Poster mariecurieconferencewarsawfinal
•Download as PPT, PDF•
0 likes•974 views
Ejemplo de Poster
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Biotechnological applications in Male Sterility and Hybrid Breeding

Biotechnological applications in Male Sterility and Hybrid Breeding
Seminar on male sterility and fertility restoration 50026 5 01-2018

Seminar on male sterility and fertility restoration 50026 5 01-2018
Agrobacterium mediated gene transfer - LIKE NEVER BEFORE!!

Agrobacterium mediated gene transfer - LIKE NEVER BEFORE!!
Recombinant Antibody Overview I - Creative Biolabs

Recombinant Antibody Overview I - Creative Biolabs
Male Sterility IN Cross Pollinated and Vegetable Crops

Male Sterility IN Cross Pollinated and Vegetable Crops
Viewers also liked
Agenda XIV Seminario InternacionalAGENDA XIV SEMINARIO INTERNACIONAL DE ACTUALIZACIÓN EN MEDICINA, NUTRICIÓN Y ...

AGENDA XIV SEMINARIO INTERNACIONAL DE ACTUALIZACIÓN EN MEDICINA, NUTRICIÓN Y ...Escuela Superior Politécnica del Chimborazo
LUGAR:
ESCUELA SUPERIOR POLITÉCNICA DE CHIMBORAZO (ESPOCH).
CONFERENCIAS: AUDITORIO DE CIENCIAS PECUARIAS.
TALLERES: LABORATORIOS Y AULAS DE LA FACULTAD DE SALUD PÚBLICA.
FECHA: 12 – 16 de Diciembre de 2016.
DURACIÓN: 40 Horas.
XV SEMINARIO INTERNACIONAL DE SALUD ALIMENTACIÓN Y NUTRICIÓN HUMANA”

XV SEMINARIO INTERNACIONAL DE SALUD ALIMENTACIÓN Y NUTRICIÓN HUMANA”Escuela Superior Politécnica del Chimborazo
LUGAR:
ESCUELA SUPERIOR POLITÉCNICA DE CHIMBORAZO (ESPOCH).
CONFERENCIAS: AUDITORIO DE CIENCIAS PECUARIAS.
TALLERES: LABORATORIOS Y AULAS DE LA FACULTAD DE SALUD PÚBLICA.
FECHA: 12 – 16 de Diciembre de 2016.
DURACIÓN: 40 Horas.
XV SEMINARIO INTERNACIONAL DE SALUD ALIMENTACIÓN Y NUTRICIÓN HUMANA”

XV SEMINARIO INTERNACIONAL DE SALUD ALIMENTACIÓN Y NUTRICIÓN HUMANA”Escuela Superior Politécnica del Chimborazo
Viewers also liked (12)
AGENDA XIV SEMINARIO INTERNACIONAL DE ACTUALIZACIÓN EN MEDICINA, NUTRICIÓN Y ...

AGENDA XIV SEMINARIO INTERNACIONAL DE ACTUALIZACIÓN EN MEDICINA, NUTRICIÓN Y ...
XV SEMINARIO INTERNACIONAL DE SALUD ALIMENTACIÓN Y NUTRICIÓN HUMANA”

XV SEMINARIO INTERNACIONAL DE SALUD ALIMENTACIÓN Y NUTRICIÓN HUMANA”
XV SEMINARIO INTERNACIONAL DE SALUD ALIMENTACIÓN Y NUTRICIÓN HUMANA”

XV SEMINARIO INTERNACIONAL DE SALUD ALIMENTACIÓN Y NUTRICIÓN HUMANA”
Similar to Poster mariecurieconferencewarsawfinal
Similar to Poster mariecurieconferencewarsawfinal (20)
Cytoplasmic inheritance and Chloroplast engineering

Cytoplasmic inheritance and Chloroplast engineering
cytoplasmic effect and genetic engineering of chloroplasts

cytoplasmic effect and genetic engineering of chloroplasts
Antisense genes in plants and their applications in crop improvement

Antisense genes in plants and their applications in crop improvement
Antisense genes in plant and their application in crop improvement

Antisense genes in plant and their application in crop improvement
S. pyogenes, its virulence, antibiotic, phytochemicals

S. pyogenes, its virulence, antibiotic, phytochemicals
Genetics of antimicrobial metabolite – production in bio

Genetics of antimicrobial metabolite – production in bio
Poster mariecurieconferencewarsawfinal
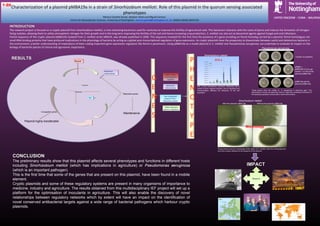
- 1. Y-B9 Characterization of a plasmid pMBA19a in a strain of Sinorhizobium meliloti. Role of this plasmid in the quorum sensing associated Characterization of a plasmid pMBA19a in a strain of Sinorhizobium meliloti. Role of this plasmid in the quorum sensing associated phenotypes phenotypes Monica Cartelle Gestal, Stephan Heeb and Miguel Camara. Monica Cartelle Gestal, Stephan Heeb and Miguel Camara. Centre for Biomolecular Sciences. University of Nottingham. monica.gestal@nottingham.ac.uk. SINOPLASMID (RH0735) Centre for Biomolecular Sciences. University of Nottingham. monica.gestal@nottingham.ac.uk. SINOPLASMID (RH0735) INTRODUCTION The research project is focused on a cryptic plasmid from Sinorhizobium meliloti, a root-colonizing bacterium used for centuries to improve the fertility of agricultural soils. This bacterium interacts with the roots of plants and induces the formation of nitrogenfixing nodules, allowing them to utilise atmospheric nitrogen for their growth and in the long term improving the fertility of the soil and hence increasing crop production, S. meliloti can also act as biocontrol agents against fungal and viral infections. Partial sequence of the cryptic plasmid pMBA19a isolated from S. meliloti strain MBA19, was already published in 2006. This sequence revealed for the first time the presence of a gene encoding an RsmA homolog carried by a plasmid. RsmA homologues are small-RNA binding proteins that have profound implications in the physiology of bacteria by acting as a global post-transcriptional regulators of gene expression. As cryptic plasmids have the propensity to disseminate between useful and deleterious bacteria in the environment, a better understanding of implications of them coding important gene expression regulators like RsmA is paramount. Using pMBA19a as a model plasmid in S. meliloti and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, we undertake to evaluate its impact on the biology of bacterial species of clinical and agronomic importance. Pseudomonas aeruginosa RESULTS RsmA RsmA Restriction Restriction endonuclease endonuclease Enzymes Metabolism Replication genes TCS TCS Conjugation genes Plasmid highly transferable Maintenance G E N E S RsmA = Posttranscriptional regulator Restriction Restriction endonuclease endonuclease Two component Two component systems (TCS) = systems (TCS) = Regulatory system Regulatory system Other unknown Other unknown genes or regulators genes or regulators P H E N O T Y P E Sinorhizobium meliloti Control (no plasmid) AHLs pBB84 = pBBR328+4.5 kb rep (vector + 4.5 Kb of the plasmid pMBA19a) pMBA19a (all the plasmid pMBA19a) AHL (n-Acyl Homoserine Lactones). Molecules that a variety of gram negative bacteria, use for signalling and communication affecting the behaviour of the cell population These photos show the motility of P. aeruginosa in swarming agar. This phenomena is known as swarming, that is a rapid and coordinate movement of the bacterial population across solid or semi-solid surface. Sinorhizobium meliloti With thw plasmid pMBA19a Without the plasmid pMBA19a Morphology These photos show the morphology of the colony of S. meliloti under the microscope and how this is clearly affected for the presence of this plasmid CONCLUSION The preliminary results show that this plasmid affects several phenotypes and functions in different hosts including Sinorhizobium meliloti (which has implications in agriculture) or Pseudomonas aeruginosa (which is an important pathogen) This is the first time that some of the genes that are present on this plasmid, have been found in a mobile element. Cryptic plasmids and some of these regulatory systems are present in many organisms of importance to medicine, industry and agriculture. The results obtained from this multidisciplinary IEF project will set up a platform for the optimisation of inoculants in agriculture. This will also enable the discovery of novel relationships between regulatory networks which by extent will have an impact on the identification of novel conserved antibacterial targets against a wide range of bacterial pathogens which harbour cryptic plasmids. IMPACT Research Research
