Report
Share
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Mechanical energy for 9th grade physics, chapter 6

Mechanical energy for 9th grade physics, chapter 6
IIT JEE NOTES work, energy and power BY ANURAG TYAGI CLASSES 

IIT JEE NOTES work, energy and power BY ANURAG TYAGI CLASSES
Similar to Physics Block Spring Friction Stop
Similar to Physics Block Spring Friction Stop (20)
Physics Block Spring Friction Stop
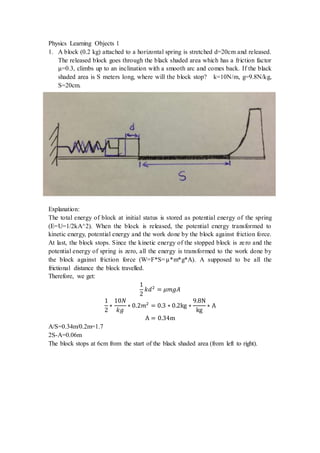
- 1. Physics Learning Objects 1 1. A block (0.2 kg) attached to a horizontal spring is stretched d=20cm and released. The released block goes through the black shaded area which has a friction factor μ=0.3, climbs up to an inclination with a smooth arc and comes back. If the black shaded area is S meters long, where will the block stop? k=10N/m, g=9.8N/kg, S=20cm. Explanation: The total energy of block at initial status is stored as potential energy of the spring (E=U=1/2kA^2). When the block is released, the potential energy transformed to kinetic energy, potential energy and the work done by the block against friction force. At last, the block stops. Since the kinetic energy of the stopped block is zero and the potential energy of spring is zero, all the energy is transformed to the work done by the block against friction force (W=F*S=μ*m*g*A). A supposed to be all the frictional distance the block travelled. Therefore, we get: 1 2 𝑘𝑑2 = 𝜇𝑚𝑔𝐴 1 2 ∗ 10𝑁 𝑘𝑔 ∗ 0.2𝑚2 = 0.3 ∗ 0.2kg ∗ 9.8N kg ∗ A A = 0.34m A/S=0.34m/0.2m=1.7 2S-A=0.06m The block stops at 6cm from the start of the black shaded area (from left to right).