Reported speech texto explicativo - 7.º ano
•Download as DOCX, PDF•
1 like•803 views
Texto explicativo sobre o Discurso Indireto
Report
Share
Report
Share
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Similar to Reported speech texto explicativo - 7.º ano
Similar to Reported speech texto explicativo - 7.º ano (20)
5 english grammar_in_use_-_grammar_reference By Engr Inayatullah Baloch

5 english grammar_in_use_-_grammar_reference By Engr Inayatullah Baloch
Fourteenth Class - Part I - Telling Stories: Intro to Clauses

Fourteenth Class - Part I - Telling Stories: Intro to Clauses
More from Marta Neto
More from Marta Neto (12)
Ficha de avaliação 2.º trimestre constituição de portugal e da ue - 4.º ano...

Ficha de avaliação 2.º trimestre constituição de portugal e da ue - 4.º ano...
The simple present of the verb to be and others+exercises

The simple present of the verb to be and others+exercises
Present simple and present continuous explicação e exercício

Present simple and present continuous explicação e exercício
Indefinite articles a vs. an - texto explicativo e exercícios

Indefinite articles a vs. an - texto explicativo e exercícios
Contrato de trabalho a termo minuta ministério do trabalho v. francesa

Contrato de trabalho a termo minuta ministério do trabalho v. francesa
Recently uploaded
YOUVE GOT EMAIL_FINALS_EL_DORADO_2024.pptx

YOUVE GOT EMAIL_FINALS_EL_DORADO_2024.pptxConquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Model Call Girl in Tilak Nagar Delhi reach out to us at 🔝9953056974🔝

Model Call Girl in Tilak Nagar Delhi reach out to us at 🔝9953056974🔝9953056974 Low Rate Call Girls In Saket, Delhi NCR
Recently uploaded (20)
Difference Between Search & Browse Methods in Odoo 17

Difference Between Search & Browse Methods in Odoo 17
Inclusivity Essentials_ Creating Accessible Websites for Nonprofits .pdf

Inclusivity Essentials_ Creating Accessible Websites for Nonprofits .pdf
Judging the Relevance and worth of ideas part 2.pptx

Judging the Relevance and worth of ideas part 2.pptx
4.18.24 Movement Legacies, Reflection, and Review.pptx

4.18.24 Movement Legacies, Reflection, and Review.pptx
ISYU TUNGKOL SA SEKSWLADIDA (ISSUE ABOUT SEXUALITY

ISYU TUNGKOL SA SEKSWLADIDA (ISSUE ABOUT SEXUALITY
Barangay Council for the Protection of Children (BCPC) Orientation.pptx

Barangay Council for the Protection of Children (BCPC) Orientation.pptx
Model Call Girl in Tilak Nagar Delhi reach out to us at 🔝9953056974🔝

Model Call Girl in Tilak Nagar Delhi reach out to us at 🔝9953056974🔝
Visit to a blind student's school🧑🦯🧑🦯(community medicine)

Visit to a blind student's school🧑🦯🧑🦯(community medicine)
Reported speech texto explicativo - 7.º ano
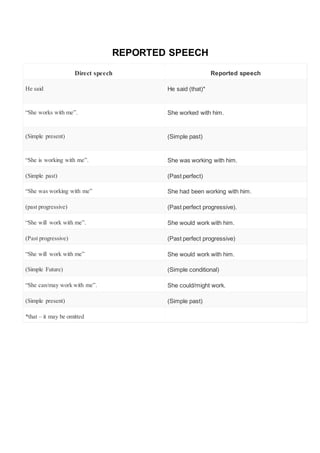
- 1. REPORTED SPEECH Direct speech Reported speech He said He said (that)* “She works with me”. She worked with him. (Simple present) (Simple past) “She is working with me”. She was working with him. (Simple past) (Past perfect) “She was working with me” She had been working with him. (past progressive) (Past perfect progressive). “She will work with me”. She would work with him. (Past progressive) (Past perfect progressive) “She will work with me” She would work with him. (Simple Future) (Simple conditional) “She can/may work with me”. She could/might work. (Simple present) (Simple past) *that – it may be omitted
- 2. Some other changes: Today That day Yesterday The day before Last night The night before Now Then Here There Tomorrow The next day This That This, that The This, these It, them When it’s an order, you use the infinitive. For example: Direct Speech: He said: “Close the door”. Reported Speech: He told me to close the door. Direct Speech: He said: “Don’t close the door”. Reported Speech: He told me not to close the door.
- 3. When you are reporting a question, you put the sentence in the affirmative making all the appropriated changes. For example: She said: Where is Bill? – She asked where Bill was. He said: “Is Mary here?” – He asked if Mary was there. Should, Could, Must, Might e would don’t change. For example: She said: -“I could go”. She said that she could go. In sentences that present suggestions: a) The verb that introduces the reported speech is to suggest b) The expression “let’s” is changed to “we should”. For example: He said: “Let’s take her to the park”. He suggested (that) we should take her to the park.
