Chapter 05 Macromolecules
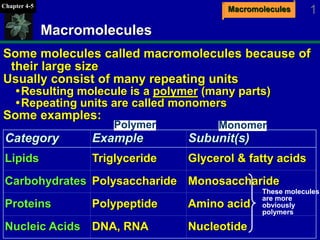
- 1. MacromoleculesChapter 4-5 1 Macromolecules Some molecules called macromolecules because of their large size Usually consist of many repeating units Resulting molecule is a polymer (many parts) Repeating units are called monomers Some examples: NucleotideDNA, RNANucleic Acids Amino acidPolypeptideProteins MonosaccharidePolysaccharideCarbohydrates Glycerol & fatty acidsTriglycerideLipids Subunit(s)ExampleCategory These molecules are more obviously polymers Polymer Monomer
- 2. MacromoleculesChapter 4-5 2 You should be able to recognize the following macromolecules . (Label the following as either fats, proteins, amino acids, carbohydrates or nucleic acids) a. ________ b. ________ c. ________ d. ________ e. ________ f. ________ g. ________
- 3. MacromoleculesChapter 4-5 3 How macromolecules are made and used. Dehydration and Hydrolysis Know: a. Organic polymers are made via a metabolic process called Dehydration synthesis b. Polymers are taken apart by a process called hydrolisis (this name should remind you that one water molecule us produced by this process.)
- 4. MacromoleculesChapter 4-5 4 Dehydration Synthesis Fig. 5.2 p69
- 5. MacromoleculesChapter 4-5 5 Hydrolysis of a polymer
- 6. MacromoleculesChapter 4-5 6Examples of the 4 classes of macromolecules. 1 - Carbohydrates I.Monosaccharides: (single sugar molecules) Glucose - 6 carbon sugars used by animals and plants for cellular respiration Ribose, deoxyribose – 5 carbon sugars which are components of DNA and RNA II. Disaccharides: (Two monosaccharides joined by dehydration) Sucrose – common form of plant sugars (glucose + fructose) III. Polysaccharides: (Polymers of monosaccharides) • Starch, cellulose, chitin – storage and structural form of sugars.
- 7. 7Models for Representing Glucose Molecules Formula: C6H12O6
- 8. 8Synthesis Disaccharides Maltose and Fructose
- 9. MacromoleculesChapter 4-5 9 Two general forms of Carbohydrates 1. Storage forms of carbohydrates. Polymers of monosaccharides Low solubility; not sweet to taste Examples Starch = Polymer of glucose Used for short-term energy storage Amylose = Plant starch (eg. corn starch) - unbranched chain, or slightly branched Glycogen = Animal starch - Highly branched - in liver and muscles
- 10. 10 Starch structure and function Storage form of carbs in plants Fig. 5.6 p72
- 11. 11 Glycogen structure and function Storage form of carbs in animals
- 12. MacromoleculesChapter 4-5 12 Structural forms of carbohydrates I. Cellulose - Long, coiled polymer of glucose - Glucoses connected differently than in starch - Structural element for plants - Main component of wood and many natural fibers - Indigestible by most animals II. Chitin - Polymer of glucose - Each glucose with an amino group - Very resistant to wear and digestion - Arthropod exoskeletons, cell walls of fungi III. Peptidoglycans - Bacterial cell walls.
- 13. MacromoleculesChapter 4-5 13 2. Carbohydrates as structural materials chitin notes: Carbohydrates for structural material : a. In plants, cellulose b. In some animals (insects and crustaceans), chitin c. In bacteria, peptidoglycan.
- 14. 14Cellulose structure and Function Notice alternate orientation Fig. 5.7 p.71
- 15. 15 Starch Exocyclic carbons All on the same Side!
- 16. MacromoleculesChapter 4-5 16 Carbohydrate summary: 1. Monosacharides: ex. Glucose, Fructose 2. Disacharides : Sucrose (glucose + fructose) 3. Polysacharides: a) Starch (plants), Glycogen (animals) -Storage b) Cellulose (structural in plants) –alternation of bond orientation c) Chitin (structural in insects and crabs etc. ) d) Peptidoglycan (structural in bacteria).
- 17. MacromoleculesChapter 4-5 17Four Classes of Organics: 2 - Lipids Insoluble in water Long chains of repeating CH2 units Renders molecule nonpolar Types of Lipids Cholesterol, Testosterone Estrogen, Progesterone, etc Component of plasma membrane; hormonesSteroids PhospholipidsComponent of plasma membranePhospholipids Fatty AcidsLong-term energy storage in plants and their seeds“Oils” TriglyceridesLong-term energy storage & thermal insulation in animals“Fats” CompoundsOrganismal UsesType Di, and Triesters..Wear resistance; retain waterWaxes TG’S
- 18. 18Types of Lipids: I. Fatty acids Saturated A. B. Fig. 5.11 p75
- 19. MacromoleculesChapter 4-5 19Types of Lipids: II. Triglycerides Animals typically store fatty acids in groups of 3 attached to a glycerol molecule. Triglycerides (Fats) Long-term energy storage Backbone of one glycerol molecule - Three-carbon alcohol - Each has an OH- group - Each fatty acid may be Saturated - no double bonds between carbons or Unsaturated - 1 double bonds between carbons - Carboxylic acid at one end - Carboxylic acid connects to –OH on glycerol in dehydration reaction
- 20. 20Dehydration Synthesis of Triglyceride from Glycerol and Three Fatty Acids
- 21. MacromoleculesChapter 4-5 21Types of Lipids: III. Phospholipids Phospholipids Glycerol backbone Two fatty acids attached instead of three Third fatty acid replaced by phosphate group - The fatty acids are nonpolar and hydrophobic (“hates water) - The phosphate group is polar and hydrophilic (“likes water) Molecules self arrange when placed in water Polar phosphate “heads” next to water (= hydrophilic) Nonpolar fatty acid “tails” overlap and exclude water (hydrophobic) Spontaneously form double layer & a sphere (cell membrane)
- 22. 22Phospholipids Form Membranes Polar head Orients toward water Fig. 5.12 p76
- 23. MacromoleculesChapter 4-5 23Types of Lipids: IV. Steroids & Waxes Steroids Cholesterol, testosterone, estrogen Skeletons of four fused carbon rings Waxes Long-chain fatty acid bonded to a long-chain alcohol -High melting point -Waterproof -Resistant to degradation
- 24. MacromoleculesChapter 4-5 24 Steriods Know this basic structure!! Side chains will vary
- 25. 25Waxes
- 27. MacromoleculesChapter 4-5 27Four Classes of Organics: 3 -Proteins Functions a. Support – Collagen b. Enzymes – Almost all enzymes are proteins c. Transport – Hemoglobin; membrane proteins d. Defense – Antibodies e. Hormones – Many hormones; insulin f. Motion – Muscle proteins, microtubules (see fig. 5.13, p. 76) Know these six functions of proteins
- 28. MacromoleculesChapter 4-5 28Protein Subunits: The Amino Acids There are 20 different amino acids that make up proteins All of them have basically the same structure except for what occurs at the sidechain R Proteins are polymers of amino acids
- 29. 29Physical / Chemical properties of amino acids: 3 Main Groups Nonpolar 1. Fig. 5.16 p79
- 31. MacromoleculesChapter 4-5 31Proteins: Making polypeptides from amino acids. Amino acids joined together end-to-end Special name for this bond - Peptide Bond - Can have 3 or 4 amino acids (AA) joined together, or several thousand Characteristics of a protein are determined by composition and sequence of AA’s Virtually unlimited number of proteins Ex. 10 AA’s can have 1020 different sequences.
- 32. 32Synthesis of a Peptide Dehydration synthesis forms a peptide bond between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another. Or: Taken apart (digestion) by hydrolysis!
- 33. MacromoleculesChapter 4-5 33Protein Molecules: Levels of Structure Primary: Literally, the sequence of amino acids A string of beads (up to 20 different colors) Secondary: The way the amino acid chain coils or folds Tertiary: Overall three-dimensional shape of a polypeptide Describing how the coils and folds interact with eachother Quaternary: Consists of more than one polypeptide Like several completed knots glued together
- 34. 34Levels of Protein Organization A. Primary structure
- 35. 35Levels of Protein Organization B. Secondary Structure
- 36. MacromoleculesChapter 4-5 36 Protein Folding nonpolar polar charged Where in a protein would you expect to find each of these groups of amino acids?
- 37. 37Levels of Protein Organization C. Tertiary Structure Hydrophobic interactions -COOH-- Charged amino acids Fig. 5.18 p81
- 38. 38Levels of Protein Organization D. Quaternary Structure 1o 2o 3o 4o
- 39. 39Examples of Fibrous Proteins Keratin Fibroin Beta-mercaptoethanol used to add more disulfide bonds (between which amino acids ?) Alpha helices Beta-pleated sheets Fibroin
- 40. MacromoleculesChapter 4-5 40 Protein Folding Chaperones Defective protein folding Is involved in human Disease: Ex: • Alzheimer's • CJD –Creutzfeldt Jacobs (“Mad Cow Disease”)
- 41. MacromoleculesChapter 4-5 41Four Classes of Organics: 4 -Nucleic Acids Polymers of nucleotides (C,T, A, G, U) Very specific cell functions DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) - Double-stranded helical spiral (twisted ladder) - Serves as genetic information center - In the nucleus of cells in chromosomes. RNA (ribonucleic acid) - Part single-stranded, part double-stranded** - Serves primarily in assembly of proteins (several types: tRNA, mRNA, rRNA and snRNP’s) - In nucleus and cytoplasm of cell
- 42. MacromoleculesChapter 4-5 42The Nucleotides of Nucleic Acids Three components: 1. 5 carbon ribose sugar 2. phosphate group 3. nitrogenous base group Nucleotide subunits connected end-to-end to make nucleic acid Sugar of one connected to the phosphate of the next Sugar-phosphate backbone
- 43. MacromoleculesChapter 4-5 43The Structure of Nucleic Acids Nucleotide subunits connected end-to-end to make nucleic acid Sugar of one connected to the phosphate of the next Sugar-phosphate backbone
- 44. 44 Nucleotides
- 45. 45DNA Structure The double alpha-helix structure of DNA that was determined by Watson and Crick 1953
- 46. 46RNA Structure RNA is mostly single stranded or folds back on itself to form double stranded structures Called “Stem-loops”
- 47. MacromoleculesChapter 4-5 47 NoYesHelix Interprets genetic info; protein synthesis Heredity; cellular control centerFunction Cell nucleus and cytoplasm Chromosomes of cell nucleusWhere Comparison of DNA & RNA Mostly single strandedDouble-stranded; Pairing across strandsStrands Cytosine, guanine; adenine, uracil Cytosine, guanine; adenine, thymineBases RiboseDeoxyriboseSugar RNADNAFeature
- 48. MacromoleculesChapter 4-5 48Other Nucleic Acids ATP – the energy currency of cells ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is composed of adenine, ribose, and three phosphates In cells, one phosphate bond is hydrolyzed – Yields: The molecule ADP (adenosine diphosphate) An inorganic phosphate molecule pi Energy Other energy sources used to put ADP and pi back together again
- 49. 49ATP The three “high energy” phosphate bonds of ATP are what Make this molecule so useful in many enzymatic reactions.
- 50. MacromoleculesChapter 4-5 50 Review Organic vs Inorganic Functional Groups / Isomers Macromolecules 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids – covalent C, O, H, N versus ionic metals and salts -Amino, carboxyl, phosphate, sulhydryl. -Iosomers = same formula, different structure -starch, glycogen, (made from polymerized glucose) -Cellulose, chitin = structural forms. -fatty acids 3 together form triglycerides, 2 together + phosphate form A phospholibid (membranes), can be saturated or unsaturated, steroids Are different (shape) , Waxes = long chain fatty acids + alcohols - Chains of 20 different amino acids linked by peptide bonds -Chains of 4 different nucleotides linked by a sugar-phosh Backbone, DNA = double stranded genetic material, RNA = primary function in interpreting genenetic code into protei