Chemical Reactions DS
- 1. Elements, Atoms, Compounds and Molecules By Darcy p. Simonsen
- 2. Element A chemical element is a pure chemical substance consisting of one type of atom distinguished by its atomic number. Common examples of elements are iron, copper, silver, gold, hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen. In total, 117 elements have been observed as of 2008, of which 94 occur naturally on Earth
- 3. Atom The atom is a basic unit of matter consisting of a dense, central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons.
- 4. metals a metal is an element, compound, or alloy characterized by high electrical conductivity . In a metal, atoms readily lose electrons to form positive ions; those ions are surrounded by delocalized electrons, which are responsible for the conductivity.
- 5. Non metals non-metal is a term used in chemistry when classifying the chemical elements. On the basis of their general physical and chemical properties, every element in the periodic table can be termed either a metal or a nonmetal.
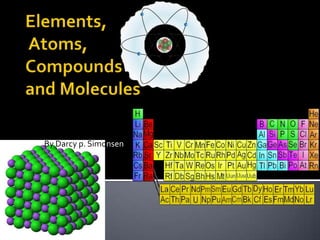
- 6. The periodiс table of the chemical elementsis a tabulardisplay of the chemical elements. Although precursors to this table exist, its invention is generally credited to Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, who intended the table Periodic table
- 7. Compounds A chemical compound is a pure chemical substance consisting of two or more different chemical elements that can be separated into simpler substances by chemical reactions and that have a unique and defined chemicalstructure.
- 8. Chemical reactions A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances toanother. There are three things that speed up chemical reactions one of them are:
- 9. chemical and physical changes 1. A physical change is reversible, a chemical change is not. For example, the freezing of water would be a physical change because it can be reversed, whereas the burning of wood is a chemical change - you can't 'unburn' it.
- 10. Identifying chemical reactions There are three types of chemical reactions, here are two: Synthesis A synthesis reaction is when there is a combination of two or more substances and a compound results. An example A + B --> AB Decomposition Decomposition is roughly the opposite of synthesis it is a breaking down of one molecule into two (or more) smaller molecules or elements. Sample decomposition reactions could include: 2 H2O + electricity -> 2 H2 + O2
- 11. make a reaction faster use a catalyst breaking a solid into something smaller (to increase its surface area) make the solution more concentrated, increase the temperature.
- 12. Bibliography Wikipedia the free encyclopaedia Google images What is the difference between a physical change and a chemical...