Bio f4c2
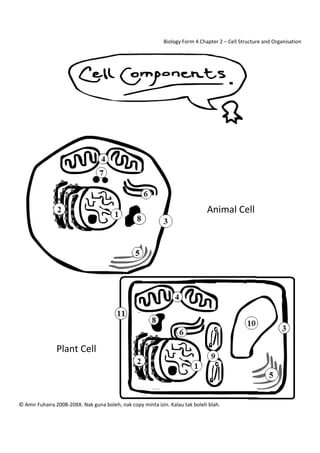
- 2. Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 – Cell Structure and Organisation Cell Components – 1. The Nucleus – Cell Prime Minister and Info Storage a. Large, dense, spherical organelle b. Enclosed by double membrane (nuclear membrane) c. Has nucleoplasm, dark sphere (nucleolus) d. Chromatin (uncondensed chromosome) in nucleoplasm e. Chromosomes carry genetic information that determine cell characteristic + function f. Controls all cell activities 2. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum – Highway + Ribosomes – Factory Workers a. RER – Network of folded membrane forming interconnected sacs b. Physically continuous with nuclear membrane c. Has ribosomes attached to surface d. Transports Made in Ribosome Proteins™ and encloses them in vesicles when exiting e. Ribosome – Compact spherical organelles attached to RER or free in cytoplasm f. Consists of 2 sub‐units (small+large) made of RNA+Protein g. Synthesises proteins based on chromosome info Synthesis – Making 3. Nuclear Membrane – Checkpoint Vesicles ‐ containers a. Made of proteins + phospholipids b. Boundary – separates cell from environment c. Semi‐permeable, selective barrier d. Regulates substance movement in and out of cytoplasm 4. MitoChondria – Power Plant a. Spherical or cylindrical organelles b. Involved in cellular respiration c. Releases energy when food (eg glucose) is broken down with mitochondrion enzymes d. Energy stored in ATP (adenosine triphosphate – try saying that 10 times) 5. Golgi Apparatus ‐ Factory a. Stack of flattened membranous sacs b. Processes, packages and transports carbohydrates, proteins, phospholipids and glycoproteins c. Vesicles fuse with GA, stuff goes into GA, modified, sorted, packaged into vesicles d. Vesicles bud off and travel to other organelles or plasma membrane 6. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum – Fat and Poison Center a. Continuous with nuclear membrane b. Detoxifies toxins and produces lipids such as steroids © Amir Fuhaira 2008‐20XX. Nak guna boleh, nak copy minta izin. Kalau tak boleh blah.
- 3. Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 – Cell Structure and Organisation 7. Centrioles – North and South (Animal Only) a. Small cylindrical structures outside nucleus, composed of microtubules b. Form spindle fibres in animal cell division ONLY 8. Lysosomes – Stuff Smasher a. Membrane‐bound sacs with hydrolytic enzymes b. Enzymes break down complex organic molecules c. Eliminate old organelles for cell renewal d. Certain lysosomes break down food in vacuoles and digest bacteria (break down cell wall) 9. Chloroplasts – Solar Panels (Plant Only) a. Lens‐shaped, contain membranous structures with green pigment chlorophyll b. Chlorophyll traps sunlight and turns light energy to chemical energy in photosynthesis 10. Vacuoles – The Refrigerator (Major in Plants/Minor in Animals) a. Fluid filled sac surrounded by tonoplast (semi‐permeable membrane) b. Fluid in vacuole is cell sap (water + dissolved substances) c. Typical plant cell has 1 large vacuole, young plant cell has many small vacuoles d. Freshwater microorganisms have contractile vacuoles + food vacuoles (Paramecium sp.) e. Contractile vacuoles regulate water balance 11. Cell Walls – Big Friggin’ Walls (Plant Only) a. Rigid outer layer, surrounds plant cell plasma membranes b. Composed of cellulose, tough and fibrous carbohydrate c. Permeable to all fluids, has tiny pores d. Gives shape and mechanical support for cell e. Protects cell from exploding for too much water Now rest your brain for a while after reading all this OK~ More to read after the break from This Guy © Amir Fuhaira 2008‐20XX. Nak guna boleh, nak copy minta izin. Kalau tak boleh blah.
- 5. Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 – Cell Structure and Organisation Multicellular • • • • Cells grow, change shape and differentiate in multicellular organisms. Mature cells carry out different functions, like different medical specialists are experts in their field, like a cardiologist in the heart, the neurologist in the brain, etc. They undergo specialization to carry out their functions more efficiently. Organisation is in this form: • • • • Cells that carry out a function are grouped into tissues. Different tissues that carry out a function are grouped into an organ. Several organs that contribute to one section of an organism’s functions (circulatory, muscular) are grouped into a system. Several systems make up an organism. Animals There are 4 main types of tissue in an animal: • Epithelial tissue (Lining and Protection) o Consists of 1 or more layers of cells o Epithelium cells are tightly interconnected, form continuous layer over body surfaces (skin + mouth) and inner cavity linings (digestive tracts and lungs) o Some have glands (exocrine and endocrine) o Skin epithelium forms a barrier against infections, mechanical injury and dehydration o Intestine epithelium has goblet cells which secrete mucus into the digestive tract o Trachea epithelium has small, hair‐like projections called cilia © Amir Fuhaira 2008‐20XX. Nak guna boleh, nak copy minta izin. Kalau tak boleh blah.
- 6. Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 – Cell Structure and Organisation • • • Muscle tissue (Movement) o Composed of muscle fibres o 3 types of muscle tissue: Smooth muscle (intestine, blood vessels, urinary and reproductive tract) • Involuntary movements • Contract slowly, for a long time Skeletal muscle (arms and legs) – On Demand • Voluntary movements • Contract, relax to move bones Cardiac muscle (heart walls) – Work, Work, Work, 24/7, 365 days a year • Blood pumping to body parts, involuntary Nerve tissue (Information Transfer) o Composed of neurones or nerve cells o Neurone has a cell body and nerve fibres (dendrites and axons) o Neuroens detect stimuli and transmit electrical signals (impulses) to muscles/glands o Directs and coordinates body activities Connective tissue (Multiple Uses) o Consists of various cells and fibres separated by extracellular matrix o Types of connective tissue: Loose connective tissue • Most widespread • Binds epithelia to underlying tissues and holds organs Dense fibrous connective tissue • A lot of closely‐packed collagenous fibres • Found in tendons (muscle‐bone connection) and ligaments (bone‐bone connection/joints) Cartilage • Strong and flexible • Support to nose, ears and covers bone ends at joints • Cartilage discs between vertebrae absorb pressure Bone • Cells embedded in collagen matrix, hardened by calcium • Harder than cartilage, protects organs, supports body © Amir Fuhaira 2008‐20XX. Nak guna boleh, nak copy minta izin. Kalau tak boleh blah.
- 7. Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 – Cell Structure and Organisation Blood cells • Produced in bone marrow (ends of long bones) • Regulating, transporting and protective functions Adipose tissue • Tightly packed cells, storing fat • Found in skin dermis and around major organs • Energy reserve, insulation and protection • Each cell has an oil droplet, energy used up, the droplet shrinks Tissues work together to perform a specific function. These are called organs. Examples are lungs, heart, kidneys, brain etc. Example: The skin: • • • • • • • Consists of various tissues joined together 2 main layers, the epidermis and the dermis Epidermis is made of epithelial tissue, which constantly divides Dermis is made of connective, nerve, epithelial and muscle tissue Blood is supplied through blood capillary network Nerve endings are scattered throughout the skin, transmit impulses to nervous system Epithelial cells produce hair follicles, sweat glands and oil glands Plants Two main types of tissue in plants: • • Meristematic tissue o Consists of small cells with thin walls, large nuclei, dense cytoplasm and no vacuoles o Young, actively dividing cells, undifferentiated, located at root tips and shoot buds Permanent tissue o Differentiated/partly differentiated mature tissues o Threee types of permanent tissue: Epidermal tissue • Outermost layer, covering stems, leaves and roots of young plants • Flat, with large vacuoles • Walls that are exposed to air covered with waxy waterproof cuticle • Cuticle reduces water loss, mechanical injury and infection • Root cells have root hairs to increase water absorption • Guard cells, containing chloroplasts, open and close stomata © Amir Fuhaira 2008‐20XX. Nak guna boleh, nak copy minta izin. Kalau tak boleh blah.
- 8. Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 – Cell Structure and Organisation Ground tissue • Consists of parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma tissue • Form the bulk of a plant o Parenchyma Least specialized cells Thin primary walls, large vacuoles Store sugar and starch Turgid, gives support and shape to herbaceous plants o Collenchyma Uneven cell walls Supports herbaceous plants, young stems and petioles (leaf branches) o Sclerenchyma Uniform cell walls with Thickening Lignin™, may be dead Support + mechanical strength to mature places Vascular tissue • Continuous throughout the plant • Consists of: o Xylem Consists of xylem vessels joined end to end from root to leaf No cytoplasm, easy water, mineral transport Cell walls with Thickening Lignin™ for support ‘n strength o Phloem Sieve tubes end to end, forming tube‐like structures Transports organic compounds (carbohydrates, amino acids) Organs in plants are leaf, stem, root and flower. Systems are root and shoot systems. Root system – all plant roots. Shoot system – stem, leaf, bud, flower and fruit. Stem, branch for support system. Leaf for photosynthesis. Flowers for pollination. © Amir Fuhaira 2008‐20XX. Nak guna boleh, nak copy minta izin. Kalau tak boleh blah.
