Archaea
•
6 likes•7,408 views
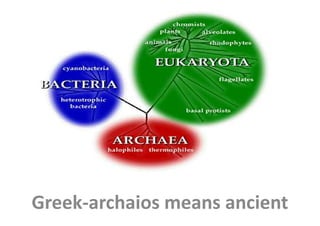
Archaea are a diverse group of microorganisms that inhabit extreme environments. They can be spherical, rod-shaped, or other morphologies, and exist as single cells or aggregates. Archaea are found in environments with high or low temperatures, pH, salt concentrations, or methane levels and can be aerobic, facultative anaerobes, or strictly anaerobes. They play important roles in ecosystems like methanogenesis and sulfate reduction. Archaea have unique cell walls and membranes adapted to extreme conditions like hyperthermophiles that can survive above 100°C. Major groups include methanogens, sulfate reducers, halophiles, and cell wall-less archaea. Archaea have economic importance in areas
Report
Share
Report
Share
Download to read offline
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Halophiles (Introduction, Adaptations, Applications)

Halophiles (Introduction, Adaptations, Applications)
B.Sc. Microbiology II Bacteriology Unit I Classification of Microorganisms

B.Sc. Microbiology II Bacteriology Unit I Classification of Microorganisms
Archaea Bacteria (Methanogens, Halophiles, Thermophiles)

Archaea Bacteria (Methanogens, Halophiles, Thermophiles)
Nomenclature, classification and identification of bacteria by Anil Shrestha

Nomenclature, classification and identification of bacteria by Anil Shrestha
B.Sc Micro II Microbial physiology Unit 1 Bacterial Photosynthesis 

B.Sc Micro II Microbial physiology Unit 1 Bacterial Photosynthesis
Viewers also liked
Viewers also liked (19)
B.Sc. Microbiology II Bacteriology Unit III Microbial Diversity

B.Sc. Microbiology II Bacteriology Unit III Microbial Diversity
Similar to Archaea
Green sulfur bactera and Green non Sulfur bacteriaGreen sulfur bacteria and Green nonsulfur bacteria.pptx

Green sulfur bacteria and Green nonsulfur bacteria.pptxSacred Heart College (Autonomous) Tirupattur.
Similar to Archaea (20)
Microbes of Extreme Environment Microbial Interaction.pptx

Microbes of Extreme Environment Microbial Interaction.pptx
Pharmaceutical Microbiology - Bacteria - Classification & Nutrition

Pharmaceutical Microbiology - Bacteria - Classification & Nutrition
Green sulfur bacteria and Green nonsulfur bacteria.pptx

Green sulfur bacteria and Green nonsulfur bacteria.pptx
More from Salman Ali
More from Salman Ali (20)
Recently uploaded
Mehran University Newsletter is a Quarterly Publication from Public Relations OfficeMehran University Newsletter Vol-X, Issue-I, 2024

Mehran University Newsletter Vol-X, Issue-I, 2024Mehran University of Engineering & Technology, Jamshoro
Recently uploaded (20)
ICT Role in 21st Century Education & its Challenges.pptx

ICT Role in 21st Century Education & its Challenges.pptx
Kodo Millet PPT made by Ghanshyam bairwa college of Agriculture kumher bhara...

Kodo Millet PPT made by Ghanshyam bairwa college of Agriculture kumher bhara...
Russian Escort Service in Delhi 11k Hotel Foreigner Russian Call Girls in Delhi

Russian Escort Service in Delhi 11k Hotel Foreigner Russian Call Girls in Delhi
Seal of Good Local Governance (SGLG) 2024Final.pptx

Seal of Good Local Governance (SGLG) 2024Final.pptx
ICT role in 21st century education and it's challenges.

ICT role in 21st century education and it's challenges.
Micro-Scholarship, What it is, How can it help me.pdf

Micro-Scholarship, What it is, How can it help me.pdf
This PowerPoint helps students to consider the concept of infinity.

This PowerPoint helps students to consider the concept of infinity.
Unit-V; Pricing (Pharma Marketing Management).pptx

Unit-V; Pricing (Pharma Marketing Management).pptx
Mixin Classes in Odoo 17 How to Extend Models Using Mixin Classes

Mixin Classes in Odoo 17 How to Extend Models Using Mixin Classes
Archaea
- 2. Introduction • Diverse group • Gram Positive or Gram Negative • Spherical, lobed, rod-shaped, spiral, cubodial, triangular, plate shaped, irregularly shaped, • Pleomorphic • Present as a single cells, or aggregates / filaments • Multiplication- binary fission, fragmentation and other mechanisms • Physiologically diverse-aerobic, facultative anaerobes, strictly anaerobes
- 3. • Chemolithoautotroph, organotroph • Psychrophiles, mesophiles and hyperthermophiles (can grow above 1000 c)
- 4. Ecology • They live in an extreme environment • Area with very high or low temperature, PH • Area with high salt concentration • Area with high concentration of methane • Area with no oxygen (anoxic)
- 6. Amazing Geyser Landscape in Nevada
- 7. the vivid red brine (teaming with halophilic archaebacteria) of Owens
- 9. Great Salt Lake of Utah
- 10. methanogens may thrive in hot springs
- 11. Archaeal Cell Wall • Lack muramic acid and D- amino acids • Eg. methanogens have peudomurein (a peptidoglycan like polymer that is cross-linked with L-amino acids • Some contain a complex carbohydrate similar to chondroitin sulfate of animal connective tissue • Hyperthermophile and methanogens have proten cell wall
- 12. Archaeal membrane • Branched chain hydrocarbon attached to glycerol by ether • Thermophile archaea have long tetraether in their cell membrane. Also pentacyclic rings in HC of some (help maintain the delicate liquid crystalline balance of membrane of membrane at high temperature) • Other lipids- polar phospholipid, sulfolipid, glycolipid.
- 13. Major Archaeal groups Methanogenic archaea Archaeal sulfate reducers Extremely halophilic archaea Cell wall-less archaea
- 14. Methanogenic Archaea • Strict anaerobes • Produces methane as a major metabolic end product • Convert sulfur to hydrogen sulphide wth no energy production • They possess co-enzyme M, factor 420/430, methanopterin • Eg. Metanobacterim, Methanococcus, Methanomicrobium, Methanosarcina
- 15. Archaeal sulfate reducers • Irregular gram-negative coccoid cells • Strictly anaerobe and extremely thermophilic • Hydrogen sulfide is formed from thiosulfate and sulfate • Heterotrophic in nature, autotrophic growth with thiosulfate and hydrogen • Forms traces of methane • Possess factor 420 and methanopterin • Eg. Archeoglobus
- 17. Extremely halophilic archaea • Rods, cocci, irregular shaped (pyramid, cube etc) • Stain gram-positive and gram-negative • Chemoorganoheterotroph • Lack peptidogycan • Most spp. require sodium chloride (> or =15M) • Mostly produce bright red colonies • Some unpigmented • Neutrophilic to alkalophilic • Generally mesophilic, one sp. is thermophilic • Possess bacteriorhodopsin and halorhodopsin ( and can use light energy to produce ATP
- 18. Cell wall-less Archaea • Pleomorphic cell lacking cell wall • Thermoacidophilic and chemoorganotrophic • Facultaive anaerobes • Mannose-rich glycoprotein and a lipoglycan
- 19. Extremely thermophilic elementary sulfur • Gram negative rods, filaments or cocci • Obligatory thermophile (70-1100 c) • Usually strictly anaerobe, some are aerobic and facultative • Acidophilic and neutrophilic • Autotrophic or heterotrophic • Reduction of sulfur to hydrogen sulfide – anaerobically and hydrogen sulfide or elemental sulfur oxidized to sulfuric acid aerobically • eg. Desulfurococcus, Sulfolobus, Thermococcus
- 20. Economic Importance • Thermophiles grow in heated water and soil rich in elemental sulfur and these environment are scattered all over the world. Eg. Sulfur rich hot springs in Yellowstone National Park • Methanogens produce methane using sewage sludge, which is a clean burning fuel(pollution free energy) • Methane production can contribute to global warming • Halophiles are used in the production of many salted food products, including soysauce • Thermoplasma oxidizes iron sulfide (in piles of coal mines) to sulfuric acid. As a result piles become hot and acidic
