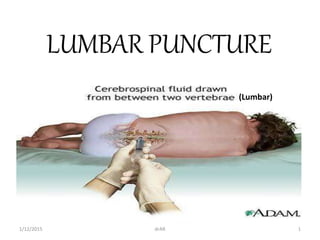
Lumbar puncture
- 2. Indication • Diagnosis : – CNS infection, eg. meningitis, encephalitis and CNS syphilis – Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) – Normal pressure hydrocephalus • Evaluation and diagnosis of demyelinating or inflammatory CNS processes – Multiple sclerosis – Guillain-Barré syndrome – Paraneoplastic syndromes • Infusion of anesthetic, chemotherapy, or contrast agents into the spinal canal • Treatment of idiopathic intracranial hypertension 1/12/2015 drAR 2
- 3. Contraindication 1. Idiopathic or Suspicion of increased ICP d/t cerebral mass • Brain tumor • Cerebral hemorrhage • Abscesses • Epidural or subdural hematomas – Rationale: LP in increased ICP may cause uncal herniation – Exception: Therapeutic use of LP to reduce ICP – Precaution • CT brain is advocated by some, especially in the following situations – Age >65 – Reduced GCS – Recent history of seizure – Focal neurological signs • Ophthalmoscopy for papilledema Signs of Increase ICP: • Decreased levels of consciousness • Focal neurological signs • Papilloedema Low-pressure shunt is formed LP site where CSF can escape. As the CSF pressure drops in the spinal column, CSF and brain mass may then shift towards the low-pressure outlet (the LP site). This cause either trans-tentorial or uncal herniation & acute neurological deterioration. 1/12/2015 drAR 3
- 5. Increase ICP Mass effect Obstruction to CSF flow or absorption Generalized brain swelling Increase in Venous pressure 1/12/2015 drAR 5
- 6. 2. Bleeding diathesis • Uncorrected Coagulopathy • Clotting defects such as disseminated intravascular coagulation, hemophilia or thrombocytopenia (<50 x 109/L) • Heparin, Warfarin – Reversal of warfarin with Vitamin K or fresh frozen plasma – Replacement of a hemophiliac's clotting factors – Transfusion of platelets to the thrombocytopenic patient 3. Skin infection – Skin infection near the site of the lumbar puncture > increases the risk of carrying the infection into the CSF with the LP needle >sepsis 4. Abnormal respiratory pattern 5. Hypertension with bradycardia and deteriorating consciousness. 6. Vertebral deformities (scoliosis or kyphosis), 7. Acute spinal trauma 8. Obtunded state with poor peripheral perfusion or hypotension 9. Seizures-prolonged or recent (within 30 minutes) 10. Inexperienced physician Tr(x) for safe LP 1/12/2015 drAR 6
- 7. Anatomy • At birth inferior end of the spinal cord is opposite the body of the third lumbar vertebrae (L3) • As the child grows, the vertebral column grows much faster than the spinal cord itself. • Adulthood the spinal cord only reaches the inferior border of the L1 vertebra, or the superior aspect of L2. In order to avoid transfixing the spinal cord during LP, the needle is placed distal to L2. This means the needle enters the subarachnoid space at the level of the mobile cauda equina. 1/12/2015 drAR 7
- 10. WHERE TO INSERT THE NEEDLE ?? • The imaginary line that crosses the lumbar region of the back joining the posterior superior iliac crests will cross the L3-L4 interspace 1/12/2015 drAR 10
- 11. • The tissues pierced are (in order): skin, subcutaneous tissue, supraspinal ligament, interspinal ligament, ligamentum flavum, dura mater, the arachnoid mater and into the subarachnoid space. 1/12/2015 drAR 11
- 12. THE LP KIT • three cleaning sponges • a 20 gauge spinal needle • a 25 gauge and a 20 gauge needle for anesthetic infiltration • a 3cc syringe • a vial of 1% lidocaine for anesthesia • a pressure manometer with tubing • four collection vials and a Band-Aid. The other tools you may need include sterile gloves, gown, proviodine cleaning solution 1/12/2015 drAR 12
- 13. Equipments A spinal or lumbar puncture tray should include the following items: • Sterile dressing • Sterile gloves • Sterile drape • Antiseptic solution with skin swabs • Lidocaine 1% without epinephrine • Syringe, 3 mL • Needles, 20 and 25 gauge • Spinal needles, 20 and 22 gauge • Three-way stopcock • Manometer • Four plastic test tubes, numbered 1- 4, with caps • Syringe, 10 mL (optional) 1/12/2015 drAR 13
- 15. Patient Preparation • Local anesthesia is employed for lumbar puncture • The patient is placed in the lateral recumbent position with the hips, knees, and chin flexed toward the chest so as to open the inter-laminar spaces or interspinous distance • A pillow may be used to support the head • Inter-laminar space • Inter-spinous diameter 1/12/2015 drAR 15
- 16. Lateral Decubitus Position • Apply topical anesthetic 30-45 min prior to procedure • Spinal cord ends at L1-L2, so sites for puncture are located at L3-L4 or L4-L5 • Restrain patient in lateral decubitus position – Maximally flex spine without compromising airway – Keep alignment of feet, knees and hips – Position head to left if right handed or vice versa
- 17. Sitting Position • Restrain infant in the seated position with maximal spinal flexion – Hold infant’s hands between flexed legs with one hand and flex head with the other hand • Drape patient below buttocks and fenestrated drape opening over puncture site • Insert needle so bevel is parallel to spinal cord (Bevel left or right) • Cannot measure pressure accurately in this position
- 18. Paramedian (Lateral) Approach • Use for patients who have calcifications from repeated LPs or anatomic abnormalities • Needle passes through erector spinae muscles, and ligamentum flavum – Bypasses supraspinal and interspinal ligaments • Less incidence of spinal headache
- 19. Equipment • Spinal needle, usually 22 gauge – 1.5 in for < 1 yr – 2.5 in for 1 year to middle childhood – 3.5 in for older children and adolescents – Larger for large adolescents • Atraumatic needles, less spinal headaches
- 20. Procedure • Cleanse skin with povidone iodine from puncture site radially out to 10 cm and ALLOW TO DRY • Drape below patient and around site with fenestrated drape • Anesthetize with lidocaine if topical not used by: – Intradermally raising a wheal at needle insertion site – Advance needle through wheal to desired interspace • Careful not to inject into a blood vessel or spinal canal • Insert spinal needle with stylet with bevel up to keep cutting edge parallel with nerve and ligament fibers 1/12/2015 drAR 20
- 21. Procedure • Aim towards umbilicus directing needle slightly cephalad • Hold needle firmly
- 22. Procedure • A “pop” of sudden decrease in resistance indicates that ligamentum flavum and dura are punctured • Remove stylet and check for flow of spinal fluid
- 23. Procedure • If no fluid, then: – Rotate needle 90° – Reinsert stylet and advance needle slowly checking frequently for CSF • Jugular vein compression can increase CSF pressure in low flow situations • If bony resistance is felt immediately then you are not in the spinal interspace • If bony resistance is felt deeply, then withdraw needle to the skin surface and redirect more cephalad and increase patient flexion • If bloody fluid that does not clear or that clots results, then withdraw needle and reattempt at a different interspace 1/12/2015 drAR 23
- 24. Manometry • When CSF flows, attach manometer to obtain opening pressure if desired • Pressure can only be accurately measured in lateral decubitus position and in the relaxed patient • Attach manometer with a 3-way stopcock when free flow of CSF is obtained • Read column when highest level is achieved and respiratory variation is noted 1/12/2015 drAR 24
- 25. PROCEDURE 1. Positioning 2. Landmark LP site 3. Marking LP site 4. Tray opening & set-up 5. Prep & drape 6. Cutaneous anaesthesia 7. Deep anaesthesia 8. Lumbar puncture 9. Attach manometer & obtain opening pressure 10. Collect CSF 11. Finishing up 1/12/2015 drAR 25
- 26. What to do with the CSF ?? • The recommended studies include (this order can be changed): Collect 1ml of CSF in each of vials o Tube#1 : Gram stain, Culture and Sensitivity o Tube#2 : Glucose, Protein o Tube#3 : Cell Count and Differentials o Tube#4 : Any special studies you require (fungal/viral/chemical studies) • Check closing pressure with manometer, if desired • Reinsert stylet and remove needle in one quick motion • Cleanse back and cover puncture site 1/12/2015 drAR 26
- 27. Opening pressure 90-180 mm H2O / 6.6 – 13.2 mmHg (with patient lying in lateral position) Appearance and color Clear, colorless Blood cell count and differential • White blood cells: < 5 (all mononuclear) • Red blood cells: 0 Glucose 2.8 – 4.4 mmol/L, 50 - 80 mg/dL (or greater than two-thirds of blood glucose) Total protein 15-45 mg/dL Bacteria (Gram stain, culture, VDRL) Negative pH 7.28-7.32 Antibodies, viral DNA None Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) < 2.0-7.2 U/mL Lactate • Newborns 10-40 mg/dL • Older children and adults 10-25 mg/dL Chloride 110-125 mmol/L Cancerous cells None Cryptococcal antigen None Glutamine 6-15 mg/dL Normal CSF Parameter 1/12/2015 drAR 27
- 28. CSF Analysis 1/12/2015 drAR 28
- 30. Study Bacterial Meningitis Viral Meningitis SAH Opening Pressure Often elevated Normal to mildly elevated Often elevated Appearance Clear to turbid Often clear Clear to bloody Xanthochromia Negative Negative Often present RBC's <5 per mm3 <5 per mm3 >50 per mm3 WBC's Elevated. Many PMNs Elevated. Many lymphocytes Slightly increased Glucose Low Normal Normal Protein Elevated Elevated Elevated Gram Stain May show organisms Normal Normal A review of the CSF values in common disorders shows: 1/12/2015 drAR 30
- 32. Conditions associated with a reactive CSF lymphocytosis include the following: • Meningitis • Syphilitic meningoencephalitis • Parasitic CNS infection • Multiple sclerosis • Guillain-Barré syndrome • Polyneuritis Conditions associated with CSF monocytosis include the following: • Chronic or treated bacterial meningitis • Syphilitic, viral, fungal, amebic meningitis • Intracranial hemorrhage • Cerebral infarct • CNS malignancy 1/12/2015 drAR 32
- 33. Conditions associated with increased CSF polymorphonuclear neutrophils include the following: • Bacterial meningitis • Acute viral meningitis • Tuberculous and fungal meningitis • Amebic encephalomyelitis • Brain abscess • Subdural empyema • CNS hemorrhage • Cerebral infarct • Malignancies • Previous lumbar puncture • Intrathecal chemotherapy • Seizure 1/12/2015 drAR 33
- 34. Complication of Lumbar Puncture 1. Post LP headache (most common) • Usually begins 24-48 hours after the procedure • Probable etiology is continued leakage of CSF • Bilateral pressure or throbbing that is intensified in the upright position • Self-limited (≤7 days), uncommon less than 10 yo 2. Post LP back pain • Occasionally with short-lived referred limp • Disc herniation if needle advanced too far 3. Bloody tap / Dry tap • Bloody: Micro-trauma caused by spinal needle • Dry: misplacement, dehydrated patient (low csf) 4. Infection to the CSF • Can occur with breaks in sterile technique, use of contaminated equipment and placement of the needle through infected skin • Cellulitis, skin abscesses, epidural abscesses, spinal abscesses 5. Hemorrhage (low platelets counts /coagulopathies) 6. Dysesthesia (impairement of sensation) 7. Post–dural puncture cerebral herniation (most serious but very rare) • risk of herniation is 0 –5 % in those patients who are known to have intracranial masses 1/12/2015 drAR 34
- 35. Spinal Headache • Most common complication • Risk factors: – female – age 18-30 – lower BMI – hx of Headache – prior spinal headache • Bilateral Headache, improves when supine • Can last hours to weeks • Treatment – Supine position for at least 2 hours – Hydration – Caffeine either PO or IV – Epidural blood patch • Prevention: – Can avoid by: • Passing needle bevel parallel to longitudinal fibers of dura • Replacing stylet before removing needle • Using small diameter needles • Using atraumatic needles – Bed rest or PO intake after LP does not reduce incidence of headache 1/12/2015 drAR 35
- 36. Nerve Root Trauma/Irritation • Can feel electric shocks or dysesthesias • Back pain can persist for months – Consider disc herniation • Rarely permanent • Withdraw needle immediately • If pain or motor weakness persists, start corticosteroids • Electromyogram/nerve conduction velocity studies should be scheduled if pain persists 1/12/2015 drAR 36
- 37. Herniation • Manifests initially as altered mental status, followed by cranial nerve abnormalities and Cushing triad • May be rapidly fatal. • Immediately remove needle and raise the head of bed to 30-45° improve venous return from the brain. • Mannitol or 3% Saline • Intubate patient and hyperventilate • Emergent neurosurgical consult 1/12/2015 drAR 37
- 38. Epidermal Inclusion Cyst • Very rare due to use of stylet • Occurs when a core of skin is driven into spinal or paraspinal space with hollow needle • Do not remove stylet until through the skin
- 39. Failure of Procedure • If sample of CSF is critical several alternatives are available: – Have someone else try • Anesthesia • Neurology – Bedside ultrasound for difficult LPs – Radiographic guided procedure • Fluoroscopy • Ultrasound • CT – Cisterna Magna tap