Weitere ähnliche Inhalte
Ähnlich wie Project artifact 2
Ähnlich wie Project artifact 2 (20)
Project artifact 2
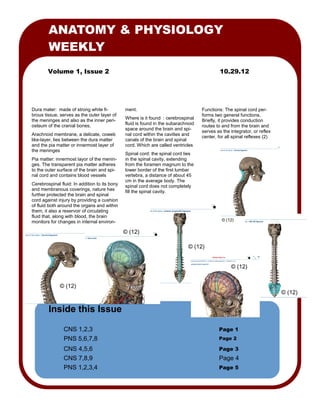
- 1. ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
WEEKLY
Volume 1, Issue 2 10.29.12
Dura mater: made of strong white fi- ment. Functions: The spinal cord per-
brous tissue, serves as the outer layer of forms two general functions.
the meninges and also as the inner peri- Where is it found : cerebrospinal
Briefly, it provides conduction
osteum of the cranial bones. fluid is found in the subarachnoid
routes to and from the brain and
space around the brain and spi-
serves as the integrator, or reflex
Arachnoid membrane, a delicate, coweb nal cord within the cavities and
center, for all spinal reflexes (2)
like-layer, lies between the dura matter canals of the brain and spinal
and the pia matter or innermost layer of cord. Which are called ventricles
the meninges
Spinal cord: the spinal cord lies
Pia matter: innermost layor of the menin- in the spinal cavity, extending
ges. The transparent pia matter adheres from the foramen magnum to the
to the outer surface of the brain and spi- lower border of the first lumbar
nal cord and contains blood vessels vertebra, a distance of about 45
cm in the average body. The
Cerebrospinal fluid: In addition to its bony spinal cord does not completely
and membranous coverings, nature has fill the spinal cavity.
further protected the brain and spinal
cord against injury by providing a cushion
of fluid both around the organs and within
them, it also a reservoir of circulating
fluid that, along with blood, the brain
monitors for changes in internal environ- © (12)
© (12)
© (12)
© (12)
© (12)
© (12)
Inside this Issue
CNS 1,2,3 Page 1
PNS 5,6,7,8 Page 2
CNS 4,5,6 Page 3
CNS 7,8,9 Page 4
PNS 1,2,3,4 Page 5
- 2. Page 2 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY WEEKLY
purpose of the sympathetic nervous
Inside the peripheral The autonomic nervous
system is to prepare the body for
nervous system there are system functions inde-
physical activity. The purpose of the
two subdivisions, the so- pendently and without
parasympathic nervous system is to
matic nervous system conscious effort. Afferent
active vegetative functions such as
and the autonomic nerv- nerves are the sensory
digestion, defecation, and urination.
ous system. The auto- nerves that travel away
(1)
nomic nervous system from the central nervous
includes fibers that con- system and efferent
nect the CNS to viscera, nerves are the motor
such as the heart, stom- nerves that travel toward
ach and glands. Within the central nervous sys-
the automatic nervous tem. As a whole the Auto-
system it is divided into nomic Nervous System
another two parts the sends impulses from the
sympathetic nervous sys- central nervous system to
tem and the parasym- smooth muscle, cardiac
pathic nervous system. muscle, and glands. The
Autonomic
Nervous System
“The
autonomic
© (12)
function
functions
independe
ntly” Efferent nerves Afferent nerves travel
travel toward the away from the CNS
CNS
© (12)
- 3. VOLUME 1, ISSUE 2 Page 3
© (12)
The ance.
Brainstem functions as our own the cerebrum. Inferior
privet is located at the lower part of cerebellar peduncles The Thalamus and the Hypothalmus are also im-
the brain directly connected to the composed cheifly if reacts portant to the brainstem. The thalamus is a dumb-
spinal cord. The brainstem is like into the cerebellum from bell shaped mass of grey matter that makes up
the spinal cord, performs sensory, the medulla and cord. many nuclei. They play two parts in the mecha-
motor, and reflex functions. It is the Middle CP are composed nism responsible for sensation.
pathway for all fiber tracts passing almost entirely of tracts It impulses from appropriate
up and down from peripheral nerves into the cerebellum from receptors, on reaching the thal-
and spinal cord to the upper areas the pons, that is, ponto- mus, produce conscious recog-
of the brain. The Medulla Oblongata cerebellar tracts. Superior nition of the crude,less crtical
is a relay station for the crossing of CP is composed to princi- sensation of pain, temperaure
motor tracts between the spinal pally of tracts from den- and touch. The neurons whose
cord and the brain. It also contains tate nuclei in the cerebel- dendrites and cell bodies lie in
the respiratory, motor and cardiac lum through the red nu- certain nuclei of the thalamus
functions, as well as several mech- cleous of the midbrain to relay all kinds of sensory im-
anisms of reflex activities such as the thalamus. The func- puses. Plays a part in the
coughing, swallowing and vomiting. tions of the cerebellum is mechanism responsible for
The midbrain is the nerve pathway that they perform three emotion, in the arousal or alert-
of the cerebral hemisphere and general functions that has ing machanism and a part in
contains auditory and visual reflex to deal with the control of the mechanism that produce
centers. The pons is the area that skeletal muscles. They complex reflex movements. It
links different parts of the brain and act with the cerebral cor- is involved in regulation of the
seves a relay station from the me- tex to produce skilled homeostatic control. Neuroen-
dulla to the higher cortical struc- movements by coordinat- docrine role in conjunction with
tures of the brain. ing the activities of groups the pituitary gland as well as by its influence on the
os muscles. They help the autonomic nervous system, which helps regu-
The Cerebellum is the second larg- control posture. It func- late body temperature, the cardiovascular system,
est part of the brain. A transverse tions below the level of and food and water intake.
fissure separates the cerebellum consciousness to make
from the cerebrum. The Gyri of the movements smooth. They
cerebellum are much more slender also control the skeletal
and less prominent than those of muscles to maintain bal-
- 4. VOLUME 1, ISSUE 2 Page 4
Somatic Motor Pathways con- Secondary sensory neurons conduct
Cerebral Cortex
sists of motor neurons that con- from the cord/brainstem up to the thala-
duct impulses from the central mus. The cerebrum is the largest and
nervous system to somatic effec- uppermost division of the brain, con-
tors. Tertiary sensory neurons conduct from
sist of two halves, the right and left
the thalamus to the post central gyros of
cerebral hemispheres.
The set of coordinated com- the parietal lobe, the somatosensory
mands that control the pro- area. Composed of gray matter
grammed muscle activity mediat-
ed by extrapyramidal pathways is Each side of the brain registers sensa-
often called a motor program. tions from the opposite side of the brain.
Functions of Cerebral Cortex
Crude touch and pressure sensations
are functions of the spin thalamic path- Consciousness, language, emotion
Somatic Sensory Pathways way. and memory are also all controlled
by the cerebral cortex
Primary sensory neurons of the
relay conduct from the periphery Mechanisms that control voluntary
to the central nervous system. movements are extremely complex
and imperfectly under-
stood (1)
© (12)
© (12)
© (12)
- 5. Page 4
At each skin surface area supplied by sensory fibers of a given spinal
Cranial Nerves- Connect
nerve is called a dermatome, a name that means “skin section”. (2)
to the undersurface of
the brain, mostly on the
© 12
brainstem. There are 12
different cranial nerves:
(2)
Olfactory (sensory)
Optic (sensory)
Oculomotor (Motor) A Myotome is a skeletal muscle or
Trochlear (Motor) group of muscles that receives mo-
Trigeminal (Mixed) tor axons from a given spinal nerve.
(2)
Abducens (Motor)
Facial (Mixed) The Ventral rami of most spinal
nerves—all but nerves T2 through
Vestibulocochlear
T12--- subdivide to form complex
(Sensory) networks called Plexuses. (2)
Glossopharyngeal
Each of the 31 pairs of spinal nerves
(Mixed) exits the spinal cavity from the inter-
Vagus (mixed) vertebral foramina. The names of
© 12 the vertebrae are given on the left
Hypoglossal (Motor) and the names of the corresponding
spinal nerves on the right. (2)
© 12
© 12
© 12