More Related Content
Similar to Chapter 3 with answer
Similar to Chapter 3 with answer (20)
More from Gabriel Chua (20)
Chapter 3 with answer
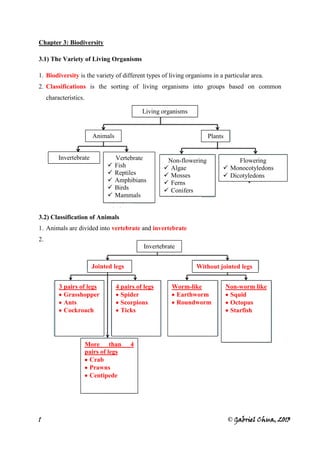
- 1. Chapter 3: Biodiversity
3.1) The Variety of Living Organisms
1. Biodiversity is the variety of different types of living organisms in a particular area.
2. Classifications is the sorting of living organisms into groups based on common
characteristics.
Living organisms
Animals Plants
Invertebrate Vertebrate Non-flowering Flowering
Fish Algae Monocotyledons
Reptiles Mosses Dicotyledons
Amphibians Ferns
Birds Conifers
Mammals
3.2) Classification of Animals
1. Animals are divided into vertebrate and invertebrate
2.
Invertebrate
Jointed legs Without jointed legs
3 pairs of legs 4 pairs of legs Worm-like Non-worm like
Grasshopper Spider Earthworm Squid
Ants Scorpions Roundworm Octopus
Cockroach Ticks Starfish
More than 4
pairs of legs
Crab
Prawns
Centipede
1 © Gabriel Chua, 2013
- 2. 3. Vertebrates
Aspect Fish Reptiles Amphibians Birds Mammals
Live in Water Mostly in Young: Air and land Mostly in
land Water land except
Adult: whales and
Land and dolphins
water
Blood Cold-blooded Cold-blooded Cold-blooded Warm- Warm-
temperature blooded blooded
Body Scales Dry scaly Moist skin Feather Fur
covered with skins
Movement Swim by fins Limbs Young: Fly using Limbs
Swim by fins wings
Adult:
Jump and
swim by
limbs
Breathe by Gills Lungs Young: Lungs Lungs
Gills
Adult:
Lungs and
skin
Reproduction Lay eggs, Lay eggs, Lay eggs, Lay eggs, Give birth
External Internal External Internal except for
fertilization fertilization fertilization fertilization platypus &
anteater,
Internal
fertilisation
3.3) Classifications of Plants
1. Plants can be divided into flowering and non-flowering plants.
2. Both flowering and non-flowering plants have chlorophyll to make their own food.
2 © Gabriel Chua, 2013
- 3. 3.
Non-flowering
Algae Mosses Ferns Conifers
Unicell or Simple plant Have true Have true
multicell No true stem, stem, leaves stems, leaves
No true stem, leaves and and roots and roots
leaves and roots Reproduce by Produce
roots Reproduce by spores cones
Live in water spores Grow in Reproduce
and moist Live in damp moist and through seeds
areas areas shady areas in cones
4. Flowering plants have flowers, reproduce by seeds and have true leaves, stems and
roots.
5.
Flowering plants
Monoctyledons Dicotyledons
Produce seeds with 1 cotyledons Produce seeds with 2 cotyledons
Leaves have parallel veins Leaves have netted veins
Flower petals in multiple of 3 Flower petals in multiple of 4 or 5
Have fibrous roots Have tap roots
Herbaceous plants (soft stem) Woody stems (hard)
3.4) Importance of Biodiversity
1. Importance of biodiversity are:
a) Balance the nature
All living organisms depend on each other for survival
b) Source of medicines and herbs
Some plants and animals have medicinal properties such as tongkat ali and
Pokok Bintangor.
c) Source of raw materials
Raw materials from plants and animals are used for making furniture, clothing
etc.
3 © Gabriel Chua, 2013
- 4. d) Source of fresh air
Air (oxygen and carbon dioxide) is recycled with the presence of both animals
and plants.
p/s: Other correct explanations are acceptable too.
4 © Gabriel Chua, 2013