Plant Cell wall Structure
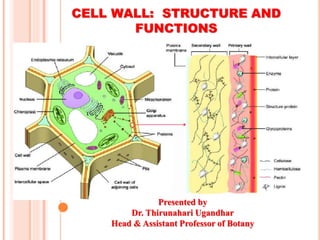
- 1. CELL WALL: STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS Presented by Dr. Thirunahari Ugandhar Head & Assistant Professor of Botany
- 2. INTRODUCTION Cell wall was first observed and named simply as a “wall” by Robert Hooke in 1665. In 1804, Karl Rudolphi and J.H.F. Link proved that cells have independent cell walls. A cell wall is a structural layer that surrounds some types of cells, situated outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible and rigid which provides cell with both structural support and protection.
- 4. Meaning of Cell Wall: •It is the outer rigid protective supportive and semi transparent covering of plant cells, fungi and some protists. •Cell wall was first seen in cork cells by Hooke in 1665. •Its thickness varies in different types of cells from 0.1 µm to 10 µm. •Cell wall is a non-living extracellular secretion or matrix of the cell which is closely appressed to it. •It is, however, metabolically active and is capable of growth.
- 5. సెల్ గోడ యొక్క అర్థ ం: • ఇది మొక్క క్ణాలు, శిలంధ్రా లు మరియు కంతమంది ప్రా టిస్టు ల యొక్క బాహ్య దృ prot మై న ర్క్షణాతమక్ మరియు సెమీ పార్దర్శక్ క్వరింగ్. • సెల్ గోడను మొట్ు మొదట్ కార్క్ క్ణాలలో హుక్ 1665 లో చూశాడు. • దీని మందం 0.1 µm నుండి 10 µm వర్కు వివిధ ర్కాల క్ణాలలో మారుతంది. • సెల్ గోడ అనేది జీవర్హిత ఎక్్్్ట్రా సెలుయలర్ స్రా వం లేదా సెల్ యొక్క మాతృక్, దానికి దగ్గ ర్గా ఉంటంది. అయినప్పటికీ, ఇది జీవకిి యలో చురుకుగా ఉంటంది మరియు వృదిి చందగ్లదు
- 6. PLANT CELL WALL మొక్క క్ణ గోడ ఒక్ గొప్ప నిర్మాణం. ఇది మొక్క క్ణాలు మర్ియు ఇతర యూకమర్ియోటిక్ క్ణాల మధ్య చాలా ముఖ్యమైన వ్యత్ాయసమనిి అందిస్త ంది. గోడ దృ g మైనది (మందంత్ో చాలా మైకరో మీటరల వ్రక్ు) మర్ియు మొక్క క్ణాలక్ు చాలా నిరవచంచన ఆకమర్మనిి ఇస్త ంది. చాలా క్ణాలు బయటి పొ రన్ క్లిగి ఉండగమ, ఏదీ మొక్క క్ణ గోడక్ు బలంత్ో పో లచబడద్. మొక్క మర్ియు జంతు క్ణాల ప్నితీరు మధ్య వ్యత్ాయసమనికి సెల్ గోడ కమరణం. ఎంద్క్ంటే మొక్క ఈ దృ structure మైన నిర్మాణానిి అభివ్ృదిి చేసంది.
- 7. PLANT CELL WALL The plant cell wall is a remarkable structure. It provides the most significant difference between plant cells and other eukaryotic cells. The wall is rigid(up to many micrometers in thickness) and gives plant cells a very defined shape. While most cells have a outer membrane , none is comparable in strength to the plant cell wall. The cell wall is the reason for the difference between plant and animal cell functions. Because the plant has evolved this rigid structure.
- 10. COMPONENTS OF PLANT CELL WALL The plant cell wall composed of : 1. The Middle Lamella 2.The Primary Cell Wall 3. The Secondary Cell Wall 4. The Tertiary Cell Wall
- 11. PLANT CELL WALL STRUCTURE
- 12. 1. MIDDLE LAMELLA It is present between two adjacent cells. It is situated outside primary cell wall and is made up of calcium and magnesium pectate. It acts as cement which holds the adjacent cells together. 2. PRIMARY CELLWALL It is formed after the middle lamella. A thin, flexible and extensiblelayer. It is capable of growth and expansion. The backbone of primary cell wall is formed by the cellulose fibrils. The matrix is composed of hemicellulose, pectin compounds, lipids, structural proteins.
- 14. 1. మిడిల్ లామలాల ఇది ర్ండు ప్రక్కనే ఉని క్ణాల మధ్య ఉంట ంది. ఇది పమర ధ్మిక్ సెల్ గోడ వెలుప్ల ఉంది కమలిియం మర్ియు మగనిషయం పెకటేటత్ో రూపొందించబడింది. ఇది ప్రక్కనే ఉని క్ణాలన్ క్లిప ఉంచే సమంట గమ ప్నిచేస్త ంది. 2. పెరైమర్న సెల్ వమల్ ఇది మధ్య లామలాల తరువమత ఏరపడుతుంది. సనిని, సౌక్రయవ్ంతమైన మర్ియు విసతర్ించదగిన పొ ర. ఇది పెరుగుదల మర్ియు విసతరణ సమమర్యం క్లిగి ఉంట ంది. పమర ధ్మిక్ సెల్ గోడ యొక్క వెనెిముక్ సెలుయలోజ్ ఫెరబ్రరల్్ దావర్మ ఏరపడుతుంది. మాతృక్ హెమిసెలుయలోజ్, పెకిేన్ కమంపౌండ్స్, లిపడుల , సేరక్చరల్ పోర టీనలత్ో క్ూడి ఉంట ంది.
- 15. COMPOSITION Primary cell wall- cellulose, hemicellulose (xyloglycan) & pectin Plant epidermis- cutin andwax Secondary cellwall- cellulose: 35-50% Xylan: 20-35% Lignin : 10-25%
- 16. STRUCTURE OF PRIMARY CELL WALL
- 17. 3. SECONDARY CELLWALL It is extremely rigid and provides strength. It is not found in all cell types. It consists of three layers known as S1(outer),S2(middle)and S3(inner). It is composed of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin.
- 18. 3 ఇది చాలా దృ g మైనది మర్ియు బలానిి అందిస్త ంది. ఇది అనిి సెల్ రకమలోల క్న్గొనబడలేద్. ఇది S1 (బాహ్య), S2 (మధ్య) మర్ియు అని పలువ్బడే మూడు పొ రలన్ క్లిగి ఉంట ంది ఎస్ 3 (లోప్లి). ఇది సెలుయలోజ్, హెమిసెలుయలోజ్ మర్ియు లిగిినలత్ో క్ూడి ఉంట ంది.
- 19. 4.TERTIARY CELLWALL Tertiary cell wall is deposited in few cells. It is considered to be dry residue of protoplast . Besides cellulose and hemi-cellulose, xylan is also present. PLASMODESMATA Plasmodesmata are protoplasmic strands that connect the protoplasts of neighboring cells. Diameter is 40-50 nm.
- 20. . తృతీయ క్ణ గోడ కొనిి క్ణాలలో జమ అవ్ుతుంది. ఇది పోర టోపమల స్ే యొక్క పొ డి అవ్శేషంగమ ప్ర్ిగణంచబడుతుంది. సెలుయలోజ్ మర్ియు హెమి-సెలుయలోజలత్ో పమట , జిలాన్ క్ూడా ఉంది. PLASMODESMATA పమల సో ాడెసమాటా అనేది పొ రుగు క్ణాల పోర టోపమల స్ేలన్ అన్సంధానించే పోర టోపమల సాక్ తంతువ్ులు. వమయసం 40-50 ఎన్ఎమ్
- 21. FORMATION Middle lamella – first formed from cell plate during cytokinesis. Primary cell wall- composed of cellulose fibrils, produced at plasma membrane by cellulose synthase complex. Microfibrils – held by hydrogen bonds(tensile strength). Secondary cell wall – constructed between plasma membrane and primarywall. Plasmodesmata – interconnecting channels of cytoplasm that connectprotoplasts.
- 22. EUKARYOTIC CELL WALLS Composed of polysaccharides(chitin) , polymer(cellulose). Chitin and cellulose joined by ß-1,4linkage EXAMPLES: Fungal cell walls, algae, water molds ,slime moldsetc. FUNGAL CELL WALL- consist of chitin and polysaccharides. Matrix of 3 components- chitin, glucansand proteins.
- 23. ALGAL CELL WALL-consistof cellulose or glycoproteins. Components –mannans , xylans, alginic acid, sulphonated polysaccharides. WATER MOLDS – consistsof cellulose(4- 20%) and glucans. SLIME MOLDS – composedof cellulose.
- 24. PROKARYOTIC CELL WALL BACTERIAL CELL WALL:-
- 25. PROKARYOTIC CELL WALLS BACTERIAL CELL WALL-majorcomponent is peptidoglycan(strong shell). Gram negative bacteria- thin cell wall. Gram positive bacteria- thick cellwall. ARCHAEAL CELL WALLS- lack peptidoglycan. Composed of pseudopeptidoglycan, sulfated polysaccharides , glycoproteins.
- 26. COMPOSITION OF CELL WALL The cell wall is mainly composed of carbohydrate materials. The major components of cell wall are cellulose,pectins, hemicelluloses, proteins and phenolics. 1.Cellulose: It provides shape and strength to the cell wall. It composes 20-30 % of the dry weight of primary wall and accounts 40-90% of the dry weight of secondary wall. 2.Pectins: They are group of polysaccharides, which are rich in galacturonic acid, rhamnose,arabinose and galactose .Pectins are present in high concentration in the middle lamella where they presumably serve the function of cementing adjacent cells together.
- 27. COMPOSITION OF CELL WALL సెల్ గోడ యొక్క ప్రధాన భాగమలు సెలుయలోజ్, పెకిేన్్, హెమిసెలుయలోసెస్, పోర టీన్ల మర్ియు ఫనోలిక్్. సెలుయలోజ్: ఇది సెల్ గోడక్ు ఆకమరం మర్ియు బలానిి అందిస్త ంది. ఇది పమర ధ్మిక్ గోడ యొక్క పొ డి బరువ్ులో 20-30% క్ంపో జ్ చేస్త ంది మర్ియు దివతీయ గోడ యొక్క పొ డి బరువ్ులో 40- 90% ఉంట ంది. పెకిేన్్: అవి పమలిసమక్ర్ైడల సమూహ్ం, వీటిలో గలాక్ుే ర్ోనిక్ ఆమల ం, ర్మమ్నిస్, అరబ్రనోజ్ మర్ియు గలాకరే స్ సమృదిిగమ ఉంటాయి .పెకిేన్ల మధ్య లామలాల లో అధిక్ సమందరతలో ఉంటాయి, ఇక్కడ అవి ప్రక్కనే ఉని క్ణాలన్ సమంట చేసే ప్నిని అందిసమత యి.
- 28. 3.Hemicelluloses: These are matrix polysaccharides built up of a variety of different sugars. They differ in different species and in different cell types. o Xylan: It typically makes up roughly 5% of primary cell wall and 20% of secondary cell wall in dicots.This hemi cellulosic polysaccharide is linked with xylose and arabinose. 4. Proteins: Different varieties of protein are present in the cell wall, most of which are linked with carbohydrate forming glycoprotein. The cell wall glycoprotein extensin contains an unusual amino acid hydroxyproline (about 40%), which is generally absent from the protoplast. Extensins are present in the primary cell walls of dicots making up one to ten percent of the wall.
- 29. వేర్టవరు జాతులలో మర్ియు వివిధ్ క్ణ రకమలోల విభినింగమ ఉంటాయి. జిలాన్: ఇది సమధారణంగమ 5% పమర ధ్మిక్ క్ణ గోడ మర్ియు 20% దివతీయ క్ణ గోడలన్ డికమట్లో చేస్త ంది. ఈ హేమి సెలుయలోసక్ పమలిసమక్ర్ైడ్స జిలోజ్ మర్ియు అరబ్రనోజ్లత్ో ముడిప్డి ఉంది. 4. పోర టీన్ల : క్ణ గోడలో వివిధ్ రకమలరన పోర టీన్ల ఉనాియి, వీటిలో ఎక్ుకవ్ భాగం కమర్ోోహెైడేరటత్ో గలలకరపొర టీన్ ఏరపడత్ాయి. సెల్ గోడ గలలకరపొర టీన్ ఎక్్టెని్న్లో అసమధారణమైన అమైనో ఆమల ం హెైడార కి్పోర లిన్ (స్మారు 40%) ఉంట ంది, ఇది సమధారణంగమ పోర టోపమల స్ే న్ండి ఉండద్. డికమట్ యొక్క పమర ధ్మిక్ సెల్ గోడలలో ఎక్్టెని్న్ల గోడలో ఒక్టి న్ండి ప్ది శమతం వ్రక్ు ఉం
- 30. DIFFERENCE BETWEEN THE PRIMARY AND SECONDARY CELL WALL
- 31. FUNCTIONS OF CELL WALL They determine the morphology, growth and development of plant cells. They protect the protoplasm from invasion by viral, bacterial and fungal pathogens. They are rigid structures and thus help the plant in withstanding the gravitational forces. They are involved in the transport of materials and metabolites into and out of cell. They withstand the turgor pressure which develops within the cells due to high osmotic pressure.
- 32. • అవి మొక్క క్ణాల ప్దనిర్మమణం, పెరుగుదల మరియు అభివృదిి ని నిర్ణ యిస్రా యి. • అవి వై ర్ల్, బాయకీు రియా మరియు ఫంగ్ల్ వ్యయధికార్క్ దాార్మ దాడి నుండి ప్రా టోపాా జమ్ను ర్కిి స్రా యి. • అవి దృ structures మై న నిర్మమణాలు మరియు గురుత్వాక్ర్ి ణ శకుు లను తటు కోవడంలో మొక్కకు సహాయప్డత్వయి. • వ్యరు ప్దార్మథ ల ర్వ్యణాలో పాల్గ ంట్రరు మరియు క్ణంలోకి మరియు వలుప్ల జీవకిి యలు. • అధిక్ ఓస్మమటిక్ పీడనం కార్ణంగా క్ణాలలో అభివృదిి చందుతనన ట్ర్గ ర్ ఒత్తా డిని ఇవి తటు కుంట్రయి.
- 33. Functions of Cell Wall: (i) Protects the protoplasm against mechanical injury, (ii) Protects the cell from attack of pathogens, (iii) Provides rigidity and shape to the cell, (iv) Counteracts osmotic pressure. (v) Gives strength to the land plants to withstand gravitational forces, (vi) By its growth the wall helps in cell expansion, (vii) Pits present in the wall help produce a protoplasmic continuum or simplest amongst cells, (viii) Walls prevent bursting of plant cells by inhibiting excessive endosmosis. (ix)
- 34. (viii) Walls prevent bursting of plant cells by inhibiting excessive endosmosis. (ix) Wall has some enzymatic activity connected with metabolism, (x) In many cases, wall takes part in offence and defense, (xi) Cutin and suberin of the cell wall reduce the loss of water through transpiration, (xii) Walls of sieve tubes, tracheids and vessels are specialised for long distance transport, (xiii) Some seeds store food in the form of hemicellulose in cell wall.
- 35. i) యాంత్తా క్ గాయానికి వయత్తరేక్ంగా ప్రా టోపాా జమ్ను ర్కిి స్టా ంది, ii) వ్యయధికార్క్ దాడి నుండి క్ణానిన ర్కిి స్టా ంది iii) క్ణానికి దృ g తాం మరియు ఆకార్మనిన అందిస్టా ంది, iv) ఓస్మమటిక్ ఒత్తా డిని ఎదురుకంటంది. v) గురుత్వాక్ర్ి ణ శకుు లను తటు కోవట్రనికి భూమి మొక్కలకు బలానిన ఇస్టా ంది, vi) దాని పెరుగుదల దాార్మ గోడ క్ణాల విసా ర్ణకు సహాయప్డుతంది, vii) గోడలో ఉనన గుంట్లు ప్రా టోపాా స్మమక్ కాంటినమ లేదా క్ణాల మధయ సర్ళమై న ఉతపత్తా ని చేయడంలో సహాయప్డత్వయి
- 36. vii) గోడలో ఉనన గుంట్లు ప్రా టోపాా స్మమక్ కాంటినమ లేదా క్ణాల మధయ సర్ళమై న ఉతపత్తా ని చేయడంలో సహాయప్డత్వయి, (viii) అధిక్ ఎండోస్మమస్మస్ను నిరోధించడం దాార్మ మొక్కల క్ణాలు ప్గిలిప్రవడానిన గోడలు నిరోధిస్రా యి. (ix) వ్యల్ జీవకిి యతో అనుసంధ్రనించబడిన కనిన ఎంజై మాటిక్ కార్యక్లాపాలను క్లిగి ఉంది, (x) అనేక్ సందర్మాలోా , గోడ నేర్ం మరియు ర్క్షణలో పాల్గ ంటంది, (xi) సెల్ గోడ యొక్క క్టిన్ మరియు స్టబెరిన్ ట్రా ని్పరేషన్ దాార్మ నీటి నష్టు నిన తగిగ స్రా యి, (xii) జల్లా డ గొట్రు లు, ట్రా చై డుా మరియు నాళాల గోడలు స్టదూర్ ర్వ్యణాకు ప్ా త్యయక్మై నవి, (xiii) కనిన వితా నాలు సెల్ గోడలో హెమిసెలుయలోజ్ రూప్ంలో ఆహార్మనిన నిలా చేస్రా యి
- 37. Functions of Cell Wall: i) యాంత్తా క్ గాయానికి వయత్తరేక్ంగా ప్రా టోపాా జమ్ను ర్కిి స్టా ంది, ii) వ్యయధికార్క్ దాడి నుండి క్ణానిన ర్కిి స్టా ంది, iii) క్ణానికి దృ g తాం మరియు ఆకార్మనిన అందిస్టా ంది, iv) ఓస్మమటిక్ ఒత్తా డిని ఎదురుకంటంది. v) గురుత్వాక్ర్ి ణ శకుు లను తటు కోవట్రనికి భూమి మొక్కలకు బలానిన ఇస్టా ంది, vi) దాని పెరుగుదల దాార్మ గోడ క్ణాల విసా ర్ణకు సహాయప్డుతంది, vii) గోడలో ఉనన గుంట్లు ప్రా టోపాా స్మమక్ కాంటినమ లేదా క్ణాల మధయ సర్ళమై న ఉతపత్తా ని చేయడంలో సహాయప్డత్వయి, viii) అధిక్ ఎండోస్మమస్మస్ను నిరోధించడం దాార్మ మొక్కల క్ణాలు ప్గిలిప్రవడానిన గోడలు నిరోధిస్రా యి. ix) వ్యల్ జీవకిి యతో అనుసంధ్రనించబడిన కనిన ఎంజై మాటిక్ కార్యక్లాపాలను క్లిగి ఉంది,
- 38. (x) అనేక్ సందర్మాలోా , గోడ నేర్ం మరియు ర్క్షణలో పాల్గ ంటంది, (xi) సెల్ గోడ యొక్క క్టిన్ మరియు స్టబెరిన్ ట్రా ని్పరేషన్ దాార్మ నీటి నష్టు నిన తగిగ స్రా యి, (xii) జల్లా డ గొట్రు లు, ట్రా చై డుా మరియు నాళాల గోడలు స్టదూర్ ర్వ్యణాకు ప్ా త్యయక్మై నవి, (xiii) కనిన వితా నాలు సెల్ గోడలో హెమిసెలుయలోజ్ రూప్ంలో ఆహార్మనిన నిలా చేస్రా యి.
- 39. THANK YOU.
