Power control devices
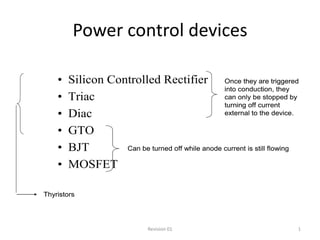
- 1. Power control devices • Silicon Controlled Rectifier Once they are triggered into conduction, they • Triac can only be stopped by turning off current • Diac external to the device. • GTO • BJT Can be turned off while anode current is still flowing • MOSFET Thyristors Revision 01 1
- 2. Power devices - SCRs • SCRs can switch high currents from about 1A – 2000A • SCRs turn ON when the +ve potential is applied to the gate terminal provided the anode is +ve with respect to the cathode. • An SCR can only turn off if the anode current is reduced below its holding value with the gate open. Revision 01 2
- 3. NE185 Power Control Systems Silicon controlled rectifier (thyristor) Anode (A) Gate (G) Large Current Small Current to “trigger” SCR Cathode (K) Revision 01 3
- 4. Silicon controlled rectifier (thyristor) Anode (A) Gate (G) Large Current Small Current to “trigger” SCR Cathode (K) Note: The process of turning an SCR ON is called TRIGGERING The process of turning an SCR OFF is called COMMUTATION Revision 01 4
- 5. Silicon controlled rectifier (thyristor) Anode (A) Gate (G) Large Current Small Current to “trigger” SCR Cathode (K) Note: The ONLY way to turn them off is to stop the current flowing. They must then be re-triggered on. Revision 01 5
- 6. Silicon controlled rectifiers Revision 01 6
- 7. Revision 01 7
- 8. Revision 01 8
- 9. Silicon controlled rectifier Revision 01 9
- 10. Silicon controlled rectifier Revision 01 10
- 11. Silicon controlled rectifier Anode Anode P P N N N Gate P P P Gate N N Cathode Cathode 4-layer device Revision 01 11
- 12. Silicon controlled rectifier Anode Q1 Load Gate Q2 Cathode Revision 01 12
- 13. SCR control: phase control Silicon Controlled Rectifier (Thyristor) A N Load Current Load Current required for triggering SCR Revision 01 13
- 14. SCR control: phase control Silicon Controlled Rectifier (Thyristor) A N Load Current Load Current required for triggering SCR Lower resistance on potentiometer. Capacitor charges quicker Revision 01 14
- 15. SCR control: phase control Silicon Controlled Rectifier (Thyristor) A N Load Current Load Current required for triggering SCR Higher resistance on potentiometer. Capacitor charges slower Revision 01 15
- 16. SCR control Silicon Controlled Rectifier (Thyristor) A N Control Control Load SCR’s only conduct in one direction. Above is one way top overcome this. Revision 01 16
- 17. TRIAC T2 GATE T1 Revision 01 17
- 18. 10k T2 500k 120V ST4 G T1 SC151D 0.27µF T1 T2 G TRIAC Light Dimmer Diac Revision 01 18
- 19. Phase control SCR1 conducts +V 90° 180° 270° 360° -V SCR2 conducts Revision 01 19
- 20. Phase control SCR1 conducts +V 90° 180° 270° 360° -V SCR2 conducts Revision 01 20
- 21. Phase control SCR1 conducts +V 90° 180° 270° 360° -V SCR2 conducts The main disadvantage of Phase Control (indeed SCR control) is RFI. Revision 01 21
- 22. Diac characteristic curves +IA FORWARD VBR(R) IHOLDING -VA +VA IHOLDING VBR(F) REVERSE 28-36V typical - IA Revision 01 22
- 23. Gate turn-off thyristers (GTO’S) • A gate turn-off switch, also known as a gate-controlled switch (GCS) or gate turn-off thyristor (GTO), is similar to an SCR but can be turned off by a negative signal on the gate terminal. GTOs generally handle much lower currents than SCRs Anode Gate Cathode Revision 01 23
- 24. Transistor • BJT Transistors • A transistor is a device which acts like a controlled valve. The current flow permitted can be controlled. • The bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a three-terminal electronic valve - the output (collector) terminal current- voltage characteristics are controlled by the current injected into the input port (base). The BJT is a semiconductor device constructed from two pn junctions. There are two types of BJT: pnp and npn. Revision 01 24
- 25. Transistor • A transistor may be thought of as an electronic tap able to control a large flow of electrons with only small variations of the 'handle'. The 'handle' in the case of a transistor is called the "base". The in and out 'pipes' are called the "emitter" and the "collector".Voltage changes at the base of the transistor result in changes to the flow of electricity through the transistor. • A transistor can be thought of as a 'tap'. • Symbol for a Transistor Revision 01 25
- 26. Transistor operation 1. Bi-Junction Transistor (BJT) P Collector N Base NPN P Emitter Emitter N P Base PNP N Collector Transistors are three layer devices Revision 01 26
- 27. Transistor operation 1. Bi-Junction Transistor (BJT) Collector Base Large current NPN Small current Emitter Small current Emitter Base Large current PNP Collector BJT’s are current operated devices Revision 01 27
- 28. Transistor operation 2. MOSFET Transistor Drain Drain Drain Drain Gate Gate Gate Gate Source Source Source Source N-Channel P-Channel N-Channel P-Channel Enhancement Enhancement Enhancement Enhancement Mode only Mode only /Depletion /Depletion Mode Mode Revision 01 28
- 29. Transistor operation 2. MOSFET Transistor Positive Drain A positive voltage RDS off = MΩ (around +5V) on the Gate RDS on = <0.1Ω gate turns the transistor fully on Source Negative In other words, they are VOLTAGE DRIVEN DEVICES. Remember?… BJT’s are CURRENT DRIVEN DEVICES. Revision 01 29
- 30. Transistor operation • Advantages of transistors over thyristors: – Lower voltage drop across transistors when conducting (0.1V as compared to 2V) This causes less heat to be developed. – Faster switching times – (less time to turn on = less heat developed while turning on) – Can easily be turned off. Revision 01 30
- 31. Revision 01 31