Endodontic surgery.pptx
- 2. INTRODUCTION DEFINITION INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION CLASSIFICATION SURGICAL DRAINAGE PERIRADICULAR SURGERY CORRECTIVE SURGERY REPLACEMENT SURGERY
- 3. Over the past decade, periradicular surgery has continued to evolve precise , biologically based adjunct to nonsurgical root canal therapy . Although nonsurgical endodontic treatment gives good results in most cases ,surgery may be indicated for teeth with peristent periradicular pathoses that have not responded to non surgical approaches.
- 4. Endodontic surgery encompases surgical procedure performed to remove the causative agents of periradicular pathosis and to restore the periodontium to a state of a biologic and functional health .
- 5. 1. Need for surgical drainage 2. Failed non surgical endodontic treatment Irretrievable root canal filling material Irretrievable intra-radicular post 3. Calcific metamorphosis of pulp space 4. Procedural Errors a. Instrument fragmentation b.Non negotiable ledging c.Root perforation d . Symptomatic overfilling
- 6. 5. Anatomic variations a. Root dilacerations b.Apical root fenestration 6. Biopsy 7. Conservative procedure a. Root resorptive defects b. Root caries c. Root resection d. Hemisection e. Bicuspidation 8. Replacement surgery a.Replacement Surgery i.Intentional replantation ii.posttraumatic b.Implant surgery i. Endodontic ii.ossteointegrated.
- 7. Poor periodontal health of the tooth Poor patient’s medical status Local anatomical factors like nasal floors , maxillary sinus , mandible canal and its neurovascular bundle and mental force .
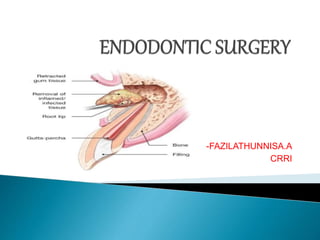
- 8. SURGICAL DRAINAGE: 1.Incision and drainage ( I&D) 2. Cortical trephination (fistulative surgery) PERIRADICULAR SURGERY a. Curette b. Biopsy c. Root-end resection d. Root-end preparation and filling
- 9. Corrective Surgery a. perforation repair I. Mechanical ( Iatrogenic) ii. Resorptive (internal and external) b. Root resection c. Hemi section d. Bicuspidisation Replacement Surgery(extraction/replantation) Implant Surgery 1.Endodontic implants 2. Root –form osseointegrated implants
- 10. Surgical drainage is indicated when purulent and haemorrhagic exudate forms within the softtissue or the alveolar bone forming Periradicular Abscess Surgical drainage may be accomplished by: i. incision and drainage (I&D) of the soft tissue ii.Trephination of the alveolar cortical plate
- 11. An incision should to be made through the focal point of the localised swelling to relieve pressure , eliminate exudate and toxins and stimulate healing Caution should always exercised with hard , indurated swelling especially when accompained by fever Incision into a diffuse or indurated swelling before its localisation is often unsuccesful.
- 12. The patient be placed on appropriate systemic antibiotic therapy Instructed to use hot salt water “MOUTH HOLDS’’(1/4 -1/2 tsp in a 10-12 oz glass of hot water)in the swolling area to assist in localisation of the swelling to a more fluctuant Clinical situation should be monitored every 24 hours As the swelling has localised and a fluctuant area has developed , surgical drainage should be performed
- 13. Nerve block injection is the preferable for obtaining local anaesthesia When block is impractical ,anaesthesia will be limited to infiltration When local anaesthesia is used , oral mucosa should be dried and a topical anaesthetic is placed Local anaesthetic should be deposited peripheral to the swollen mucoperiosteal tissue
- 14. Incision should be HORIZONTAL and placed at dependent base of the fluctuant area . The exudates should be aspirate and a sample collected for bacteriologic culture Probing with curette or haemostat into the incisional wound to release exudates entrapped in tissue compartments will facilitate a more effective result .
- 15. Insertion of drain is only indicated when initial drainage is limited incase presenting with moderate to severe cellulitis and other positive signs of an aggressive infective process. Material used:Iodoform gauze Rubber dam material-H’ and ‘christmas tree’ shape Penrose drain It may be sutured in placed for added retention and should removed after 2-3 days .
- 17. Cortical trephination is a procedure involving the perforation of the cortical plate to accomplish the release of pressure from the accumulation of exudate within the alveolar bone . No6 or 8 round bar Buccal approach A reamer or k type file Is then passed into the cancellous Bone into the vicnity of the Periradicular tissue.
- 19. PRINCIPLES: Need for profound local anaesthesia and haemostasis Management of soft tissue Management of hard tissue Surgical access,both visual and operative Access to root structure Periradicular curettage Root-end resection Root –end preparation Root –end filling Soft tissue repositioning and suturing Postsurgical care.
- 20. ANTIINFLAMMATORY: The patient (average weight of 150 lbs) take ibuprofen (400 mg) just before surgery is recommended to minimise the postsurgical inflammatory response. TRANQUILLISERS: If patient is very anxious about the surgery , sublingual triazolam or DIAZEPAM 10 mg taken 15-30 minutes before surgery. ANTIBIOTICS : As stated previously , medically compromised patients must be premedicated (eg with advanced diabetes , heart valve disease) ANTIBACTERIAL RINSE : To reduce the oral microflora the patient instructed to use a 0.12% CHLORHEXIDINE GLUCONATE mouth rinse the night before surgery and morning of surgery and 1 hour before surgery .
- 21. The injection of local anaesthetic agent that contains a vasoconstrictor has two equally important objective: . To obtain profound and prolonged anaesthesia . To provide good haemostasis both during surgical procedure HAEMOSTASIS: Presurgical haemostasis surgical haemostasis postsurgical haemostasis .
- 22. PRESURGICAL HAEMOSTASIS : The choice of vasoconstrictor in the local anaesthesic will have an effect on both duration of anaesthesia and quality of hemorrhage control at the surgical site . Vasopresser agents used in dentistry are direct acting sympathomimetic amines that exert their action by stimulating special receptor ( Alpha- and Beta- adenergic receptors )on the smooth muscle cells in microcirculation of various tissue EPINEPHRINE is the most effective and most widely used vasoconstrictor agent in dental anaesthetics,
- 23. Local haemostasis can be achieved by pressure technique of pressing cotton pellets or gauze in the bony crypts Topical hemostatic agent: A. MECHANICAL AGENTS: Bone wax B.CHEMICAL AGENTS : Epinephrine saturated cotton pellets other vasoconstrictors Ferric sulphate solution C.BIOLOGIC AGENTS Thromobin USP D.ABSORBABLE HEMOSTATIC i. Intrinsic action gelfoam Absorable collagen ii. EXTRINSIC ACTION Surgicel iii. MECHANICAL ACTION Calcium sulphate
- 24. After the flap is sutured, hemostasis is achieved by a ice –cold wet sterilised gauze placed over the sutures to stabilise the flap and control oozing of the blood from the surgical sites The gauze should be placed into the mucobuccal fold for about one hour and an ice-pack should be applied to the cheek 10 minutes on, 5 minutes off for 1- 2 hours.
- 25. FULL MUCOPERIOSTEAL (sulcus full thickness flap) . Triangular flaps ( one vertical releasing incision) . Rectangular flaps (two vertical releasing incision) . Trapezoidal flaps(broad-base rectangular)not used , Horizontal flaps(no vertical releasing incision LIMITED MUCOPERIOSTEAL FLAP: . Submarginal curved (semiluar) . Submarginal scalloped rectangular(Lubeke- ochsenbein) flap . Free rectilinear submarginal flaps.
- 27. Hard tissue management of periradicular surgery involves four stages : i. Osteotomy ii. Curettage and biopsy iii. Root-end resection iv . Root –end retropreparation.
- 28. Osteotomy is defined as the removal of facial cortical plate to expose the root-end and must be approached with a visualized 3D mental image to ensure that it is made exactly over the apices.
- 29. Periapical radiographs imaged perpendicular to the roots from two different horizontal angles are done to ascertain of the length and curvature of the roots , position of the apices in relation to the crown and number of roots The exact location of the apex determined by two methods: Using the tooth length measurement obtained from a Well angled radiograph .A small amount of radioopaque material is placed and direct radiograph exposed Root surfaces generally has a yellowish colour Roots does not bleed Root texture is smooth and hard as opposed to granular porous nature of bone The periodontal ligament that can be stained be methylene blue dye surrounds root .
- 30. Generation of heat is a major importance during osseous tissue removal by bur as heating bone tissue above 60 degree C in interruption of blood flow and tissue necrosis The heat production can be minimised by LIQUID COOLANT during bone removal i. dissipating the heat generated ii. Keeping the cutting flutes of the instrument free of debris LIQUID BRUSH STROKES with short, intermittent cutting.
- 31. Periradicular curretage involves removal of the periradicular inflammatory tissue and is best accomplished by using sharp surgical bone curettes and angled periodontal curettes .
- 32. INDICATIONS: BIOLOGIC FACTORS: Persistent symptoms and continued presence of a periradicular symptoms. TECHNICAL FACTORS: a. Intra radicular posts b. Crowned teeth without posts c. Irretrievable root canal filling materials d. procedural accidents Three important factors to be considered before performing a root –end resection 1. INSTRUMENTATION 2. Extent of root end resection 3. Angle of root –end resection.
- 33. INSTRUMENTATION: Plain fissure bur and a low speed hand piece results in the least gutta percha distortion A smooth , flat resected root surface is preferred clinically and may promote tissue healing EXTENT OF ROOT END RESECTION: Visual and operative access to the surgical site Anatomy of root Incidence of lateral canals and apical ramification at the root end 3 mm significantly eliminates the major anatomic entities Number of canals and their position in the root Need to place a retrofilling material surrounded by solid dentine Presence and location of procedural error Presence and extent of periodontal defects Level of remaining crestal bone
- 34. ANGLE OF ROOT END RESECTION: The root end resection must be done perpendicular to the long axis of the root . In situation where a perpendicular bevel may not possible as in the mesiolingual root of the mandibular first molar 10 degree bevel can be used.
- 35. PURPOSE: Retropreparation is to create a cavity to receive a root-end filling Class -1 cavity preparation at least 3 mm into root dentine with walls parallel to the anatomic outline of the pulp space FIVE Requirements Apical 3 mm of the root canal must be freshly cleaned and shaped Preparation must be parallel to the anatomic outline of the pulp space Adequate retention must be created All isthmus tissue must be removed Remaining dentine walls should not be weakned.
- 36. TRADITIONAL RETROPREPARATION: Involves use of either miniature contra – angle or straight hand piece with a small round or inverted cone bur placed obliquely into the root , resulting in risk of perforation and /or weakening of the dentine walls TRADITIONAL ULTRASONIC
- 37. ULTRASONIC RETROPREPARATION: Solves the inadequacies of the traditional bur preparation Ultrasonic microtips are very narrow in diameter (one-tenth of a conventional microhead handpiece) Produce smooth cutting with relatively the tips are activated against the dentine wall of the apical preparation ADVANTAGES: Better access especially in difficult to reach areas (eg. Lingual apex) Debridement of the tissue debris Conservative preparation tracing the long axis at a precise depth of 3mm Precise isthmus preparation
- 39. PURPOSE: Provide a tight , biocompatible apical seal which prevents the leakage of potential irritants from the root canal into the periradicular tissue IDEAL PROPERTIES: Well tolerated by periapical tissue Adhere to the tooth structure Dimensionally stable Resistant to dissolution Promote cementogenesis Bacteriocidal or bacteriostatic Non corrosive Electrochemically inactive should not stain the tooth Readily available and easy to handle Allow adequate working time then set quickly Radioopaque
- 40. RETROGRADE FILLING MATERIAL: Amalgam Gutta percha Gold foil Glass ionomers Zinc oxide eugenol Composite resins Mineral trioxide aggregate(MTA) INSTRUMENTS: Reverse fill carriers reverse fill pluggers Amalgam squeeze clothes Miniature reverse fill mirror Miniature head aspirator tips
- 41. The elevated mucoperiosteum gently replaced to its original position with the incision lines approximated as closely as possible Tissue compression: using a surgical gauze moistened with sterile saline gently apply firm pressure to the flapped tissue 2 to 3 minutes before suturing enhances intravascular clotting in the several blood vessels SUTURING: To approximate the incised tissue and stabilized the flapped mucoperiosteum until reattachment occurs.
- 42. Most like surgically sequelae include Pain Bleeding and swelling Ecchymosis Infection Transient paraesthesia Post operative instructions: Do not do any difficult activity for the rest of the day Good Diet and drink plenty of water Do not lift up the lip or pull back the cheek to look at where surgery was done Place an ice bag After 8 hours ice bag should not be used Rinse the mouth with 1 table spoon of chlorhexidine mouthwash two times a day Remove the suture after 2 days
- 43. Corrective surgery involves the correction of defects in the body of the root other than the Corrective surgery necessary for Procedural accidents Resorption Root caries Root fracture Periodontal disease classified 1. Perforationrepair Mechanical Resorptive and Root caries 2. Periodontal repair Guided tissue regeneration Root resection Bicuspidisation
- 44. Perforations are procedural accidents that can occur during root canal or postspace preparation High potential areas of perforations are pulp chamber , floor of the molars, distal aspect of mesial root of mandibular molar and mesial buccal root of maxillary molars Midroot perforation such as those resulting from postspace preparation should be immediately sealed internally , if possible calcium hydroxide should be placed as an intracanal dressing
- 45. In case of resportive defect that opens in to the gingival sulcus . It is approachable from the buccal or facial side a full mucoperiosteal flap is raised and the extent is visualised If the defect extent into the pulp space a temporary matrix (large gutta percha is placed into the canal) After that the flap is repositioned and stabilised with sutures and endodontic treatment can be completed at the same or subsequent appointment
- 46. Guided tissue (bone regeneration) Root resection/ Hemisection Bicuspidisation.
- 47. This refers to the removal of one or more roots of a multirooted tooth while others roots are retained logical way to eliminate a weak diseased root to allow the stronger root to survive .
- 48. Advantages Salvaging and retaining the two thirds or even one Half of a tooth might add sufficient support to maintain arch integrity . The most posterior abutment retaining even half of the tooth can avoid the need for removable prosthesis and enable the patient to use fixed prosthesis or a splint INDICATIONS: Existence of periodontal bone loss to the extent that periodontal therapy and patient maintainence do not sufficiently improve the condition Destructive of a root through resorptive process, caries or mechanical perforations Fracture of one root that does not involve other.
- 49. CONTRAINDICATIONS: Lack of necessary osseous support for the remaining roots or root . Fused root or roots in unfavourable proximity to each other . Remaining root or roots endodontically inoperable . Lack of patient motivation to properly perform home care procedure.
- 50. Bisection or bicuspidisation refers to a division of the crown that leaves the two halves and their respective root INDICATION:severe bone destruction in the bifurcation but excellent support on the non furcation area
- 51. DEFINITION: Intentional replantation as the act of deliberately removing a tooth and a- after the examination, diagnosis ,endodontic manipulation and repair, returning the tooth to its original socket. INDICATIONS: Difficult access Anatomic limitations Perforation in areas not access surgically Failed apical surgery Apical surgery creating defect Accidental avulsion
- 52. CONTRAINDICATION: Preexisting moderate to severe periodontal disease Curved and flared roots Non restorable tooth Missing interseptal bone 3 factors that directly affect the outcome of intentional replantation: Extraoral time Keeping PDL cells Minimizing damage to the cementum and pdl ligament cells during elevation and extraction