoma, and pheochromocytoma is therefore a less likely etiology for the findings demonstrated. B) Incorrect. Carcinoid is a highly octreotide-avid neoplasm in general, and often produces multiple hepatic metastases as well. The primary lesion is most often located within the small bowel or lung, neither of which areas demonstrate focal lesions in this case. Therefore, while not unlikely, this diagnosis is less likely than an islet cell pancreatic tumor. C) Incorrect. Again, small cell lung carcinomas may demonstrate neuroendocrine features, and may have significant somatostatin receptor activity. However, the pattern of involvement in this case within the liver and epigastric region, without a focal pulmonary or mediastinal lesion, make small cell lung carcinoma less likely than islet cell tumor or carcinoid. D) Correct. Islet cell carcinoma is the most likely diagnosis in this case. The focal lesion in the epigastric region is secondary to uptake within the primary neoplasm in the body of the pancreas. Multiple hepatic metastases containing somatostatin receptor activity are also common in this entity. There is no evidence of focal lesions within the lungs or mediastinum to suggest small cell carcinoma of the lung and no focal extrahepatic abdominal lesions in the region of the small bowel to suggest a primary lesion in that location. E) Incorrect. Medullary carcinoma of the thyroid is often associated with somatostatin receptor activity, but less so than carcinoid or islet cell pancreatic tumors. There is also no focal increased tracer uptake in the neck to suggest a primary thyroid lesion, and widespread hepatic metastases are less common than in carcinoid or islet cell tumor. Citations: Mettler FA, Jr. and Guiberteau MJ: Essentials of Nuclear Medicine Imaging, 4th ed., W. B. Saunders Co., Philadelphia, 1998, pp. 379-382. Diagnostic In-Training Exam 2003 11
