Floor of the mouth
- 1. FLOOR OF THE MOUTH. Dr Nida Sumra
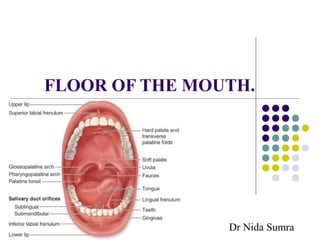
- 2. The floor of the mouth is a small horseshoe-shaped region situated beneath the movable part of the tongue and above the muscular diaphragm formed by the mylohyoid muscles and above this diaphragm is the genohyoid muscle.
- 3. Sublingual gland and its duct. The deep part of the submandibular gland and its duct. Lingual frenum Deep lingual artery and veins. Lingual nerve.
- 5. Inner surface of the mandible. Superior and inferior genial tubercles. Mylohyoid line. Sublingual fossa. Submandibular fossa.
- 6. Hyoid bone. A body. Two larger greater horns (greater cornu.) Two conical lesser horns (lesser cornu.) Hyoid bone connects floor of the mouth with the pharynx behind and the larynx below.
- 7. Inferior surface of the tongue. The inferior surface of the tongue is covered with a thin transparent mucous membrane through which one can see the underlying veins A sublingual caruncle (papilla) - opening of the submandibular duct 1- frenulum, 2- lingual vein, dashed-circle- sublingual gland. Arrow- Wharton's duct opening,
- 8. Lingual frenum. The inferior surface of the tongue is connected to the floor of the mouth by a midline fold called the frenulum of the tongue. The frenulum allows the anterior part of the tongue to move freely.
- 9. Ankyloglossia. Tongue tie. Commonly congenital in origin due to abnormally short and thick lingual frenulum . It restricts tongue movements. Treatment is frenulectomy.
- 10. Frenulectomy.
- 11. Diagram of the human head at the level of the first molars, depicting the most important structures in relation to periodontal surgery.
- 12. MUSCLES.
- 13. Mylohyoid. Geniohyoid. ORIGIN - Mylohyoid line of the mandible. INSERTION – Median fibrous raphe and adjacent part of hyoid body. ORIGIN - Inferior mental spines of mandible. INSERTION - Body of the hyoid bone. .
- 14. Functions. Contributes structural support to the floor of the oral cavity. Participates in elevating and pulling forward the hyoid bone. When the hyoid bone is in fixed position depress the mandible and open the mouth. Mainly pulls the hyoid bone. When the hyoid bone is fixed they can act with the mylohyoid muscle to depress the mandible. MYLOHYOID GENIOHYOID
- 15. Vascular supply. sublingual branch of the lingual artery, The maxillary artery, via the mylohyoid branch of the inferior alveolar artery, The submental branch of the facial artery. lingual artery (sublingual branch). MYLOHYOID GENIOHYOID.
- 16. Innervation. Geinohyoid - C1 via the hypoglossal nerve. Mylohyoid - Nerve to the mylohyoid from the inferior alveolar branch of the mandibular nerve.
- 17. Gateway into the floor of the mouth.
- 18. The free posterior border of the mylohyoid muscle on each side forms one of the three margins of a larger triangular aperture - a major route by which structures in the upper neck and infra temporal fossa of the head pass to and from structures in the floor of the oral cavity. Structures that pass through the aperture - includes muscles (hyoglossus , styloglossus ) ,vessels (lingual artery and vein) , nerves (lingual , hypoglossal , glossopharyngeal) and lymphatics. The submandibular gland.
- 19. VASCUALTURE.
- 20. Arteries. Veins. The major artery that supplies the oral mucosa of the floor of the mouth is the Lingual artery. Deep lingual veins Dorsal lingual vein.
- 21. Lingual nerve. Originates in the infra temporal fossa and passes anteriorly into the floor of the oral cavity.
- 22. Lymphatics. Submental nodes. Submandibular nodes. Drainage from the above two into the deep cervical nodes.
- 23. GLANDS.
- 24. Submandibular gland. Hook shaped. Divided into deeper and superficial part by the mylohyoid muscle. Submandibular duct emerges from the deep part and lies on the summit of the sublingual papilla besides the frenulum of the tongue.
- 25. Sublingual gland. Almond shaped. Lies against the medial surface of the mandible where it forms the sublingual fossa. Drains via numerous small ducts.
- 26. Chorda tympani. Presynaptic parasympathetic secretomotor fibres conveyed from the facial nerve to the lingual nerve by the chorda tympani nerve which synapse with post synaptic neurons in the submandibular ganglion.
- 28. Boundaries. Anteriorly – lingual surface of the mandible. Posteriorly – body of the hyoid bone. Superiorly – oral mucosa. Inferiorly – mylohyoid muscle. Medially – muscles of the tongue. Laterally – lingual surface of the mandible. CONTENTS. Sublingual gland Whartons duct Sublingual artery and nerve Lingual nerve
- 29. Source of infection and neighbouring spaces. Schematic diagram of the relationship of the tooth roots to the sublingual, submandibular, and buccal spaces. Infection extending through the lingual cortex from premolar and molar teeth will involve the sublingual space, whereas infection from molar teeth will involve the submandibular space. (Courtesy of Indiana University School of Medicine Office of Visual Media, Indianapolis, IN; with permission.)
- 30. Clinically. Swelling is seen on the anterior part of the floor of the oral cavity. Interferes with swallowing and is extremely painful. Infections might pass anteromedially across the genial muscles into the sublingual space on the other side. Infections can also spread to submental and submandibular spaces and lead to ludwigs angina. Sublingual space also communicates with the parapharyngeal space at the posterior border of the mylohyoid muscle lateral to the hyoid bone.
- 32. Haemorrhage. The floor of the mouth is richly vascularised by a number of branches of submental and sublingual arteries. During a dental implant procedure in the anterior zone of the mandible perforation of the lingual cortex may invade the floor of the mouth and hence damage structures within the sublingual space.
- 33. Sublingual haematoma. Sublingual haematoma also known as pseudo ludwigs phenomenon is an entity commonly described in patients on anticoagulant therapy. Spontaneous sublingual haematoma is a rare subtype. It is thought to be due to aneursymal changes in facial or lingual arteries occurring mostly in elderly hypertensive patients
- 34. Exotosis. Found along the body of the mandible and most commonly in the region of canines and premolars above the mylohyoid muscle medial to molar roots. Large tori can interfere with flap placement or correction of infrabony defects through osseous recontouring. Tissue overlying tori can be very thin and can be easily torn during flap reflection
- 35. Haematomas. Floor of the mouth haematomas with periodontal surgery with torus and exotoses reduction is a common occurrence The haematoma occurring as a result of extensive bone reduction on the lingual surface of mandible is worrisome because of the anatomic site and the potential for serious infection through loose aerolar facial planes. Vascular injury can lead to serious morbidity and potential mortality as a result of airway obstruction due to immense enlargement of sublingual haematoma View of the hematoma on the morning after periodontal surgery( torus reduction) on the mandibular left quadrant. Note the edema and erythema of the floor of the mouth (journal of contemporary dental practice Vol 8 num-3 march 1 2007)
- 36. Treatment. Administration if antibiotics preoperatively NSAID regimen Application of pressure on surgical site Seven days after periodontal surgery. Note the dramatic improvement
- 37. Significant soft tissue oedema of the neck. Seen here is the large expanding haematoma in the floor of the mouth resulting in elevation and protrusion of the tongue. Bony window resolution of the anterior mandible that demonstrates the site of perforation lingual to site number 25 Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2006; 35: 961–964 47-year-old female presented to her dentist for extraction of her remaining mandibular teeth (#s 21–28) and placement of 4 immediate endosseous implants
- 38. Arteriovenous malformation. Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) is a vascular abnormality resulting in an abnormal connection between an artery and a vein without capillary connections. An AVM in the floor of the mouth has been reported in an elderly male supplied by multiple vessels and it caused difficulty in speaking and swallowing. (J Craniofac Surg. 2012 Mar;23(2):e86-8.)
- 39. PATHOLOGIES.
- 40. Sialolith. Salivary calculi or stones may obstruct salivary flow. Usually occurs in the submandibular gland because of the tortuous course of the duct and because of the viscosity of the secretions. Acute symptoms occur during mealtime. Secondary infection may occur.
- 41. Dermoid cyst. Painless dome shaped dome shaped mass. Dough like consistency and tongue is slightly elevated. Slow growth and treatment is surgical enuleation. Epidermoid cyst is the same but without skin appendages.
- 42. Ranula. Mucocele arising in the floor of the mouth. Unilateral , dome shaped, fluctuant and painless. Plunging or cervical ranula extend beyond the mylohyoid muscle beyond the sublingual space and involves the submandibular space and adjacent structures.
- 43. Conclusion. Consideration of the surgical anatomy serves as a basis for surgical procedures involving periodontal tissues and implants. Damage to nerves, such as the mental nerve, the mandibular nerve and the lingual nerve can be avoided with proper technique. Treatment planning should include three-dimensional radiographs when these structures are likely to be within the vicinity of surgical approaches. Inadvertent surgical incision of major blood vessels can be avoided by knowledge of their anatomic positioning.
- 44. REFERENCES- GRAYS ANATOMY BD CHAURASIA 4TH EDITION CLINICALLY ORIENTED ANATOMY – MOORE DALLEY SHAFERS FIFTH EDITION J Craniofac Surg. 2012 Mar;23(2):e86-8.) journal of contemporary dental practice Vol 8 num-3 march 1 2007 Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2006; 35: 961–964