Protochordata by Tiasha De (University of Calcutta)
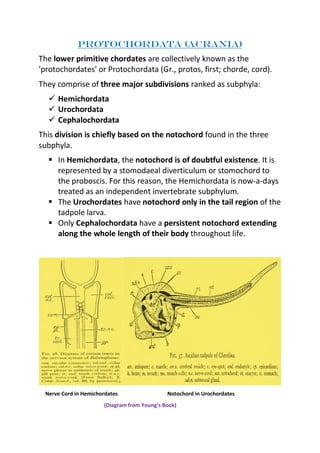
- 1. PROTOCHORDATA (ACRANIA) The lower primitive chordates are collectively known as the 'protochordates' or Protochordata (Gr., protos, first; chorde, cord). They comprise of three major subdivisions ranked as subphyla: ✓ Hemichordata ✓ Urochordata ✓ Cephalochordata This division is chiefly based on the notochord found in the three subphyla. ▪ In Hemichordata, the notochord is of doubtful existence. It is represented by a stomodaeal diverticulum or stomochord to the proboscis. For this reason, the Hemichordata is now-a-days treated as an independent invertebrate subphylum. ▪ The Urochordates have notochord only in the tail region of the tadpole larva. ▪ Only Cephalochordata have a persistent notochord extending along the whole length of their body throughout life. Nerve Cord in Hemichordates Notochord in Urochordates (Diagram from Young’s Book)
- 2. Hemichordate with STOMOCHORD Urochordate larva with NOTOCHORD Cephalochordate with NOTOCHORD
- 4. Sub Phylum 1: HEMICHORDATA General Characteristics: ❖ HABITAT: Exclusively marine, solitary or colonial, mostly tubicolous. ❖ STRUCTURE: Body soft, fragile, vermiform, unsegmented, bilaterally symmetrical and triploblastic. ❖ DIVISION: Body typically divided into 3 distinct regions: proboscis, collar and trunk. ❖ Body wall of a single layered, epidermis with mucous glands. No dermis. ❖ Coelom enterocoelous, usually divided into protocoel, mesocoel and metacoel, corresponding to 3 body regions. ❖ Digestive tube complete, straight or U-shaped. ❖ Foregut gives out a hollow buccal diverticulum into proboscis, earlier considered as 'notochord'. ❖ Dorso-lateral pharyngeal gill slits, when present, one to several pairs. ❖ Pharynx with endostyle. They are ciliary filter feeders. ❖ Circulatory system simple and open, including a dorsal heart and two longitudinal vessels, one dorsal and one ventral. ❖ Excretion by a single proboscis gland or glomerulus connected to blood vessels. ❖ Nervous system primitive consisting mainly of a sub-epidermal nerve plexus. Dorsal collar nerve cord hollow. ❖ Reproduction is mainly sexual. Sexes are usually separate. Gonads one to several pairs. ❖ Fertilization external, in sea water. Development direct or indirect with a free-swimming tornaria larva. EXAMPLES: Balanoglossus sp. (Acorn Worm), Cephalodiscus sp., etc. Balanoglossus sp. (From Young’s Book)
- 5. Balanoglossus sp. (Another diagram) CLASSes : According to J.Z. Young (1981), this phylum is divided into 2 classes: I. Enteropneusta Balanoglossus sp., Glossobalanus sp., Ptychodera sp., Saccoglossus sp. II. Pterobranchia Cephalodiscus sp., Rhabdopleura sp. CLASS 1- ENTEROPNEUSTA (Gr. enteron, gut + pneustos, breathed) General Characteristics: ❖ Solitary, free-swimming or burrowing animals, commonly called the 'acorn' or 'tongue worms'. ❖ Body elongated, vermiform, with no stalk. ❖ Proboscis cylindrical and tapering. ❖ Collar without ciliated arms (lophophore). ❖ Alimentary canal straight. Mouth and anus at opposite ends. Filter feeding.
- 6. ❖ Several pairs of U-shaped gill-slits. ❖ Sexes separate. Gonads numerous, sac like. ❖ Development includes tornaria larva in some. Asexual reproduction lacking. EXAMPLES: Balanoglossus sp., Saccoglossus sp. (= Dolichoglossus), Protoglossus sp., Ptychodera sp., Spengelia sp.
- 7. CLASS 2 – PTEROBRANCHIA (Gr. pteron, feather + branchion, gill) General Characteristics: ❖ Solitary or colonial, sessile and tubicolous animals living inside secreted chitinous tubes. ❖ Body short, compact, with stalk for attachment. ❖ Proboscis shield like. ❖ Collar bearing ciliated arms (lophophore). ❖ Alimentary canal U-shaped. Anus dorsal lying near mouth. Ciliary feeding. ❖ Gill slits one pair or absent, never U-shaped. ❖ Sexes separate or united. Gonads one or 1 pair. ❖ Development direct or with a larval stage. Asexual reproduction by budding in some. EXAMPLES: Rhabdopleura sp., Cephalodiscus sp., Atubaria sp.
- 8. ❖ The class Pterobranchia has 2 orders: ✓ Rhabdopleurida ✓ Cephalodiscida (Orders are not in syllabus) Sub Phylum 2: uroCHORDATA General Characteristics: ❖ Exclusively marine and cosmopolitan, found in all seas and at all depths. ❖ Mostly sedentary (fixed), some pelagic or free-swimming. ❖ Simple (solitary), aggregated in groups or composite (colonial). ❖ Size (0.25 to 250 mm), shape and colour variable. ❖ Adult body degenerate, sac-like, unsegmented, without paired appendages and usually without tail. ❖ Body covered by a protective tunic or test composed largely of tunicine, (C6H10O5)n, similar to cellulose, hence the name Tunicata. ❖ A terminal branchial aperture and a dorsal atrial aperture usually present. ❖ Coelom absent. Instead, an ectoderm-lined atrial cavity present, which opens to outside through atrial aperture. ❖ Notochord present only in larval tail, hence the name Urochordata. ❖ Alimentary canal complete. Pharynx (branchial sac) large, with endostyle and two to several pairs of gill-slits. Ciliary feeders. ❖ Respiration through test and gill-slits. ❖ Blood-vascular system open. Heart simple, tubular and ventral. Flow of blood periodically reversed. Special vanadocytes in blood extract vanadium from sea water. ❖ Excretion by neural gland, pyloric gland and nephrocytes. ❖ Dorsal tubular nerve cord only in larval stage, reduced to a single dorsal nerve ganglion in adult. ❖ Mostly hermaphrodite. Fertilization cross and external.
- 9. ❖ Development indirect including a free-swimming tailed larva with basic chordate characters. ❖ Metamorphosis retrogressive. ❖ Asexual reproduction by budding common. EXAMPLES: Ascidia sp., Ciona sp., Herdmania sp. (Sea Squirt), Botryllus sp., Malgula sp., Doliolum sp., Salpa sp., Pyrosoma sp., Oikopleura sp. CLASSes : According to J.Z. Young (1981), this phylum is divided into 3 classes: I. Ascidiacea Ascidia sp., Ciona sp., Herdmania sp. (Sea Squirt), Botryllus sp., Malgula sp. II. Thaliacea Doliolum sp., Salpa sp., Pyrosoma sp. III. Larvacea Oikopleura sp., Kowaleviskia sp. CLASS 1- ASCIDIACEA General Characteristics: ❖ Solitary, colonial or compound. Bottom living. ❖ Body form and size variable. ❖ Test permanent, well developed and thick. ❖ Atrium opens dorsally by atriopore. ❖ Pharynx large with many persistent gill-slits. ❖ Sexes united. Larva free-swimming and highly developed. ❖ Adults usually sessile after retrogressive metamorphosis when larval notochord, nerve cord and tail are lost and brain reduced to a solid dorsal ganglion. ❖ Stolon simple or none. EXAMPLES: Ascidia sp., Ciona sp., Herdmania sp. (Sea Squirt), Botryllus sp., Malgula sp., Doliolum sp.
- 10. Diagram of Herdmania sp. from Young’s book. Ciona sp. Botryllus sp. ❖ The class Ascidiacea has 2 orders: ✓ Enterogona ✓ Pleurogona (Orders are not in syllabus)
- 11. CLASS 2- THALIACEA General Characteristics: ❖ Adults free living, pelagic, in warm and temperate seas. Solitary or colonial. ❖ Body shape and size variable. ❖ Tunic permanent, thin and transparent, with ❖ circular muscle bands. ❖ Atriopore located posteriorly. ❖ Pharynx with 2 large or many small gill-slits. ❖ Sexes united. Larva formed or absent. ❖ Adult without notochord, nerve cord and tail. ❖ Asexual budding from a complex stolon. ❖ Life history with an alternation of generations. EXAMPLES: Doliolum sp., Salpa sp., Pyrosoma sp. Pyrosoma sp.
- 12. Salpa sp. ❖ The class Thaliacea has 3 orders: ✓ Pyrosomida ✓ Doliolida ✓ Salpida (Orders are not in syllabus)
- 13. CLASS 3- LARVACEA (=Appendicularia) General Characteristics: ❖ Small (5 mm long), solitary, free-swimming, pelagic, neotenic, larva-like forms with persistent tail, notochord, nerve cord and brain. ❖ Test forming a temporary house, renewed periodically. ❖ Atrium and atrial aperture absent. ❖ Gill-slits 2, opening directly to outside. ❖ Sexes united. No metamorphosis. EXAMPLES: Oikopleura sp., Kowaleviskia sp. Oikopleura sp. ❖ The class Larvacea has 2 orders: ✓ Endostylophora ✓ Polystylophora (Orders are not in syllabus)
- 14. Sub Phylum 3: CephaloCHORDATA General Characteristics: ❖ Marine, widely distributed in shallow waters. ❖ Mostly sedentary, and buried with only anterior body end, projecting above bottom sand. ❖ Body small, 5 to 8 cm long, slender, fish-like, metameric and transparent. ❖ Lacks head. Body has trunk and tail. ❖ Lacks paired appendages. Median present. ❖ Exoskeleton absent. Epidermis single layered. ❖ Muscles dorso-lateral, segmented into myotomes. ❖ Coelom enterocoelous, reduced in the pharyngeal region. ❖ Notochord rod-like, persistent, extending from rostrum to tail. ❖ Digestive tract complete. ❖ Pharynx large, perforated by numerous persistent gill-slits. ❖ Filter feeders. ❖ Respiration through general surface. ❖ Circulatory system well-developed, closed and without heart and respiratory pigment. ❖ Hepatic portal system developed. ❖ Excretion by protonephridia and solenocytes. ❖ Nerve cord dorsal, tubular, without ganglia and brain. ❖ Sexes separate. Gonads numerous and metamerically repeated. ❖ Sexual reproduction. ❖ Fertilization external, in sea water. ❖ Development indirect, including a free-swimming larva. EXAMPLES: Branchiostoma sp., Asymmetron sp. CLASSes : According to J.Z. Young (1981), this phylum is divided into 1 class: I. Leptocordii Branchiostoma sp., Asymmetron sp.
- 16. General table for Comparison of 3 Protochordata Sub-phyla
