Chap 1 intro and terminology
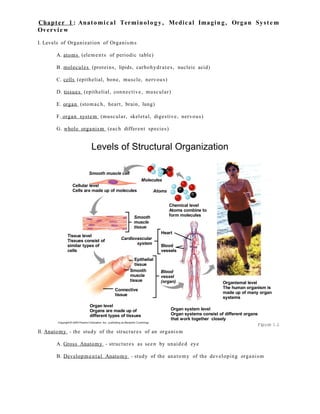
- 1. Chapt e r 1 : Anatomi c al Terminol o g y , Medical Imagin g , Organ Sys t em Overvi ew I. Levels of Organization of Organisms A. atoms (eleme n t s of periodic table) B. molecul e s (proteins, lipids, carbohydr a t e s , nucleic acid) C. cells (epithelial, bone, muscle, nervous ) D. tissue s (epithelial, conne ctive, muscul ar) E. organ (stoma c h, hear t, brain, lung) F. organ system (muscul ar, skelet al, diges tive, nervous ) G. whole organi sm (each different species ) Levels of Structural Organization Chemical level Atoms combine to form molecules Smooth muscle cell Cellular level Cells are made up of molecules Tissue level Tissues consist of similar types of cells Organismal level The human organism is made up of many organ systems Heart Blood vessels Blood vessel (organ) Organ system level Organ systems consist of different organs that work together closely Smooth muscle tissue Cardiovascular system Epithelial tissue Smooth muscle tissue Connective tissue Organ level Organs are made up of different types of tissues Molecules Atoms II. Anatomy - the study of the structur e s of an organi sm A. Gross Anatomy - structur e s as seen by unaide d eye Figure 1.1 B. Developme n t a l Anatomy - study of the anatomy of the developing organi sm
- 2. 1. Embryology - fertilization to third month of fetus C. Histology ("tissue s" "to study") - structur e s that can be seen with the microscop e such as cells and tissue s 1. Cytology - study of cell structur e/function D. Systemic Anatomy - study of individual organ syst em E. Regional Anatomy - study of structur e s in particular are a F. Pathology ("dise a s e" "to study") - study of chang e s in structur e due to dise a s e /injury III. Structur e - Function Relationships A. Anatomy - study of structur e Physiology - study of function B. Structur e det ermin e s Function Function det ermin e s Structur e C. Charles Darwin - "Origin of the Species" (1858) - Chang e s in structur e affect function: basis of evolution of all organisms IV. Anatomical Terminology - The Langua g e of Anatomy 1. Prefixes Indicating Location, Direction, and Tendency Prefix Meaning Example_________________ Ab- from, away abnormal - away from normal Ad- to, near, toward adrenal - near the kindey Ante- before antepartum - before delivery of child Brady- slow bradycardia - slow heart beat Brev- short brevity - in a short time Circum- around circumocular - around the eye Co- with, together coordinate - work together Con- with, together congenital - with birth Contra- against contraindicated - not indicated Counter- against counterirritant - against irritation Dis- apart from disarticulated - taking a joint apart Ect- outside ectonuclear - outside the nucleus End- within endocardium - lining inner heart Epi- upon, on top of epidermis - upon the skin Ex- out from exhalation - breathe out Hypo- under, lower hypodermic - under the skin Hyper- above, higher hyperactive - higher level activity Im- not immature - not mature In- not incurable - not curable Infra- under, below infrapatellar - below the knee Peri- around pericardium - sac around the heart Post- after postmortem - after death
- 3. Pre- before prenatal - before birth Pro- before prognosis - a fore-knowing Super- above, on top superciliary - above the eyebrow Supra- above, on top suprapubic - above the pubic bone Sym- with, together symphony - sounds played together Syn- with, together synarthrosis - union of bones Trans- through, across transurethral - through the urethra 2. Prefixes Indicating Number and Measurement Uni- one unicycle - one wheel Mono- one mononuclear - one nucleus Bi- two bilateral - two sides Bin- two binocular - two eyes Di- two dicephalic - two heads Ter- three tertiary - the third part or stage Tri- three trilobar - three lobes Quadr- four quadriceps - muscle w four heads Tetra- four tetracylcine - four-ringed molecule Poly- many polydactyly - many digits (more than 5) Oligo- few oligosaccharide - few sugars linked together Micro- small microscope - equipment to view small things Macro- large macrophage - large eating cell Mega- great/enormous megadontia - huge teeth 3. Prefixes Denoting Organs, Structures, Things Acoust- sound acoustics - quality of sound Aud- ear, hear audition - to hear someone Abdomin/o abdomen abdominal - relating to the abdomen Acr/o extremity, limbs acromegaly - abnormally large limbs Blast/o early, embryonic blastocyte - embryonic type cell Aden/o gland adenopathy - disease of a gland Angi/o vessel angiogram - picture of a vessel Arthr/o joint arthritis - inflammation of a joint Bucc/o cheek buccolabial - relating to cheek and lip Cardi/o heart cardiology - study of the heart Corp- body corpus callosum - connecting body Chondr/o cartilage chondrocyte - cartilage cell Cephal/o head cephalic - relating to the head Cyst/o bladder cystoscopy - view of the bladder Cyt/o cell cytokinesis - cell movement Dent/o tooth dental - referring to teeth
- 4. Dermat/o skin dermatitis - skin inflammation Duoden/o duodenum duodenal - relating to the duodenum Encephal/o brain encephalitis - brain inflammation Gastr/o stomach gastrointestinal - stomach and intestine Hepat/o liver hepatitis - liver inflammation Gloss/o tongue glossopathy - tongue disease Glute- buttocks gluteus minimus - small buttocks muscle Laryng/o larynx laryngitis - larynx inflammation My/o muscle myocardium - heart muscle Nephr/o kidney nephrologist - one who studies kidneys Neur/o nerve neurosurgeon - surgeon of nervous system Oste/o bone osteocyte - bone cell Ot/o ear otitis media - middle ear inflammation Ophthalm/o eye exophthalmos - eyes bulge out Path/o disease pathological - relating to disease Pneumon/o lung pneumonia - condition of the lung Rhin/o nose rhinoplasty - reform the nose Stomat/o mouth, opening stomatitis - mouth inflammation Thorac/o chest or thorax thoracocentesis - puncture of the thora 4. Suffixes Denoting Relations, Conditions, and Agents Suffix Meaning Example____________________________ -ac related to cardiac - related to the heart -ious related to contagious - communicable by contact -ic related to pyloric - related to pyloric valve of stomach -ism condition mutism - condition of being mute -osis condition scoliosis - S-shaped condition of backbone -tion condition constipation - constant blockage condition -ist agent (a person) opthalmologist - eye doctor -or agent operator -er agent examiner -ician agent physician -centesis to puncture amniocentesis - puncture the amnion (fluid) -ectomy to cut out and remove appendectomy - cut out & remove appendix -ostomy to cut and form opening colostomy - opening to drain the colon -otomy to cut or slice tracheotomy - cut the trachea -pexy to fix or repair gastropexy - repair the stomach
- 5. -plasty to reform or repair rhinoplasty - reform the nose -rraphy to suture, sew ateriorraphy - suture an artery -scopy to view otoscope - instrument to view ear -algia pain neuralgia - nerve pain -cide kill or destroy germicide - substance that kills germs -emia of the blood cholesterolemia - cholesterol in the blood -gram writing or record electrocardiogram - record of heart action -graph recording instrument electrocardiograph - records the heart -itis inflammation appendicitis - appendix inflammation -ology the study of ophthalmology - study of the eye -oma tumor lymphoma - tumor of lymphatics -orrhea flow menorrhea - flow during menstruation -malacia soft osteomalacia - bone softening -phasia speech dysphasia - slurred or blunted speech -phobia fear arachnophobia - fear of spiders B. Anatomic al Position 1. subject stands erect 2. upper limbs placed at sides with palms forward 3. feet flat on floor in natur al forward direction C. Directional Terms (practice using them in the lab!) 1. superior (ceph alic) : inferior (caud al) 2. ant erior (ventr al) : post erior (dorsal) 3. medi al : later al 4. ipsilat er al (same side) : contrala t er al (opposit e) 5. proximal : distal 6. superficial : deep 7. pariet al : viscer al D. Planes and Sections 1. sagitt al - divides into right and left part s a. midsa gi tt al - right down the middle b. para s a gi t t al - away from the midline 2. frontal (coronal) - divides anterior & post erior 3. horizont al (transve r s e) - divide superior & inferior
- 6. E. Body Cavities 1. Dorsal Body Cavity a. cranial cavity (brain) b. vertebr al cavity (spinal cord) 2. Ventral Body Cavity (viscera - organs found here) a. thoracic cavity i. pleural cavity (spac e separ a ting the pariet al pleura and viscer al pleura of lungs - like balloon pushe d in with fist) ii. medi a s tinum - all cont ent s of thoracic cavity except the lungs (eg. hear t) b. abdominop elvic cavity i. abdomin al - stoma c h, sple en, liver, gallbladd e r , pancr e a s , small intes tine ii. pelvic - urinary bladd er , cecum, appe n dix, sigmoid colon, rectum, reproductive organs
- 8. 3. Other Body Cavities a. oral cavity (mouth) b. nasal cavity (sinus e s for air pas s a g e ) c. orbital cavities (eyes) d. middle ear cavities (in tempor al bone) e. synovial cavities (freely move a bl e joints) V. Divisions of Abdominop elvic Cavity A. Quadr a nt s (from the umbilicus - belly button) 1. right upper quadr a nt (RUQ) 2. left upper quadr a nt (LUQ) 3. right lower quadr a nt (RLQ) 4. left lower quadr a n t (LLQ)
- 9. B. Regions (nine regions around umbilicus) VI. Specific Terms for Various Regions
- 10. VII. Medical Imaging Technique s A. Classic X-ray : radiogr a p hy (radiogr a p h) 1. good for dens e structur e s (bone s and tumor s)
- 11. B. Comput e d Tomogr a p h y (CT) or Comput e r ize d Axial Tomogr ap h y (CAT) Scanning 1. employs X-ray technology to creat e clearer image 2. tumor s , aneurysms , kidney stone s , gallston e s , etc. D. Magnetic Resona nc e Imaging (MRI) 1. uses magn e t ic proper tie s of molecul e s , not X-rays 2. pres e n c e of canc er cells, chemic al disea s e of brain, spinal cord disorder s , blood flow problems , injury after stroke, mea s ur e effect s of drugs on tissue s 3. used chiefly on soft tissue s such as brain & hear t
- 12. D. Dynamic Spatial Recons t ruc tion (DSR) 1. employs X-ray technology to see organ action/motion 2. me a s ur e s physiology of hear t, lungs, ves s el s; can indicat e abnormality/deformi ty in structur e; tissue dama g e E. Ultrasoun d (US) 1. uses high freque ncy sound waves 2. gall stone s , pelvic organs , blood flow, fetal developme n t F. Positron Emission Tomogr a p hy (PET) 1. uses radioisotop e s such as Carbon- 11, Nitrogen- 13 2. effect s of drugs, site of molecul e s , cancer cells 3. very good at studying glucos e absorption by neurons in the brain during certain tasks
- 13. G. Digital Subtr action Angiogra phy (DSA) 1. takes X-ray picture before and after adminis tr a tion of contr as t subs t a n c e to the ves s el s 2. used to study ves s el s of the brain and hear t to help preve nt stroke s and hear t attacks VIII. Major Organ Systems A. There are 12 major organ systems of the body: 1. integume nt a ry (skin) 2. skeletal (bone) 3. muscular (muscles) 4. nervous (CNS and PNS) 5. endocrine (hormone s /r egulation)
- 14. 6. cardiovascular (heart and blood vessels) 7. lymphatic (lymph fluid) 8. respiratory (lungs) 9. digestive (stomach, intestine) 10. urinary (kidneys, bladder) 11. reproductive (male and female genitalia) 12. immune (not really organs, cells in the blood/body) IX. Integume nt a ry System A. Major Compone nt s 1. skin (epidermi s, dermis, etc.) 2. hair 3. sweat and oil glands 4. sensory organs and glands B. Major Functions 1. helps to regulat e body temper a tur e 2. protect s agains t external injury and desiccation 3. eliminate s salts and urea 4. produce s vitamin D 5. responds to temper atur e, pressur e, and pain X. Skeletal System A. Major Compone nt s 1. bone 2. cartilage s 3. tendons 4. ligament s 5. joints B. Major Functions 1. provide protection for internal organs (skull, ribs) 2. provide support for body 3. mechanical advant ag e for muscular actions (levers) 4. storage of vital minerals - calcium 5. site of blood cell formation (marrow) XI. Muscular System A. Major Compone nt s 1. muscles of different type/function a. striated muscle (voluntary) b. smooth muscle (involunt ary) c. cardiac muscle (heart) B. Major Functions 1. striated muscle
- 15. a. primarily to contract on comman d b. allows voluntary motions such as walking, grasping, and moving in general, facial expres sions 2. smooth muscle a. contract s to allow involuntary motion b. along arteries, digestive tract 3. cardiac muscle a. contract s in rhythmic fashion involuntarily b. propels blood through lungs and body XII. Nervous System A. Major Compone nt s 1. brain and spinal cord (Central Nervous System) 2. nerves and sensory organs (Peripher al N S)
- 16. B. Major Functions 1. detect change s in internal and external environment 2. respond to change s to keep body homeos t a tic 3. organize activities of muscles and glands XIII. Endocrine System A. Major Compone nt s 1. pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pineal glands 2. ovaries, testes, pancre a s B. Major Functions 1. maintains body homeos t a si s, growth, developme nt 2. produc e hormone s in respons e to a variety of stimuli (increas e d sugar level, impending doom, sexual attraction, length of day) 3. hormone s then act on target organ to cause change XIV. Cardiovascular System A. Major Compone nt s 1. heart 2. blood vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries) 3. blood (serum, proteins, red & white cells) B. Major Functions 1. primarily a transport system moving blood a. oxygen, carbon dioxide, ions (salts Na,K,Ca,Cl) b. nutrient s and waste c. hormone s and proteins d. white blood cells and antibodies XV. Lymphatic System A. Major Compone nt s 1. lymph nodes and vessels 2. spleen 3. thymus 4. other scatter ed lymph tissue B. Major Functions 1. location of lymphocyt e s involved in body immunity 2. remove pathoge ns and debris from blood 3. returns leaked fluid to blood vessels
- 17. XVI. Respiratory System A. Major Compone nt s 1. nasal passag e s 2. pharynx, larynx, trache a, bronchi 3. lungs B. Major Functions 1. remove carbon dioxide from blood 2. allow blood to uptake oxygen from environment XVII. Digestive System A. Major Compone nt s 1. oral cavity, esophag us 2. stomach 3. small and large intestine 4. rectum 5. other: teeth, salivary glands, liver, pancre a s B. Major Functions 1. breakdown foods into minute particles to be absorbed by the blood and delivered to body 2. remove unused foodstuff from the body as feces XVIII. Urinary System A. Major Compone nt s 1. kidneys 2. ureters 3. bladder 4. urethra B. Major Functions 1. remove nitrogen- based waste molecules (urea, uric acid, ammonia) from the blood and body 2. maintain water balance and ion/acid balanc e of blood XIX. Reproductive System A. Major Compone nt s Male : testes, scrotum, penis, and duct system for sperm Female : ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, vagina B. Major Functions 1. produce gamet e s (sperm and egg)
- 18. 2. allow means for conception to occur 3. provide environme nt for fetal developme nt XIII. Immune System (Special) A. Major Compone nt s 1. white blood cells and other special immune cells B. Major Functions 1. identify foreign material and eliminate it
- 19. Levels of Structural Organization Chemical level Atoms combine to form molecules 1 2 3 Cellular level Cells are made up of molecules Tissue level Tissues consist of similar types of cells 4 Heart Blood vessels 5 Organ system level Organ systems consist of different organs that work together closely Epithelial tissue Smooth muscle tissue Organ level Organs are made up of different types of tissues 6 Organismal level The human organism is made up of many organ systems Molecules Atoms Smooth muscle cell Smooth muscle tissue Connective tissue Blood vessel (organ) Cardiovascular system Figure 1.1