vdocument.in_taxonomy-taxonomy-science-of-classifying-living-things-based-on-similarities.ppt
- 1. Taxonomy
- 2. Taxonomy: Science of classifying living things based on similarities.
- 3. Aristotle • Over 2,000 years ago • Developed the first system of classification All Living Things Plants Animals Herbs Shrubs Trees Land Air Water
- 4. Using Common Language • Using Common Names creates many problems with taxonomy • There are language and culture barriers • Fish ? Oak ? Difference ? Crayfish Silverfish Shellfish Starfish Jellyfish Red Oak White Oak Chestnut Oak Cougar Mountain Lion Panther Puma
- 5. Carolus (Carl) Linneaus • “Father of Taxonomy” • Introduced Binomial Nomenclature The process by which all living things are given a two word scientific name. • Based in Latin & Greek languages
- 6. Binomial Nomenclature Scientific Names • First Name = Genus Second Name = Species (Must be capitalized) (Must be lowercase) Both must be italics or underlined ! Examples: Felis domesticus = House cat Homo sapien = Humans Felis leo = African Lion Drosophilia melanogaster = fruit fly Felis concolor = Mountain Lion Canis lupus = Gray wolf
- 7. Scientific Names • All scientific names are chosen to describe an organisms features, its geography, or some other trivia (person who named it). • Trifolium = 3 leaves agraium = fields • Linnaea = Linneaus borealis = northern • Quercus = oak alba = white
- 8. 8 Categories of Classification • Domain • Kingdom (King) • Phylum (Philip) • Class (Came) • Order (Over) • Family (For) • Genus (Good) • Species (Spaghetti) Remember by Mnemonics !
- 9. Sub-Groupings • Subspecies (ssp) – same species, but notable morphological differences due to geographic isolation. (common in animal species) Subspecies of the rat snake Elaphe obsoleta, which interbreed where their ranges meet.
- 10. • Varieties (var.) – same species but notable morphological differences not due to isolation. (common in plants, breeds of animals, even races of people)
- 11. • Strains – refer to biochemically dissimilar microorgamisms (bacteria, viruses) Typical Staph Bacteria MRSA Bacteria
- 12. Criteria/Evidence for Classification • Comparing anatomical structures in order to determine similarities between organisms • Homologous Structures: similar parts between organisms (related) • Analogous Structures: different anatomical parts between two organisms (un-related) 1. Morphology
- 14. 2. Embryology • Comparing the early development of organisms in order to group similar organisms.
- 15. 3. Genetics • Comparing DNA sequences to determine similarities. Humans and Chimps share 99.6% of the same exact DNA !
- 16. 4. Phylogeny • Family tree that shows evolutionary relationships. • Base of tree = common ancestor of all the living things in the tree • Branching = change of organism into a new species
- 17. Phylogeny • Tips of Branches = Current day species • The closer the branches, the more similar • The farther the branches, the more different
- 18. 5. Biosystematics • The study of reproductive capabilities in organisms (can two species reproduce with one another?) bi·o·sys·tem·at·ics The statistical analysis of data obtained from genetic, biochemical, and other studies to assess the taxonomic relationships of organisms or populations, especially within an evolutionary framework.
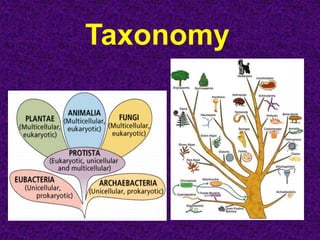
- 20. Kingdom Cell Type # Cells Nutrition Archaebacteria Prokaryotic Unicellular Autotrophic & (Primitive Bacteria) Heterotrophic Eubacteria Prokaryotic Unicellular Autotrophic & (Normal Bacteria) Heterotrophic Protista Eukaryotic Mostly Autotrophic & (Amoeba, Paramecium, algae) Unicellular Heterotrophic Fungi Eukaryotic Mostly Heterotrophic (Mushrooms, mold, yeast) Multicellular Plantae Eukaryotic Multicellular Autotrophic Animal Eukaryotic Multicellular Heterotrophic